The Neuron: Building Block of the Nervous System
... charge travels down the axon and causes neurotransmitters to be released by the terminal buttons. Sets off a chain reaction like a set of falling dominos. ...
... charge travels down the axon and causes neurotransmitters to be released by the terminal buttons. Sets off a chain reaction like a set of falling dominos. ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... Major Internal Features of a Neuron Similarities with other cells: • Contains a nucleus that holds genetic information • Contains organelles that support the life of the cell, including mitochondria and ribosomes • Surrounded by a membrane that protects the cell Differences with other cells: • Stop ...
... Major Internal Features of a Neuron Similarities with other cells: • Contains a nucleus that holds genetic information • Contains organelles that support the life of the cell, including mitochondria and ribosomes • Surrounded by a membrane that protects the cell Differences with other cells: • Stop ...
Luis V. Colom, MD, PhD VP of Research Center for Biomedical Studies
... amyloid beta peptides (Aβ), senile plaques in cerebral cortical regions, constitutes a hallmark lesion of AD. In addition, diminished basal forebrain cholinergic and cortical glutamatergic functions observed in AD cause most of the neuropsychological deficits in AD patients. Current Studies: ...
... amyloid beta peptides (Aβ), senile plaques in cerebral cortical regions, constitutes a hallmark lesion of AD. In addition, diminished basal forebrain cholinergic and cortical glutamatergic functions observed in AD cause most of the neuropsychological deficits in AD patients. Current Studies: ...
Using the State-Space Paradigm to Analyze Information Representation in Neural Systems
... point process nature of neural encoding. The advent in the last 10 years of the capability to record with multiple electrode arrays the simultaneous spiking activity of many neurons (¿100) has made it possible to study information encoding by ensembles rather than by simply single neurons. Hence, an ...
... point process nature of neural encoding. The advent in the last 10 years of the capability to record with multiple electrode arrays the simultaneous spiking activity of many neurons (¿100) has made it possible to study information encoding by ensembles rather than by simply single neurons. Hence, an ...
Chem 5336_Potentiometry
... These ion activities control the membrane potentials, E1 and E2 and so control EB, at 25 oC EB = E1 – E2 = 0.0592 log (a1/a2) Ecell = const + 0.0592 log (a1) Ecell = const - 0.0592 pH In practice, pH meter incorporates these equations And relates them to measurements with standard buffer, And the ou ...
... These ion activities control the membrane potentials, E1 and E2 and so control EB, at 25 oC EB = E1 – E2 = 0.0592 log (a1/a2) Ecell = const + 0.0592 log (a1) Ecell = const - 0.0592 pH In practice, pH meter incorporates these equations And relates them to measurements with standard buffer, And the ou ...
1050927abstract
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
The human brain is a 3 pound mass of fatty tissue that controls all
... synapses formed by the ends of axons of other neurons. Neurons signal by transmitting electrical impulses along their axons, which can range in length from a tiny fraction of an inch to three or more feet. Glia cells: Glia cells are support cells for neurons. They insulate the axons to speed transmi ...
... synapses formed by the ends of axons of other neurons. Neurons signal by transmitting electrical impulses along their axons, which can range in length from a tiny fraction of an inch to three or more feet. Glia cells: Glia cells are support cells for neurons. They insulate the axons to speed transmi ...
Nervous Tissue [PPT]
... Much smaller than the neurons 10 times more numerous than neurons 4 types: Astrocytes(Fibrous and ...
... Much smaller than the neurons 10 times more numerous than neurons 4 types: Astrocytes(Fibrous and ...
Document
... 13. Capable of generating action potentials propagating them and synaptic transmission 14.Primarily engaged with conduction and transmission ...
... 13. Capable of generating action potentials propagating them and synaptic transmission 14.Primarily engaged with conduction and transmission ...
Vocabulary Terms
... analgesic found in opium and is capable of inducing sleep and causing addiction. ...
... analgesic found in opium and is capable of inducing sleep and causing addiction. ...
Applicator - Research - Vanderbilt University
... •Ammons et al. (1983) proposed that there are sites on the brain stem that can activate descending inhibitory pathways via the stimulation of the vagal nerves and the surrounding nerves. •Hammond et al. (1992) reported that “synchronous bursts of potentials could be dispersed to widespread areas of ...
... •Ammons et al. (1983) proposed that there are sites on the brain stem that can activate descending inhibitory pathways via the stimulation of the vagal nerves and the surrounding nerves. •Hammond et al. (1992) reported that “synchronous bursts of potentials could be dispersed to widespread areas of ...
Action Potential Web Quest
... 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 major types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: ...
... 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 major types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: ...
Perception, learning and memory - Max-Planck
... individual neurons and synapses, but much less about their coordinated action in ensembles of millions. The brain derives its magic from coordinated activity on the large scale and high degrees of specialization on the small scale7. Networks, neurons and molecular constituents need to be studied in ...
... individual neurons and synapses, but much less about their coordinated action in ensembles of millions. The brain derives its magic from coordinated activity on the large scale and high degrees of specialization on the small scale7. Networks, neurons and molecular constituents need to be studied in ...
Feb. 11
... molecules • Keeps cytoplasm in and water soluble molecules out • Need for membrane proteins: receptors; surface proteins; cytoplasmic proteins ...
... molecules • Keeps cytoplasm in and water soluble molecules out • Need for membrane proteins: receptors; surface proteins; cytoplasmic proteins ...
Lectures 26-27 Study Guide
... Oligodendrocytes (CNS) and Schwann (PNS) cells: form the myelin sheaths around axons. This increases the speed at which an action potential (AP) travels along the axon (more on this in Lecture 27). When comparing neurons and glia, which cell type do brain tumors arise from? 6. Ion channels and the N ...
... Oligodendrocytes (CNS) and Schwann (PNS) cells: form the myelin sheaths around axons. This increases the speed at which an action potential (AP) travels along the axon (more on this in Lecture 27). When comparing neurons and glia, which cell type do brain tumors arise from? 6. Ion channels and the N ...
Neurons and how they communicate
... potassium ions The signal does not travel through electrical conduction like an electrical current ...
... potassium ions The signal does not travel through electrical conduction like an electrical current ...
Histology of Nerve the Nervous System
... system,consisting of the brain and the spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system,composed of nerve fibers and small aggregates of nerve cells called nerve ganglia Structurally,nerve tissue consists of two cell types:nerve cells,or neurons, Usually show numerous long processes, and several types ...
... system,consisting of the brain and the spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system,composed of nerve fibers and small aggregates of nerve cells called nerve ganglia Structurally,nerve tissue consists of two cell types:nerve cells,or neurons, Usually show numerous long processes, and several types ...
Overview of the Day
... Peripheral Nervous System (carries info. to and from the CNS) somatic/skeletal nervous system (controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles autonomic nervous system (controls glands and muscles of internal organs [e.g., heart]). The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work together to k ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (carries info. to and from the CNS) somatic/skeletal nervous system (controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles autonomic nervous system (controls glands and muscles of internal organs [e.g., heart]). The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work together to k ...
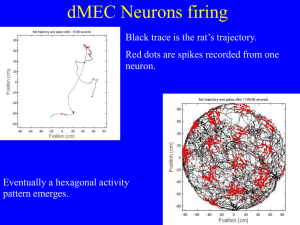
How grid cells neurons encode rat position
... -A rat running over an activity blob -A rat running a past a blob (at the resolution limit) We model the firing rate as constant background plus gaussian ...
... -A rat running over an activity blob -A rat running a past a blob (at the resolution limit) We model the firing rate as constant background plus gaussian ...
Neuron Notes Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the
... 1. cell body: largest part, contains nucleus and most of cytoplasm – most metabolic activity of cell occurs here 2. dendrites: spread out from cell body; short, branched extensions; carry impulses toward the cell body 3. axons: (transmit/send signals) long fiber that carries impulses away from cell ...
... 1. cell body: largest part, contains nucleus and most of cytoplasm – most metabolic activity of cell occurs here 2. dendrites: spread out from cell body; short, branched extensions; carry impulses toward the cell body 3. axons: (transmit/send signals) long fiber that carries impulses away from cell ...
Supplementary Figure Legends
... well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma with compressed hepatic parenchyma (left). A representative liver section from an animal with BEP neuronal transplants shows almost normal liver morphology with mild fibrosis septae (right). ...
... well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma with compressed hepatic parenchyma (left). A representative liver section from an animal with BEP neuronal transplants shows almost normal liver morphology with mild fibrosis septae (right). ...
Work toward real-time control of a cortical neural prothesis
... be related back to the original arm movement for comparison. Over a two-month time period (83 640 time windows of activity analyzed), the system correctly predicted when the hand was in motion 81% of the time—with the most consistent errors occurring at the beginning and end of the movements. Overal ...
... be related back to the original arm movement for comparison. Over a two-month time period (83 640 time windows of activity analyzed), the system correctly predicted when the hand was in motion 81% of the time—with the most consistent errors occurring at the beginning and end of the movements. Overal ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... • Structural units of the nervous system – Composed of a body, axon, and dendrites – Long-lived, amitotic, and have a high metabolic ...
... • Structural units of the nervous system – Composed of a body, axon, and dendrites – Long-lived, amitotic, and have a high metabolic ...







![Nervous Tissue [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000313628_1-63044c543d97a5d91f1cbdf37558ffd7-300x300.png)