Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
Learning, Memory and Perception.
... way to describe the neuronal substrates of percepts (for example, a rabbit, a child’s voice, the smell of burning toast), they would be meaningless if it were not for our ability to link them to corresponding memories: my seeing a rabbit now is useful because I already know what a rabbit looks like ...
... way to describe the neuronal substrates of percepts (for example, a rabbit, a child’s voice, the smell of burning toast), they would be meaningless if it were not for our ability to link them to corresponding memories: my seeing a rabbit now is useful because I already know what a rabbit looks like ...
What are Neurons
... Interneurons are responsible for communicating information between different neurons in the body. ...
... Interneurons are responsible for communicating information between different neurons in the body. ...
Sensing the Environment
... other neurons, and the effect of the different incoming signals determines what the neuron ...
... other neurons, and the effect of the different incoming signals determines what the neuron ...
File
... ___________________ The branching filaments that conduct nerve impulses towards the cell. ___________________ The sense organ or cells that receive stimuli from within and outside the body. ___________________ The reaction to a stimulus by a muscle or gland. ___________________ The part of the nerve ...
... ___________________ The branching filaments that conduct nerve impulses towards the cell. ___________________ The sense organ or cells that receive stimuli from within and outside the body. ___________________ The reaction to a stimulus by a muscle or gland. ___________________ The part of the nerve ...
Introduction
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
Plasticity, Hippocampal Place Cells, and Cognitive Maps
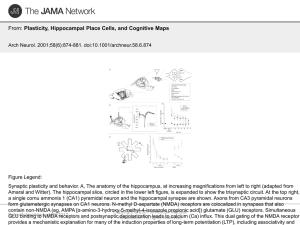
... Hippocampal place fields, learning, and synaptic plasticity. A, Cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) and CA3 pyramidal neurons have distinct complex-spike action potentials whether recorded intracellularly or extracellularly. These signature complex-spike cells occasionally fire in bursts of 2 to 7 action potentia ...
... Hippocampal place fields, learning, and synaptic plasticity. A, Cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) and CA3 pyramidal neurons have distinct complex-spike action potentials whether recorded intracellularly or extracellularly. These signature complex-spike cells occasionally fire in bursts of 2 to 7 action potentia ...
PPT
... inspection systems, beer testing, welding quality analysis, paper quality prediction, computer chip quality analysis, analysis of grinding operations, chemical product design analysis, machine maintenance analysis, project bidding, planning and management, dynamic modeling of chemical process system ...
... inspection systems, beer testing, welding quality analysis, paper quality prediction, computer chip quality analysis, analysis of grinding operations, chemical product design analysis, machine maintenance analysis, project bidding, planning and management, dynamic modeling of chemical process system ...
Introduction to electrophysiological recordings
... forces 3Na+ out of the cell and picks up 2K+ into the cell on the return trip. Due to these pumps, neurons at rest show greater concentration of K+ inside the cell than outside and greater concentration of Na+, Cl- and Ca2+ outside the cell than inside. Any transient change in the permeability of th ...
... forces 3Na+ out of the cell and picks up 2K+ into the cell on the return trip. Due to these pumps, neurons at rest show greater concentration of K+ inside the cell than outside and greater concentration of Na+, Cl- and Ca2+ outside the cell than inside. Any transient change in the permeability of th ...
document
... cell result in a temporary hyperpolarized membrane potential. Ion channels reset and the Na+/K+ pump returns the ions to the normal gradients. ...
... cell result in a temporary hyperpolarized membrane potential. Ion channels reset and the Na+/K+ pump returns the ions to the normal gradients. ...
Nerves Part 1 Powerpoint
... • Sensory and motor neurons form the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
... • Sensory and motor neurons form the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
PPT and questions for class today.
... the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
... the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
Structure of the Nervous System
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
Lecture 2 - Nerve Impulse
... Nerve Impulses Action Potential: Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the ...
... Nerve Impulses Action Potential: Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the ...
PowerPoint Slides
... • The Von Neumann architecture uses a single processing unit; – Tens of millions of operations per second – Absolute arithmetic precision ...
... • The Von Neumann architecture uses a single processing unit; – Tens of millions of operations per second – Absolute arithmetic precision ...
neurobiological-basis-of-behavior
... neurons in the brain. Nerves – bundles of axons - Often located in the peripheral nervous system - Transmit information to various parts of the body Types of Neurons 1. Sensory neuron (afferent neuron) – carry information from the senses to the spinal cord 2. Interneuron – makes connections to oth ...
... neurons in the brain. Nerves – bundles of axons - Often located in the peripheral nervous system - Transmit information to various parts of the body Types of Neurons 1. Sensory neuron (afferent neuron) – carry information from the senses to the spinal cord 2. Interneuron – makes connections to oth ...
4-Calculate the Equilibrium Potential of Potassium, Sodium, and
... 2) Calculate the Equilibrium Potential of Potassium, Sodium, and Chloride (separately) using the following values? What is the name and expression of the Equation used to calculate the Equilibrium Potentials? ...
... 2) Calculate the Equilibrium Potential of Potassium, Sodium, and Chloride (separately) using the following values? What is the name and expression of the Equation used to calculate the Equilibrium Potentials? ...
General histology of nervous system
... – short processes receive multiple stimuli – becomes thinner as they subdivide into branches ...
... – short processes receive multiple stimuli – becomes thinner as they subdivide into branches ...
Nervous System
... The function of the nervous system is to allow the animal to quickly detect, communicate and coordinate information about its external and internal environment. The two major parts of our nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is made of ...
... The function of the nervous system is to allow the animal to quickly detect, communicate and coordinate information about its external and internal environment. The two major parts of our nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is made of ...
Nervous System II: Development & Plasticity
... tree cells. (Gk) type of neuroglia which myelinate axons in the Central Nervous System (CNS). • Neurons: are nerve cells electrically excitable cells that process and transmit information. ...
... tree cells. (Gk) type of neuroglia which myelinate axons in the Central Nervous System (CNS). • Neurons: are nerve cells electrically excitable cells that process and transmit information. ...
4/12 - bio.utexas.edu
... Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. Fig 46.1 ...
... Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. Fig 46.1 ...
A.1 Neural Development
... Single nerve myriad of synapses to neighboring nerve cells best fit wins, others die off Strengthening communication in that single connection Controlled by IgCAM (neural adhesion molecule) ...
... Single nerve myriad of synapses to neighboring nerve cells best fit wins, others die off Strengthening communication in that single connection Controlled by IgCAM (neural adhesion molecule) ...
Synapses
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
1. Receptor cells
... interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting – touching). receive various types of stimulation from environment, which are then transmitted to the brain. ...
... interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting – touching). receive various types of stimulation from environment, which are then transmitted to the brain. ...