Powerpoint
... – Na+ permeability suddenly increases, resulting in an inward rush (action potential) ...
... – Na+ permeability suddenly increases, resulting in an inward rush (action potential) ...
Introduction to the nervous system
... III) The signal leaves through the synapse to be passed along to the next nerve cell. 2)Neurons pass messages to each other using an electrical signal. Synapse- it triggers the neuron to release a chemical neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitters- brain chemicals that communicate information throughout o ...
... III) The signal leaves through the synapse to be passed along to the next nerve cell. 2)Neurons pass messages to each other using an electrical signal. Synapse- it triggers the neuron to release a chemical neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitters- brain chemicals that communicate information throughout o ...
Introduction to the nervous system
... III) The signal leaves through the synapse to be passed along to the next nerve cell. 2)Neurons pass messages to each other using an electrical signal. Synapse- it triggers the neuron to release a chemical neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitters- brain chemicals that communicate information throughout o ...
... III) The signal leaves through the synapse to be passed along to the next nerve cell. 2)Neurons pass messages to each other using an electrical signal. Synapse- it triggers the neuron to release a chemical neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitters- brain chemicals that communicate information throughout o ...
Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
Carrie Heath
... you use each one? 7. What experiment could be done to determine that the cell membrane of a neuron is most permeable to Potassium? 8. What experiment could you do to test the effect Sodium has on the amplitudes of peaks of action potentials? What would you find from this experiment? 9. What did Hodg ...
... you use each one? 7. What experiment could be done to determine that the cell membrane of a neuron is most permeable to Potassium? 8. What experiment could you do to test the effect Sodium has on the amplitudes of peaks of action potentials? What would you find from this experiment? 9. What did Hodg ...
Chapter 7: the Nervous System
... Many types of sensory receptors • In response to physical stimulation, sensory receptor cells create electrical signals that travel to the central nervous system • Specialized senses (hearing, sight, smell & taste) have special receptor cells to be discussed in chapter 8 ...
... Many types of sensory receptors • In response to physical stimulation, sensory receptor cells create electrical signals that travel to the central nervous system • Specialized senses (hearing, sight, smell & taste) have special receptor cells to be discussed in chapter 8 ...
NeuroReview3
... growth cones, and use guidance molecules to guide them • Later axons use trail blazed by pioneer growth cones • Fasciculation: tendency for developing axons to stick together and grow along established pathways • Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs): on surface of growing axons that cause axons proceeding ...
... growth cones, and use guidance molecules to guide them • Later axons use trail blazed by pioneer growth cones • Fasciculation: tendency for developing axons to stick together and grow along established pathways • Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs): on surface of growing axons that cause axons proceeding ...
PPt #2 Human Body Nervous system
... • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and their functions. • 5. I can explain how the nervous system passes information between the external environment and the many parts of the body. ...
... • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and their functions. • 5. I can explain how the nervous system passes information between the external environment and the many parts of the body. ...
Myers Module Four
... extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body. For the biology students: dendrites are complex microtubules, proof that neurons are specializations from simpler cell structures. Axon: the neuron extension that passes messagesthrough its branches to other neurons. ...
... extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body. For the biology students: dendrites are complex microtubules, proof that neurons are specializations from simpler cell structures. Axon: the neuron extension that passes messagesthrough its branches to other neurons. ...
Signalling Adapter Expression Boosts Induced Neuron
... neuronal markers (TuJ1, NeuN, and TH) than IBM iNs cells. The researchers noted spontaneous firing of action potentials in S-IBM iNs at day 14 with high peak amplitudes (+5268 mV) compared to IBM iNs, where only one of 4 cultures fired action potentials and at a lower amplitude (+10 mV). Analysis of ...
... neuronal markers (TuJ1, NeuN, and TH) than IBM iNs cells. The researchers noted spontaneous firing of action potentials in S-IBM iNs at day 14 with high peak amplitudes (+5268 mV) compared to IBM iNs, where only one of 4 cultures fired action potentials and at a lower amplitude (+10 mV). Analysis of ...
Chapter 28- Nervous System
... • Space between 2 neurons or a neuron and an effector cell – Signal sent can be electrical or chemical – Synaptic cleft- gap between neurons, prevents action potential from sending info, action potentials can be converted to chemical signals (neurotransmitters) • The action potential triggers vesicl ...
... • Space between 2 neurons or a neuron and an effector cell – Signal sent can be electrical or chemical – Synaptic cleft- gap between neurons, prevents action potential from sending info, action potentials can be converted to chemical signals (neurotransmitters) • The action potential triggers vesicl ...
Nerve activates contraction - Silver Falls School District
... Carry impulses from sensory receptors to CNS a. Cutaneous sense organs ...
... Carry impulses from sensory receptors to CNS a. Cutaneous sense organs ...
01Integrated Normal Cells of CNS
... Based on number of processes 2. Bipolar Neuron (spindle-shaped neuron): Has two processes (one arising from each pole of the cell body). One of them is the dendrite and the other is the axon, e.g. retina & ...
... Based on number of processes 2. Bipolar Neuron (spindle-shaped neuron): Has two processes (one arising from each pole of the cell body). One of them is the dendrite and the other is the axon, e.g. retina & ...
Organization and Development of the Nervous System
... Isn’t cancer when mitosis has gone wild??!! ...
... Isn’t cancer when mitosis has gone wild??!! ...
Document
... __A__3. Which of the following is true about a motor neuron? a. Dendrites carry information toward the cell body. b. Dendrites carry information away from the cell body. c. Axons carry information toward the cell body. d. None of the above __C__4. Neurons that have repolarized will have a high conce ...
... __A__3. Which of the following is true about a motor neuron? a. Dendrites carry information toward the cell body. b. Dendrites carry information away from the cell body. c. Axons carry information toward the cell body. d. None of the above __C__4. Neurons that have repolarized will have a high conce ...
Slide ()
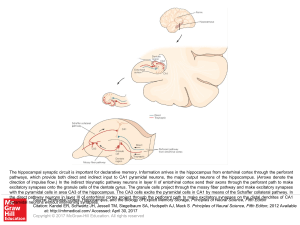
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
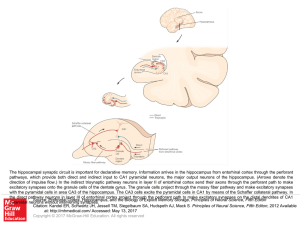
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
CNS Cellular Components - Johns Hopkins Medicine
... exposure to toxins. In adults, the pyramidal neurons of the CA1 field of the hippocampus and layers 3 and 5 of the cortex are especially vulnerable to hypoxic damage, as are purkinje cells in the cerebellum. Chronic neuronal atrophy/degeneration, such as occurs in neurodegenerative diseases, genera ...
... exposure to toxins. In adults, the pyramidal neurons of the CA1 field of the hippocampus and layers 3 and 5 of the cortex are especially vulnerable to hypoxic damage, as are purkinje cells in the cerebellum. Chronic neuronal atrophy/degeneration, such as occurs in neurodegenerative diseases, genera ...
Neuronal Anatomy - VCC Library
... located at one end of the nerve cell or in the middle. Cell bodies tend to be grouped near each other or clustered together. These groups of clustered nerve cell bodies are called ganglia, and are usually only found in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) (i.e. outside the brain and spinal cord), rat ...
... located at one end of the nerve cell or in the middle. Cell bodies tend to be grouped near each other or clustered together. These groups of clustered nerve cell bodies are called ganglia, and are usually only found in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) (i.e. outside the brain and spinal cord), rat ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Parietal – somatosensory – phantom limb - V. S. Ramachandran Phantoms in the Brain Temporal - auditory Frontal – movement, executive control systems Primary functions and associated functions Language – Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas – loss of language – aphasia ...
... Parietal – somatosensory – phantom limb - V. S. Ramachandran Phantoms in the Brain Temporal - auditory Frontal – movement, executive control systems Primary functions and associated functions Language – Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas – loss of language – aphasia ...