Choir Terms List
... sings the lowest bass notes relationship of a voice to those around it transitional, moving from one section to another at the end of each phrase, the point of arrival or rest an elaborate passage at the end of a vocal solo a single melody begun by one part and followed in imitation by one or more v ...
... sings the lowest bass notes relationship of a voice to those around it transitional, moving from one section to another at the end of each phrase, the point of arrival or rest an elaborate passage at the end of a vocal solo a single melody begun by one part and followed in imitation by one or more v ...
Music Music Functions: Physical
... previously stated themes helps the audience draw relationships among the characters and events in the film; gives the film a unified personality of its own. ...
... previously stated themes helps the audience draw relationships among the characters and events in the film; gives the film a unified personality of its own. ...
Popular Music Theory - The Academy Of Popular Music
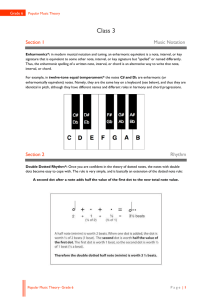
... For example, in twelve-tone equal temperament* the notes C♯ and D♭ are enharmonic (or enharmonically equivalent) notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard (see below), and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressi ...
... For example, in twelve-tone equal temperament* the notes C♯ and D♭ are enharmonic (or enharmonically equivalent) notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard (see below), and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressi ...
20th Cent Definitions
... Works which make extensive use of quotations from earlier music Slight holding back or pressing forward of tempo to intensify the expression of the music How music moves through time; how the music sounds against even pulses An expansion of the 12-tone method that uses a system to govern every aspec ...
... Works which make extensive use of quotations from earlier music Slight holding back or pressing forward of tempo to intensify the expression of the music How music moves through time; how the music sounds against even pulses An expansion of the 12-tone method that uses a system to govern every aspec ...
1 Terms and Definitions Characteristics of Modern and Postmodern
... Characteristics of Modern and Postmodern Music Chromatic harmony: harmony utilizing chords built on the five chromatic notes of the scale in addition to the 7 diatonic ones; producing rich harmonies Impressionism and Impressionist Music (See textbook and lecture notes) Modernism and Modernist Music ...
... Characteristics of Modern and Postmodern Music Chromatic harmony: harmony utilizing chords built on the five chromatic notes of the scale in addition to the 7 diatonic ones; producing rich harmonies Impressionism and Impressionist Music (See textbook and lecture notes) Modernism and Modernist Music ...
Score Reading Vocabulary Key signature: The sharps or flats that
... whole step, flats lower the note a half step, the naturals return the note to the original pitch Notation: The art of writing musical notes on paper Note: A symbol used to indicate the duration and pitch of sound, as in whole notes, and quarter notes Pitch: The highness or lowness of a tone Score: T ...
... whole step, flats lower the note a half step, the naturals return the note to the original pitch Notation: The art of writing musical notes on paper Note: A symbol used to indicate the duration and pitch of sound, as in whole notes, and quarter notes Pitch: The highness or lowness of a tone Score: T ...
TERMS AND CONCEPTS OF 20TH C. MUSIC GENERAL: ostinato
... methods of establishing a tonal center -accent dynamics ostinato pedal point register reiteration / repetition return mixed-interval chords -- a chord that combines 2 or more interval types (with their inversions / compounds) to form a complex sonority neotonality -- music that is tonal but in which ...
... methods of establishing a tonal center -accent dynamics ostinato pedal point register reiteration / repetition return mixed-interval chords -- a chord that combines 2 or more interval types (with their inversions / compounds) to form a complex sonority neotonality -- music that is tonal but in which ...
File
... basically of numbers representing intervals above the bass to be formed by the members of the chord, but the notes could actually be played in any octave above the bass. The system dwelt only with intervals, not with roots of chords, because the theory of chord roots had not been derived when figu ...
... basically of numbers representing intervals above the bass to be formed by the members of the chord, but the notes could actually be played in any octave above the bass. The system dwelt only with intervals, not with roots of chords, because the theory of chord roots had not been derived when figu ...
Course Description
... Analysis of repertoire, including analysis of motivic treatment and harmonic analysis The course includes the following scales: major, minor, modal, pentatonic, and whole tone. The course covers the following concepts or procedures based in common-practice tonality: ...
... Analysis of repertoire, including analysis of motivic treatment and harmonic analysis The course includes the following scales: major, minor, modal, pentatonic, and whole tone. The course covers the following concepts or procedures based in common-practice tonality: ...
notes from guest lecturer from the
... feeling, even racial/ cultural make up. uses for music: all occasions, weddings, funerals,etc. live music - has moments that can never be recaptured but are of the moment of performance. special, having a spark, energy that is there for the moment. ...
... feeling, even racial/ cultural make up. uses for music: all occasions, weddings, funerals,etc. live music - has moments that can never be recaptured but are of the moment of performance. special, having a spark, energy that is there for the moment. ...
Harmonic Progression - LearnMusicTheory.net
... A harmonic progression is a goal-directed succession of chords. Composers from the 1600s through the 1800s favored certain strong harmonic progressions. The strongest of all progressions involves the root of the chord moving down a fifth (or up a fourth), especially dominant (V) to tonic (I or i). ...
... A harmonic progression is a goal-directed succession of chords. Composers from the 1600s through the 1800s favored certain strong harmonic progressions. The strongest of all progressions involves the root of the chord moving down a fifth (or up a fourth), especially dominant (V) to tonic (I or i). ...
Musical Terms - Rogers State University
... – moves in whole or half steps • Disjunct melody – many large skips and may sound “jagged” – moves in more than a whole step ...
... – moves in whole or half steps • Disjunct melody – many large skips and may sound “jagged” – moves in more than a whole step ...
Music Appreciation Class Fall 2014 Chapter 1
... Provides the basic harmonic and melodic material for a given piece of music. A selection of pitches within the interval of an octave. Major scales (diatonic) pattern: WWhWWWh in steps. Tonic- the home key, original note. Semitone- a half-step (ex. Bb to B, one note to the next on a piano) Also calle ...
... Provides the basic harmonic and melodic material for a given piece of music. A selection of pitches within the interval of an octave. Major scales (diatonic) pattern: WWhWWWh in steps. Tonic- the home key, original note. Semitone- a half-step (ex. Bb to B, one note to the next on a piano) Also calle ...
Harmony from the Inside
... Only barbershoppers call them this! (Others call them: dominant sevenths or major-minor sevenths.) Like a major triad, but with an extra note on top. Called ‘7th chord’ because of number of steps between root and the top note. There are different types of 7th, like there are different types of triad ...
... Only barbershoppers call them this! (Others call them: dominant sevenths or major-minor sevenths.) Like a major triad, but with an extra note on top. Called ‘7th chord’ because of number of steps between root and the top note. There are different types of 7th, like there are different types of triad ...
level 11 - Hlubek Piano Studio
... supertonic: second degree of the scale submediant: sixth degree of the scale deceptive cadence: a cadence consisting of V-vi chordal progression half cadence: a cadence consisting of the chord progression ii-V or I-V ...
... supertonic: second degree of the scale submediant: sixth degree of the scale deceptive cadence: a cadence consisting of V-vi chordal progression half cadence: a cadence consisting of the chord progression ii-V or I-V ...
Symbolic Music Representations
... A chord is a set of two or more notes that sound simultaneously. A chord label can also be applied to a music excerpt (typically a measure) by inferring, using various rules of harmony, what theoretical chord would sound “good” with the underlying music material. The basis of the western classical a ...
... A chord is a set of two or more notes that sound simultaneously. A chord label can also be applied to a music excerpt (typically a measure) by inferring, using various rules of harmony, what theoretical chord would sound “good” with the underlying music material. The basis of the western classical a ...
A Guide to Part Writing Involving Root Position Triads
... Important exception: In major mode, it's possible to resolve the leading tone down to the next available chord tone when it is in an inner voice (tenor or alto), circumventing the above procedure, and resulting in a normal doubling for the submediant triad. This is not acceptable in the minor mod ...
... Important exception: In major mode, it's possible to resolve the leading tone down to the next available chord tone when it is in an inner voice (tenor or alto), circumventing the above procedure, and resulting in a normal doubling for the submediant triad. This is not acceptable in the minor mod ...
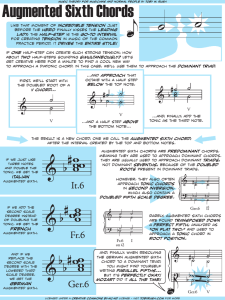
Augmented Sixth Chords
... Augmented Sixth Chords like that moment of incredible tension just before the hero finally kisses the leading lady, the half-step is the go-to interval for creating tension in music of the common practice period. it drives the entire style! ...
... Augmented Sixth Chords like that moment of incredible tension just before the hero finally kisses the leading lady, the half-step is the go-to interval for creating tension in music of the common practice period. it drives the entire style! ...
Learning Outcome
... Understand syncopated figures Recognize scale degree and relation to chord progressions (i.e. I - IV – V) Know all basic open chords Identify and play dotted quarter note rhythms. Identify the key signatures for C, G and D major Understand the concept of syncopation. Play a simple syncopated melody ...
... Understand syncopated figures Recognize scale degree and relation to chord progressions (i.e. I - IV – V) Know all basic open chords Identify and play dotted quarter note rhythms. Identify the key signatures for C, G and D major Understand the concept of syncopation. Play a simple syncopated melody ...
Glossary of Terms
... Staff: five lines and four spaces on which music is notated Clef: sign that fixes the tone represented by each line and space on the staff Key: tonic note, and the major or minor scale on which a composition is based Tonal: music that uses one notes of a scale as a reference pitch is said to be tona ...
... Staff: five lines and four spaces on which music is notated Clef: sign that fixes the tone represented by each line and space on the staff Key: tonic note, and the major or minor scale on which a composition is based Tonal: music that uses one notes of a scale as a reference pitch is said to be tona ...
Harmony Rules - Jeanie`s Online Music Studio
... bring the music to a close. Write down the available notes. • We work these exactly as for the perfect cadence except there is no leading note. * Write in the bass notes (the root of each chord). * Keep the note in common to both chords in the same part (this is the tonic of the key). * The other tw ...
... bring the music to a close. Write down the available notes. • We work these exactly as for the perfect cadence except there is no leading note. * Write in the bass notes (the root of each chord). * Keep the note in common to both chords in the same part (this is the tonic of the key). * The other tw ...
Required Graduate Music Theory Examinations
... Note: The levels should be completed in the order given with the program in practice mode, not mastery mode. Individuals may work on more or fewer levels depending on their own review needs. ...
... Note: The levels should be completed in the order given with the program in practice mode, not mastery mode. Individuals may work on more or fewer levels depending on their own review needs. ...
Guide to Analysis of Music
... Tempo – fast, slow, changes (use appropriate Italian words) Rhythm – prominence of rhythmic element (ex. running 16ths, triplets) 3. HARMONY Major, Minor, Modal, Whole-tone, Pentatonic Kinds of intervals Chords structure/progression Intervals of root movement Figured bass Emphasis on different scale ...
... Tempo – fast, slow, changes (use appropriate Italian words) Rhythm – prominence of rhythmic element (ex. running 16ths, triplets) 3. HARMONY Major, Minor, Modal, Whole-tone, Pentatonic Kinds of intervals Chords structure/progression Intervals of root movement Figured bass Emphasis on different scale ...
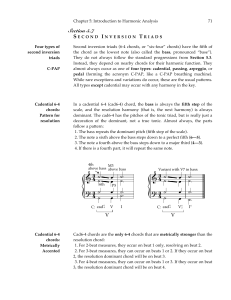
Second Inversion Triads
... They do not always follow the standard progressions from Section 5.3. Instead, they depend on nearby chords for their harmonic function. They almost always occur as one of four types: cadential, passing, arpeggio, or pedal (forming the acronym C-PAP, like a C-PAP breathing machine). While rare excep ...
... They do not always follow the standard progressions from Section 5.3. Instead, they depend on nearby chords for their harmonic function. They almost always occur as one of four types: cadential, passing, arpeggio, or pedal (forming the acronym C-PAP, like a C-PAP breathing machine). While rare excep ...
Music Fundamentals Primer Lesson 4
... A triad is a group of three notes that sound at the same time. In much tonal music, chords are built by stacking thirds on top of each other, creating what is known as tertian harmony. A tertian triad is a chord with three notes that is built with thirds. Even when a chord is spread out over several ...
... A triad is a group of three notes that sound at the same time. In much tonal music, chords are built by stacking thirds on top of each other, creating what is known as tertian harmony. A tertian triad is a chord with three notes that is built with thirds. Even when a chord is spread out over several ...