File - Seomra Ranga
... Musical Notation Music notes are written on a Stave. A stave is made up of five lines and four spaces. Music notes are written either on the line or in the space between two lines. These are the notes as they appear on the stave: ...
... Musical Notation Music notes are written on a Stave. A stave is made up of five lines and four spaces. Music notes are written either on the line or in the space between two lines. These are the notes as they appear on the stave: ...
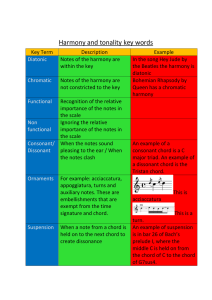
Tonality vs. Atonality
... Characteristics of Traditional Harmony: • Tonality. A tonal center embodied in the tonic triad. • Tonality is established by the progression V-I and the resolution of the leading tone to the tonic pitch. Harmonic progressions point towards the tonic. • Functional harmony. Chords are polarized around ...
... Characteristics of Traditional Harmony: • Tonality. A tonal center embodied in the tonic triad. • Tonality is established by the progression V-I and the resolution of the leading tone to the tonic pitch. Harmonic progressions point towards the tonic. • Functional harmony. Chords are polarized around ...
AP-Music-Theory-Study-Guide
... • Imitation- musical gesture is repeated later in a different form, but retaining its original character • Imitative polyphony- two or more equally prominent, simultaneous melodic lines, those lines being similar in shape and sound • Nonimitative polyphony- two or more melodic lines playing distinct ...
... • Imitation- musical gesture is repeated later in a different form, but retaining its original character • Imitative polyphony- two or more equally prominent, simultaneous melodic lines, those lines being similar in shape and sound • Nonimitative polyphony- two or more melodic lines playing distinct ...
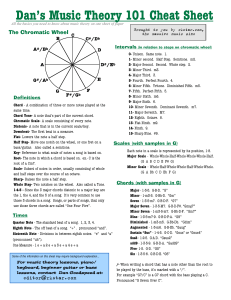
Dan`s Music Theory 101 Cheat Sheet []
... Chord Tone- A note that’s part of the current chord. Chromatic Scale- A scale consisting of every note. Diatonic- A note that is in the current scale/key. Downbeat- The first beat in a measure. Flat- Lowers the note a half step. Half Step- Move one notch on the wheel, or one fret on a bass/guitar. A ...
... Chord Tone- A note that’s part of the current chord. Chromatic Scale- A scale consisting of every note. Diatonic- A note that is in the current scale/key. Downbeat- The first beat in a measure. Flat- Lowers the note a half step. Half Step- Move one notch on the wheel, or one fret on a bass/guitar. A ...
Dan`s Music Theory 101 Cheat Sheet
... Chord Tone- A note that’s part of the current chord. Chromatic Scale- A scale consisting of every note. Diatonic- A note that is in the current scale/key. Downbeat- The first beat in a measure. Flat- Lowers the note a half step. Half Step- Move one notch on the wheel, or one fret on a bass/guitar. A ...
... Chord Tone- A note that’s part of the current chord. Chromatic Scale- A scale consisting of every note. Diatonic- A note that is in the current scale/key. Downbeat- The first beat in a measure. Flat- Lowers the note a half step. Half Step- Move one notch on the wheel, or one fret on a bass/guitar. A ...
Benward Chapter 6
... creating the feeling of a tonal center by using all the twelve chromatic tones in a prearranged order that does not lay particular emphasis on any one pitch in the composition as a whole. This method of composing is based on a twelvetone row rather than on a scale. Music that avoids the feelings of ...
... creating the feeling of a tonal center by using all the twelve chromatic tones in a prearranged order that does not lay particular emphasis on any one pitch in the composition as a whole. This method of composing is based on a twelvetone row rather than on a scale. Music that avoids the feelings of ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 5 Pinciples of Voice Leading
... Objectionable parallels: result when two parts that are separated by a P5 or a P8, or by their octave equivalents, move to as new pitch classes that are separated by the same interval Parallel 4ths are acceptable Contrary 5ths and 8ves: also called consecutive 5ths and 8ths by contrary motion ...
... Objectionable parallels: result when two parts that are separated by a P5 or a P8, or by their octave equivalents, move to as new pitch classes that are separated by the same interval Parallel 4ths are acceptable Contrary 5ths and 8ves: also called consecutive 5ths and 8ths by contrary motion ...
definitions - St. Joseph`s High School Crossmaglen
... Glissando- a rapid sliding up or down the scale on a musical instrument. Disco- dance music, melodic with a regular bass beat, intended mainly for dancing. Hi Hat Cymbal-2 cymbals and a stand used as part of a drum kit. Harpsichord-a keyboard instrument whose strings are plucked by quills or plectru ...
... Glissando- a rapid sliding up or down the scale on a musical instrument. Disco- dance music, melodic with a regular bass beat, intended mainly for dancing. Hi Hat Cymbal-2 cymbals and a stand used as part of a drum kit. Harpsichord-a keyboard instrument whose strings are plucked by quills or plectru ...
Twentieth Century New scales New chords (almost any combination
... Firebird‐ 7 beats in the measure (meter), triads with added dissonant tones Petroushka‐ two chord progressions at once, two scales at once (polytonality) Rite of Spring‐ Primitivism No traditional chord progression or construction Large emphasis on rhythm instead of melody or harmony Crude, som ...
... Firebird‐ 7 beats in the measure (meter), triads with added dissonant tones Petroushka‐ two chord progressions at once, two scales at once (polytonality) Rite of Spring‐ Primitivism No traditional chord progression or construction Large emphasis on rhythm instead of melody or harmony Crude, som ...
Music 11, 7/24/06 Fundamental of harmony Melodies are often built
... Melodies are often built around the triad. This means that by looking at a melody, we can easily understand the harmony that it expresses. A harmony will often emerge in melody as an “outline” that fills in the space of the triad. For example, a melody C-D-EF-G might imply a C-major triad by the way ...
... Melodies are often built around the triad. This means that by looking at a melody, we can easily understand the harmony that it expresses. A harmony will often emerge in melody as an “outline” that fills in the space of the triad. For example, a melody C-D-EF-G might imply a C-major triad by the way ...
Voice-Leading Guidelines:
... chord progression is specifically I 6-4, V, I (with respect to the bass notes). The I 6-4 chord occurs on a strong beat or strong portion of a beat. This chord is really an embellishment of the dominant chord at a cadence. Passing: The bass steps up (or down) over the three notes. Therefore, the 6-4 ...
... chord progression is specifically I 6-4, V, I (with respect to the bass notes). The I 6-4 chord occurs on a strong beat or strong portion of a beat. This chord is really an embellishment of the dominant chord at a cadence. Passing: The bass steps up (or down) over the three notes. Therefore, the 6-4 ...
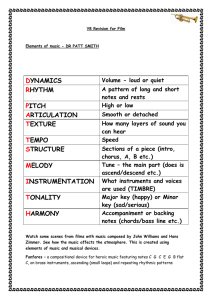
dynamics rhythm pitch articulation texture tempo
... How many layers of sound you can hear Speed Sections of a piece (intro, chorus, A, B etc.) Tune – the main part (does is ascend/descend etc.) What instruments and voices are used (TIMBRE) Major key (happy) or Minor key (sad/serious) Accompaniment or backing notes (chords/bass line etc.) ...
... How many layers of sound you can hear Speed Sections of a piece (intro, chorus, A, B etc.) Tune – the main part (does is ascend/descend etc.) What instruments and voices are used (TIMBRE) Major key (happy) or Minor key (sad/serious) Accompaniment or backing notes (chords/bass line etc.) ...
• Melody = a succession of pitches at specific durations that begins
... a 'piece' = a musical composition which is played on instruments. ...
... a 'piece' = a musical composition which is played on instruments. ...
Inversions
... useful rule applying to all intervals (that is those of one octave or less). The number of any interval and the number of its inversion always add up to nine. Thus a fifth (number 5) and its inverse or complement, a fourth (number is 4) add up to 9. Do not forget that chord quality is still a factor ...
... useful rule applying to all intervals (that is those of one octave or less). The number of any interval and the number of its inversion always add up to nine. Thus a fifth (number 5) and its inverse or complement, a fourth (number is 4) add up to 9. Do not forget that chord quality is still a factor ...
Baroque-Era Algorithmic Composition Kevin Deisz 1st Step – Keys
... Can also be resolved in the modulated key, i.e. V/IV → ii Allows the map to change based off of the current progression within the piece ...
... Can also be resolved in the modulated key, i.e. V/IV → ii Allows the map to change based off of the current progression within the piece ...
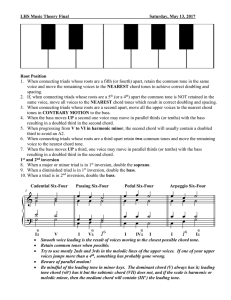
lhs music theory final exam review sheet
... 2. If, when connecting triads whose roots are a 5th (or a 4th) apart the common tone is NOT retained in the same voice, move all voices to the NEAREST chord tones which result in correct doubling and spacing. 3. When connecting triads whose roots are a second apart, move all the upper voices to the ...
... 2. If, when connecting triads whose roots are a 5th (or a 4th) apart the common tone is NOT retained in the same voice, move all voices to the NEAREST chord tones which result in correct doubling and spacing. 3. When connecting triads whose roots are a second apart, move all the upper voices to the ...
Document
... chord – two or more notes sounded at the same time dominant – the fifth note of a scale (“SOL”) harmony – two or more notes played or sung at the same time leading tone – the seventh note of a scale (“TI”) octave – the 8th note above or below a given pitch; it is the same letter of the music alphabe ...
... chord – two or more notes sounded at the same time dominant – the fifth note of a scale (“SOL”) harmony – two or more notes played or sung at the same time leading tone – the seventh note of a scale (“TI”) octave – the 8th note above or below a given pitch; it is the same letter of the music alphabe ...
Defintions - WordPress.com
... Form- organizton of musical ideas in time FanfareHalf Note- quick note Harmony- how chords are constructed and follew Home Key- both the beginning and end note of a piece Homophonic- main melody is accompanied by chords Indefinite PitchIdiomaticKey Signature- sharp or flat signs following the clef L ...
... Form- organizton of musical ideas in time FanfareHalf Note- quick note Harmony- how chords are constructed and follew Home Key- both the beginning and end note of a piece Homophonic- main melody is accompanied by chords Indefinite PitchIdiomaticKey Signature- sharp or flat signs following the clef L ...
Document
... Melodic leaps of an A2 or A4 should be avoided Consecutive P1, P4,P5, or P8 are forbidden 3. Write the alto and tenor for the second chord in each case without change in structure. ...
... Melodic leaps of an A2 or A4 should be avoided Consecutive P1, P4,P5, or P8 are forbidden 3. Write the alto and tenor for the second chord in each case without change in structure. ...
the schenkerian analysis in the modern context of the
... insights. Thus, it is important for analysts to try out multiple readings of a piece, and work on incorporating the richness provided by each into a sort of meta-reading of the surface. Functions can be any aspect of a Schenkerian graph including the “effect of being passing”, or more simple functio ...
... insights. Thus, it is important for analysts to try out multiple readings of a piece, and work on incorporating the richness provided by each into a sort of meta-reading of the surface. Functions can be any aspect of a Schenkerian graph including the “effect of being passing”, or more simple functio ...
Power Point presentation: basics of music
... – Riff = motive with a distinct rhythm that repeats throughout piece ...
... – Riff = motive with a distinct rhythm that repeats throughout piece ...



![Dan`s Music Theory 101 Cheat Sheet []](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007752700_2-d39806ec781c16b3e6c991a5c61a970a-300x300.png)