FROM BRAHMS TO THE SECOND VIENNESE SCHOOL by Sara Yong Rosado
... in music which stretched the boundaries of tonality. Seeing themselves as direct heirs of Brahms and his musical legacy, they composed works they perceived as taking the next logical step: exploring atonality and twelve note composition to emancipate pitches from their conventional melodic and harmo ...
... in music which stretched the boundaries of tonality. Seeing themselves as direct heirs of Brahms and his musical legacy, they composed works they perceived as taking the next logical step: exploring atonality and twelve note composition to emancipate pitches from their conventional melodic and harmo ...
polychoral - WordPress.com
... though it is established in a modal way with a II-I cadence (bars 46-7) and a plagal cadence (IVI) in bars 48-9. • The music ends in G minor with frequent E flats detracting from a sense of Dorian modality. There is a perfect cadence in bar 77, though the final cadence is plagal. ...
... though it is established in a modal way with a II-I cadence (bars 46-7) and a plagal cadence (IVI) in bars 48-9. • The music ends in G minor with frequent E flats detracting from a sense of Dorian modality. There is a perfect cadence in bar 77, though the final cadence is plagal. ...
Voice-Leading Guidelines:
... § The 3 , when doubled goes in contrary motion th § The 5 can resolve freely – when doubled, use contrary motion nd th 2 inversion: double 5 nd o 2 inversion should use the type categories ...
... § The 3 , when doubled goes in contrary motion th § The 5 can resolve freely – when doubled, use contrary motion nd th 2 inversion: double 5 nd o 2 inversion should use the type categories ...
Understanding Chord Symbols - Florida Music Education Associations
... educators. Our college music education curricula often don’t allow the opportunity to become versed in this area, and as a result many music teachers are uncomfortable trying to function within this idiom. Perhaps one of the reasons is that even after 100 years, we have yet to definitively decide on ...
... educators. Our college music education curricula often don’t allow the opportunity to become versed in this area, and as a result many music teachers are uncomfortable trying to function within this idiom. Perhaps one of the reasons is that even after 100 years, we have yet to definitively decide on ...
Prime Numbers in Music Tonality
... instantly to be different from the first, but one so like the first that we deny it a separate identity.” [Partch, 88] This gave birth to what is now known as octave equivalency and is the first step of the N-Limit concept: any pitches that are related by a factor of two are considered to have the ...
... instantly to be different from the first, but one so like the first that we deny it a separate identity.” [Partch, 88] This gave birth to what is now known as octave equivalency and is the first step of the N-Limit concept: any pitches that are related by a factor of two are considered to have the ...
Expressionism and Impressionism in the 20th Century
... 20th century after years of stagnant musical development. As Robert Morgan well puts it, “In France, where the principles of functional tonality had never been so strongly anchored as in Germany, musical evolution was destined to follow a different path” (Morgan, 40). Debussy’s early String Quartet ...
... 20th century after years of stagnant musical development. As Robert Morgan well puts it, “In France, where the principles of functional tonality had never been so strongly anchored as in Germany, musical evolution was destined to follow a different path” (Morgan, 40). Debussy’s early String Quartet ...
Troubles with Tonal Terminology
... Other serious conceptual problems were with polyphony and counterpoint (Tagg 2009a: 81‐82, 86‐89). ...
... Other serious conceptual problems were with polyphony and counterpoint (Tagg 2009a: 81‐82, 86‐89). ...
Block Class Revision 2015 Set A
... Perfect V-I – found at end or middle Plagal IV-I – found at end or middle Imperfect I – V - found in the middle – never at end. ii – V- found in the middle – never at end. IV-V- found in the middle – never at end. Interrupted V-vi- found in the middle – never at end. Never repeat the same chord twic ...
... Perfect V-I – found at end or middle Plagal IV-I – found at end or middle Imperfect I – V - found in the middle – never at end. ii – V- found in the middle – never at end. IV-V- found in the middle – never at end. Interrupted V-vi- found in the middle – never at end. Never repeat the same chord twic ...
Victor Ewald`s Brass Quintet No.1, Op. 5 John Eagan, Michael
... Construction Materials at the Institute of Civil Engineers. However, those who know his name today may find it more relevant and important to know that for sixteen years he performed as the cellist with the Beliaeff Quartet, the most influential ensemble in St. Petersburg during the late 19th centur ...
... Construction Materials at the Institute of Civil Engineers. However, those who know his name today may find it more relevant and important to know that for sixteen years he performed as the cellist with the Beliaeff Quartet, the most influential ensemble in St. Petersburg during the late 19th centur ...
41. George Gershwin Summertime from Porgy and Bess
... Avoidance of conventional perfect cadences. In bar 15, beat 4, the top three notes form part of a V7 chord, but instead of an F# in the bass, Gershwin slips chromatically down through C natural. In bars 21-22 a progression from E- G/A leads not to the expected D major, but to Bm with prominent seven ...
... Avoidance of conventional perfect cadences. In bar 15, beat 4, the top three notes form part of a V7 chord, but instead of an F# in the bass, Gershwin slips chromatically down through C natural. In bars 21-22 a progression from E- G/A leads not to the expected D major, but to Bm with prominent seven ...
Example Paraphrase/ synonym ...when it comes to that music which
... Paraphrase/ synonym ...when it comes to that music which enables players to commune with each other or with a few friends... ...some taking part in the ceremonies and others dreaming of being singled out by the Sun King to hold a candle... Accompanying parts were completely subordinated to the princ ...
... Paraphrase/ synonym ...when it comes to that music which enables players to commune with each other or with a few friends... ...some taking part in the ceremonies and others dreaming of being singled out by the Sun King to hold a candle... Accompanying parts were completely subordinated to the princ ...
Higher Music Concepts
... Sonata form is the structure of the first movement of many sonatas, symphonies and often overtures. It contains three sections: exposition (introduction of two contrasting themes in related keys), development (the original ideas are built upon) and recapitulation (the original ideas are heard again, ...
... Sonata form is the structure of the first movement of many sonatas, symphonies and often overtures. It contains three sections: exposition (introduction of two contrasting themes in related keys), development (the original ideas are built upon) and recapitulation (the original ideas are heard again, ...
Night in Tunisia thoughts,
... find it more useful to associate a half/whole dim scale with a dominant seventh chord, and consider the whole half as just a mode of the diminshed scale (which is symmetrical). There are only three unique dim scales for you to learn. (so no excuses). C7, Eb7, F#7, and A7 all share the same dim scale ...
... find it more useful to associate a half/whole dim scale with a dominant seventh chord, and consider the whole half as just a mode of the diminshed scale (which is symmetrical). There are only three unique dim scales for you to learn. (so no excuses). C7, Eb7, F#7, and A7 all share the same dim scale ...
Secondary Functions 1 - Appoquinimink High School
... #1. Is the altered chord a major triad or major-minor seventh chord? If not, than it is not a secondary dominant #2. Find the note a P5 below the root of the altered chord #3. Would a major or minor triad built on that note be a diatonic triad in this key? If so, the altered chord is a secondary dom ...
... #1. Is the altered chord a major triad or major-minor seventh chord? If not, than it is not a secondary dominant #2. Find the note a P5 below the root of the altered chord #3. Would a major or minor triad built on that note be a diatonic triad in this key? If so, the altered chord is a secondary dom ...
Powerpoint
... the Baroque, were much less commonly used later Continuous movement in short note values without ‘periodic phrasing’ (i.e. without clearly-articulated two- and four-bar phrases) Fugal writing in parts of the Gigue – although similar contrapuntal styles were used before the Baroque period and were ne ...
... the Baroque, were much less commonly used later Continuous movement in short note values without ‘periodic phrasing’ (i.e. without clearly-articulated two- and four-bar phrases) Fugal writing in parts of the Gigue – although similar contrapuntal styles were used before the Baroque period and were ne ...
Music Theory Terms
... work’s tempo may also be indicated by a metronome marking, which indicates the number of a certain type of note per minute (e.g., quarter note = 120). Tempos are often modified with Italian adjectives, such as allegro con fuoco (fast, with fire), which can make them more unique. Movements from large ...
... work’s tempo may also be indicated by a metronome marking, which indicates the number of a certain type of note per minute (e.g., quarter note = 120). Tempos are often modified with Italian adjectives, such as allegro con fuoco (fast, with fire), which can make them more unique. Movements from large ...
Harmonics - Homework References
... sound (so dissonant, it was historically associated with the devil) The ratio between a tri-tone and fundamental frequency is √2:1 (a complex ratio, resulting in dissonance) Pythagoras discovered that when an octave (not a string’s harmonic) is divided exactly in half, a tri-tone is produced; each o ...
... sound (so dissonant, it was historically associated with the devil) The ratio between a tri-tone and fundamental frequency is √2:1 (a complex ratio, resulting in dissonance) Pythagoras discovered that when an octave (not a string’s harmonic) is divided exactly in half, a tri-tone is produced; each o ...
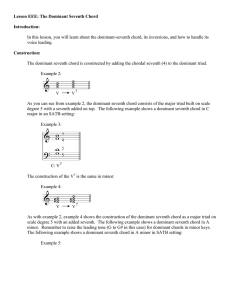
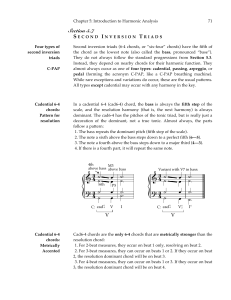
Second Inversion Triads
... They do not always follow the standard progressions from Section 5.3. Instead, they depend on nearby chords for their harmonic function. They almost always occur as one of four types: cadential, passing, arpeggio, or pedal (forming the acronym C-PAP, like a C-PAP breathing machine). While rare excep ...
... They do not always follow the standard progressions from Section 5.3. Instead, they depend on nearby chords for their harmonic function. They almost always occur as one of four types: cadential, passing, arpeggio, or pedal (forming the acronym C-PAP, like a C-PAP breathing machine). While rare excep ...
File
... In analyzing music we often use numbers to indicate the bass positions of chords. We use numbers derived from the Baroque Period called Figured Bass or Thoroughbass. During the Baroque period, the keyboard player in an ensemble read from a part consisting only of a bass line and some symbols indicat ...
... In analyzing music we often use numbers to indicate the bass positions of chords. We use numbers derived from the Baroque Period called Figured Bass or Thoroughbass. During the Baroque period, the keyboard player in an ensemble read from a part consisting only of a bass line and some symbols indicat ...
Tonality

Tonality is a musical system in which pitches or chords are arranged so as to induce a hierarchy of perceived relations, stabilities, and attractions. The pitch or chord with the greatest stability is called the tonic. The most common use of the term ""is to designate the arrangement of musical phenomena around a referential tonic in European music from about 1600 to about 1910"" (Hyer 2001). While today classical musics may practice or avoid any sort of tonality, harmony in popular musics remains tonal in some sense, and harmony in folk and jazz musics include many, if not all, modal or tonal characteristics, while having different properties from common-practice classical music.""All harmonic idioms in popular music are tonal, and none is without function"" (Tagg 2003, 534).""Tonality is an organized system of tones (e.g., the tones of a major or minor scale) in which one tone (the tonic) becomes the central point to which the remaining tones are related. In tonality, the tonic (tonal center) is the tone of complete relaxation, the target toward which other tones lead"" (Benward & Saker 2003, 36).""Tonal music is music that is unified and dimensional. Music is unified if it is exhaustively referable to a precompositional system generated by a single constructive principle derived from a basic scale-type; it is dimensional if it can nonetheless be distinguished from that precompositional ordering"" (Pitt 1995, 299).The term tonalité originated with Alexandre-Étienne Choron (1810) and was borrowed by François-Joseph Fétis in 1840 (Reti 1958,; Simms 1975, 119; Judd 1998a, 5; Heyer 2001; Brown 2005, xiii). According to Carl Dahlhaus, however, the term tonalité was only coined by Castil-Blaze in 1821 (Dahlhaus 1967, 960; Dahlhaus 1980, 51).Although Fétis used it as a general term for a system of musical organization and spoke of types de tonalités rather than a single system, today the term is most often used to refer to major–minor tonality, the system of musical organization of the common practice period. Major-minor tonality is also called harmonic tonality, diatonic tonality, common practice tonality, functional tonality, or just tonality.