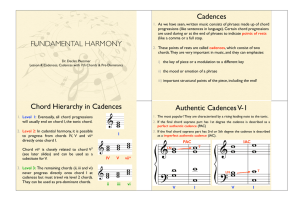
Cadences Chord Hierarchy in Cadences Authentic Cadences V
... 1. Like authentic cadences they are characterised by a rising leading note, but instead of going from chord V to I, interrupted cadence move from chord V to vi. 2. Expected chord I missing, so it is known as a deceptive cadence (DC) 3. If the leading note is in the soprano part of chord V (very comm ...
... 1. Like authentic cadences they are characterised by a rising leading note, but instead of going from chord V to I, interrupted cadence move from chord V to vi. 2. Expected chord I missing, so it is known as a deceptive cadence (DC) 3. If the leading note is in the soprano part of chord V (very comm ...
New Harmonic Resources
... b. As a scale: related to the whole-tone scale (with A-natural instead of A-flat) c. As a dominant thirteenth/sharp eleven chord (with added G) d. As a chord with mixed intervals ...
... b. As a scale: related to the whole-tone scale (with A-natural instead of A-flat) c. As a dominant thirteenth/sharp eleven chord (with added G) d. As a chord with mixed intervals ...
6. Michael Tippett Concerto for double string orchestra: movement I
... character, although it tends to glide around its tonal centres, treating them as reference points rather than establishing them firmly. There is little feeling here that harmony guides and supports the tonality – there are few instances where a new tonic is preceded by a dominant for example (bb.904 ...
... character, although it tends to glide around its tonal centres, treating them as reference points rather than establishing them firmly. There is little feeling here that harmony guides and supports the tonality – there are few instances where a new tonic is preceded by a dominant for example (bb.904 ...
Music Theory Vocabulary - Trinity Bend Performing Arts
... Chords which are next to one another in scale degree ranking; thus, their notes are separated by a step or half step ...
... Chords which are next to one another in scale degree ranking; thus, their notes are separated by a step or half step ...
Schenkerian Theory, Neo-Riemannian Theory and Late Schubert: A
... Drawing from Tovey’s concept of key-relations, this article offers a new way of understanding how a Schenkerian and neo-Riemannian view of Schubert’s late tonal practices may be complementary. As I suggest, Tovey’s concept of key-relations can function as a bridge between these two theories because ...
... Drawing from Tovey’s concept of key-relations, this article offers a new way of understanding how a Schenkerian and neo-Riemannian view of Schubert’s late tonal practices may be complementary. As I suggest, Tovey’s concept of key-relations can function as a bridge between these two theories because ...
UNIT 1: Intervals and Scales
... Secondary triads can be found in either major, minor, diminished or augmented form depending on the scale represented. ...
... Secondary triads can be found in either major, minor, diminished or augmented form depending on the scale represented. ...
Popular Music Theory - The Academy Of Popular Music
... When written on its own a semiquaver has 2 tails instead of one, to distinguish it from a quaver. A semiquaver rest looks like a quaver rest with 2 lines instead of one. B Minor has the same key signature as D Major. The B Natural Minor Scale contains the notes B, C#, D, E, F#, G, A and B. The triad ...
... When written on its own a semiquaver has 2 tails instead of one, to distinguish it from a quaver. A semiquaver rest looks like a quaver rest with 2 lines instead of one. B Minor has the same key signature as D Major. The B Natural Minor Scale contains the notes B, C#, D, E, F#, G, A and B. The triad ...
Confutatis from Mozart`s Requiem One of the most renowned and
... above it, which is E. Now, in the key of A-minor, D# does not exist in the scale. It would be considered a non-harmonic tone. However, sometimes when non-harmonic tones exist, they actually act as leading tones into a new key. In the key of A-minor, D is the root of a minor-iv chord. But because th ...
... above it, which is E. Now, in the key of A-minor, D# does not exist in the scale. It would be considered a non-harmonic tone. However, sometimes when non-harmonic tones exist, they actually act as leading tones into a new key. In the key of A-minor, D is the root of a minor-iv chord. But because th ...
The History of Music, Second Edition
... 10. What were Johannes Ockeghem's contributions to music? [Ockeghem was a powerfully influential composer and teacher of the time who pioneered choral music, a new Flemish style. Renaissance composers strove for this ideal sound.] What other Flemish styles became popular at this time? [The Latin Ma ...
... 10. What were Johannes Ockeghem's contributions to music? [Ockeghem was a powerfully influential composer and teacher of the time who pioneered choral music, a new Flemish style. Renaissance composers strove for this ideal sound.] What other Flemish styles became popular at this time? [The Latin Ma ...
One page overview of set works
... A3 – Drums enter, plus a synth-strings countermelody A4 – Bass enters, plus held synth-string chords A5 – Syncopated piano chords introduced After the breakdown, texture becomes thinner as piano & drums drop out (for Bx2). They re-enter for the next 8 bars (By2), then drop out again until the end CO ...
... A3 – Drums enter, plus a synth-strings countermelody A4 – Bass enters, plus held synth-string chords A5 – Syncopated piano chords introduced After the breakdown, texture becomes thinner as piano & drums drop out (for Bx2). They re-enter for the next 8 bars (By2), then drop out again until the end CO ...
Flow My Tears - davenantperformingarts
... Harmony • (Another common type of suspension is heard at the start of bar 2, where the lute holds a 7th (E) above F in the bass and then resolves this dissonance by falling to a D, a 6th above the same bass note. This is known as a 7-6 suspension for similar reasons) • Bars 15(4)-16 feature a Phryg ...
... Harmony • (Another common type of suspension is heard at the start of bar 2, where the lute holds a 7th (E) above F in the bass and then resolves this dissonance by falling to a D, a 6th above the same bass note. This is known as a 7-6 suspension for similar reasons) • Bars 15(4)-16 feature a Phryg ...
SEVENTH CHORDS Every triad can be extended by adding another
... A seventh chord is said to be in root position when all the intervals are types of thirds. Root position is designated simple by a 7, meaning there is a third, fifth and seventh above the bass. (The third and the fifth above the bass are understood in the Arabic numeral designation.) ...
... A seventh chord is said to be in root position when all the intervals are types of thirds. Root position is designated simple by a 7, meaning there is a third, fifth and seventh above the bass. (The third and the fifth above the bass are understood in the Arabic numeral designation.) ...
Modulation I: Diatonic common chords
... Common Tone • Pivot on an emphasized tone that is common to two keys (not only in melody) • The two chords linked by a common tone might share a chromatic mediant relationship (a foreign relationship) • The roots of the two chords (of the common tone are a M/m 3rd apart • They are both major or both ...
... Common Tone • Pivot on an emphasized tone that is common to two keys (not only in melody) • The two chords linked by a common tone might share a chromatic mediant relationship (a foreign relationship) • The roots of the two chords (of the common tone are a M/m 3rd apart • They are both major or both ...
01_front - Massey Research Online
... topics of scales, melody, voicings, harmony and rhythm are examined in separate chapters with over two hundred notated musical examples used to demonstrate the materials in their context. This thesis also seeks to explain the relationships between these elements and presents the material in a fonn a ...
... topics of scales, melody, voicings, harmony and rhythm are examined in separate chapters with over two hundred notated musical examples used to demonstrate the materials in their context. This thesis also seeks to explain the relationships between these elements and presents the material in a fonn a ...
Chopin: Prelude No.15 in D flat Major
... rival teenage gangs, the Jets (American) and the Sharks (Puerto Rican). Tony, the male lead character (Jet) falls in love with Maria (Sharks) and as in the Shakespeare play, their love is doomed. The song ‘Something’s Coming’ is Tony’s first solo, and establishes his optimistic character. ...
... rival teenage gangs, the Jets (American) and the Sharks (Puerto Rican). Tony, the male lead character (Jet) falls in love with Maria (Sharks) and as in the Shakespeare play, their love is doomed. The song ‘Something’s Coming’ is Tony’s first solo, and establishes his optimistic character. ...
About Diapason
... beginning and the end of the piece, the “diapason” includes harmonics from the 48th through 64th (thus defining an interval of a perfect fourth), whereas at the dynamic climax of the piece (at about two-thirds to three-quarters of the way through) it includes the first through the seventeenth partia ...
... beginning and the end of the piece, the “diapason” includes harmonics from the 48th through 64th (thus defining an interval of a perfect fourth), whereas at the dynamic climax of the piece (at about two-thirds to three-quarters of the way through) it includes the first through the seventeenth partia ...
PowerPoint Lecture Slides
... The Western pitch system is just one of many great musical systems worldwide. Indian music recognizes 22 pitches per octave, but like Western music, builds scales upon seven ascending and seven descending pitches. Middle Eastern music in the Arab tradition uses 24 pitches per octave, and recognizes ...
... The Western pitch system is just one of many great musical systems worldwide. Indian music recognizes 22 pitches per octave, but like Western music, builds scales upon seven ascending and seven descending pitches. Middle Eastern music in the Arab tradition uses 24 pitches per octave, and recognizes ...
Pitch - AceHSC
... - Wide narrow range? - Describe contour (smooth, jagged, ascending, descending, sequence) - Draw contour - Phrases are long or short? (count number of bars in each phrase) - Ornamentation or improvisation? ...
... - Wide narrow range? - Describe contour (smooth, jagged, ascending, descending, sequence) - Draw contour - Phrases are long or short? (count number of bars in each phrase) - Ornamentation or improvisation? ...
Tonality

Tonality is a musical system in which pitches or chords are arranged so as to induce a hierarchy of perceived relations, stabilities, and attractions. The pitch or chord with the greatest stability is called the tonic. The most common use of the term ""is to designate the arrangement of musical phenomena around a referential tonic in European music from about 1600 to about 1910"" (Hyer 2001). While today classical musics may practice or avoid any sort of tonality, harmony in popular musics remains tonal in some sense, and harmony in folk and jazz musics include many, if not all, modal or tonal characteristics, while having different properties from common-practice classical music.""All harmonic idioms in popular music are tonal, and none is without function"" (Tagg 2003, 534).""Tonality is an organized system of tones (e.g., the tones of a major or minor scale) in which one tone (the tonic) becomes the central point to which the remaining tones are related. In tonality, the tonic (tonal center) is the tone of complete relaxation, the target toward which other tones lead"" (Benward & Saker 2003, 36).""Tonal music is music that is unified and dimensional. Music is unified if it is exhaustively referable to a precompositional system generated by a single constructive principle derived from a basic scale-type; it is dimensional if it can nonetheless be distinguished from that precompositional ordering"" (Pitt 1995, 299).The term tonalité originated with Alexandre-Étienne Choron (1810) and was borrowed by François-Joseph Fétis in 1840 (Reti 1958,; Simms 1975, 119; Judd 1998a, 5; Heyer 2001; Brown 2005, xiii). According to Carl Dahlhaus, however, the term tonalité was only coined by Castil-Blaze in 1821 (Dahlhaus 1967, 960; Dahlhaus 1980, 51).Although Fétis used it as a general term for a system of musical organization and spoke of types de tonalités rather than a single system, today the term is most often used to refer to major–minor tonality, the system of musical organization of the common practice period. Major-minor tonality is also called harmonic tonality, diatonic tonality, common practice tonality, functional tonality, or just tonality.