Chord Symbols Handout
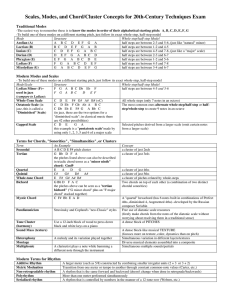
... Minor Seventh Chords The minor seventh chord root, fifth, and seventh of the dominant seventh chord, but lowers the third by a half step, like this: ...
... Minor Seventh Chords The minor seventh chord root, fifth, and seventh of the dominant seventh chord, but lowers the third by a half step, like this: ...
Musica Ficta and
... brought into question many of the assumptions on which much of this work was based, including the assumptions that 16th-century music was uniformly modal; that Monteverdi’s tonal language represents a transitional stage between ‘modality’ and ‘tonality’; that the establishment of modern tonality inv ...
... brought into question many of the assumptions on which much of this work was based, including the assumptions that 16th-century music was uniformly modal; that Monteverdi’s tonal language represents a transitional stage between ‘modality’ and ‘tonality’; that the establishment of modern tonality inv ...
Slide 1
... Any minor dominant chord is built with a b3 and b7 (relative to the root of the chord). An Am7 chord “fits” the key of C because every note in Am7 (the vi7 if C is the I) is in the key of C: th (octave) 8 b7th ...
... Any minor dominant chord is built with a b3 and b7 (relative to the root of the chord). An Am7 chord “fits” the key of C because every note in Am7 (the vi7 if C is the I) is in the key of C: th (octave) 8 b7th ...
NJCCS Elements of Music
... Quintuple meter, with 5 beats to the measure, and septuple meter, with 7 beats to the measure, occur frequently in twentieth-century music and are found occasionally in earlier music. Each of these meters combines duple and triple meter. In quintuple meter, for example, the measure is subdivided in ...
... Quintuple meter, with 5 beats to the measure, and septuple meter, with 7 beats to the measure, occur frequently in twentieth-century music and are found occasionally in earlier music. Each of these meters combines duple and triple meter. In quintuple meter, for example, the measure is subdivided in ...
Scales, Modes, and Chord/Cluster Concepts for 20th
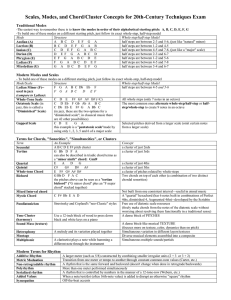
... All whole steps (only 7 notes in an octave) Octatonic Scale (in C D Eb F Gb Ab A B C The most common ones alternate whole-step/half-step or halfjazz, this is called a C Db Eb E F# G A Bb C step/whole-step to create 9 notes in an octave "Diminished" Scale) (in jazz, these are the two options for a "d ...
... All whole steps (only 7 notes in an octave) Octatonic Scale (in C D Eb F Gb Ab A B C The most common ones alternate whole-step/half-step or halfjazz, this is called a C Db Eb E F# G A Bb C step/whole-step to create 9 notes in an octave "Diminished" Scale) (in jazz, these are the two options for a "d ...
Elements of Music
... it as a bass note. Bass players can usually stick to going with the second note. Another popular chord is a suspended chord. It would be written like Asus, Dsus, Esus A suspended chord is when the 3rd is raised. An Esus would have be made up of E, A, and B This is usually used as a prolongation of t ...
... it as a bass note. Bass players can usually stick to going with the second note. Another popular chord is a suspended chord. It would be written like Asus, Dsus, Esus A suspended chord is when the 3rd is raised. An Esus would have be made up of E, A, and B This is usually used as a prolongation of t ...
View - Ross Hamilton`s Music Education Resources
... (snobs in vests). Their frenetic hurrahs are depicted through staccato articulation and a rising 5th in b.31-32. There is a movement towards A major (the dominant key) in b.31-32, without actually settling there; the harmony moves in a circle of 5ths back to the tonic chord of D major in b.31-33 (in ...
... (snobs in vests). Their frenetic hurrahs are depicted through staccato articulation and a rising 5th in b.31-32. There is a movement towards A major (the dominant key) in b.31-32, without actually settling there; the harmony moves in a circle of 5ths back to the tonic chord of D major in b.31-33 (in ...
Ben Johnston Pantonality Generalized
... simple rational proportions, and in the process has begun inventing musical idioms of extended just intonation. To certain 19th century theorists, among them Moritz Hauptmann, Hermann von Helmholtz, Arthur von Oettingen and Hugo Riemann, the common practice of composition in their time represented t ...
... simple rational proportions, and in the process has begun inventing musical idioms of extended just intonation. To certain 19th century theorists, among them Moritz Hauptmann, Hermann von Helmholtz, Arthur von Oettingen and Hugo Riemann, the common practice of composition in their time represented t ...
6/26/06 Introduction We all have a mental/aural image of “music
... If we know where these pitches are in the given clef, the rest all fall into place. For example, since the treble clef tells us that the pitch G is the second line from the bottom, we know that the names of the pitches ascending (moving higher on the staff “stepwise” to the space, line, space, line, ...
... If we know where these pitches are in the given clef, the rest all fall into place. For example, since the treble clef tells us that the pitch G is the second line from the bottom, we know that the names of the pitches ascending (moving higher on the staff “stepwise” to the space, line, space, line, ...
Tonal structure and scales - Jacobs University Mathematics
... of a tone ( "the probe-tone") which is randomly chosen among the 12 pitches. 3. Participants are asked to rate on a scale from 1 to 7 ( 1 = very bad to 7 = very good) how ell the probe tone fit in the previously heard experiment. A.Diederich – International University Bremen – USC – MMM – Spring 200 ...
... of a tone ( "the probe-tone") which is randomly chosen among the 12 pitches. 3. Participants are asked to rate on a scale from 1 to 7 ( 1 = very bad to 7 = very good) how ell the probe tone fit in the previously heard experiment. A.Diederich – International University Bremen – USC – MMM – Spring 200 ...
Tonal Function and Metrical Accent: A Historical Perspective
... not only generates a consonanttriad, but also gives rise to a tonality.6In isolation, an individualsound naturallyfunctionsas a ton principal or note tonique, and the triad that is built upon that note represents the tonal center of a key. Rameau is so convinced of the power of a single triad to exp ...
... not only generates a consonanttriad, but also gives rise to a tonality.6In isolation, an individualsound naturallyfunctionsas a ton principal or note tonique, and the triad that is built upon that note represents the tonal center of a key. Rameau is so convinced of the power of a single triad to exp ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 3 Introduction to Triads and Seventh
... Root position Root position (7), first inversion ( 65 ) , second inversion ( 43 ), third inversion ( 42 ) Inversion Symbols and Figure Bass Analyzing music using numbers derived from the Baroque (1600-1750) system called figured bass or thoroughbass Keyboard player in an ensemble read from a ...
... Root position Root position (7), first inversion ( 65 ) , second inversion ( 43 ), third inversion ( 42 ) Inversion Symbols and Figure Bass Analyzing music using numbers derived from the Baroque (1600-1750) system called figured bass or thoroughbass Keyboard player in an ensemble read from a ...
Scales, Modes, and Chord/Cluster Concepts for 20th
... All whole steps (only 7 notes in an octave) Whole-Tone Scale Octatonic Scale (in C D Eb F Gb Ab A B C The most common ones alternate whole-step/half-step or halfjazz, this is called a C Db Eb E F# G A Bb C step/whole-step to create 9 notes in an octave "Diminished" Scale) (in jazz, these are the two ...
... All whole steps (only 7 notes in an octave) Whole-Tone Scale Octatonic Scale (in C D Eb F Gb Ab A B C The most common ones alternate whole-step/half-step or halfjazz, this is called a C Db Eb E F# G A Bb C step/whole-step to create 9 notes in an octave "Diminished" Scale) (in jazz, these are the two ...
supplementaryMaterial_08Dec15
... piano, beginning on C, form a Major scale (C, D, E, F, G, A, B, C). The scale degrees form a hierarchy of stability (the tonal hierarchy), enabling notes to be used for different structural purposes throughout a musical piece (e.g., highly stable notes are more likely to occur at boundaries than uns ...
... piano, beginning on C, form a Major scale (C, D, E, F, G, A, B, C). The scale degrees form a hierarchy of stability (the tonal hierarchy), enabling notes to be used for different structural purposes throughout a musical piece (e.g., highly stable notes are more likely to occur at boundaries than uns ...
Lesson_SSS_-_Diatoni..
... Db and Cb). The descending-fifth sequence that follows, beginning with iv in m. 26, completes the cycle from the initial i chord to the tonic in m. 32. Harmonically, the iv chord in m. 33 continues the descending-fifth series, but by then, the melodic pattern in the upper voice is broken. Sequences ...
... Db and Cb). The descending-fifth sequence that follows, beginning with iv in m. 26, completes the cycle from the initial i chord to the tonic in m. 32. Harmonically, the iv chord in m. 33 continues the descending-fifth series, but by then, the melodic pattern in the upper voice is broken. Sequences ...
Grade 4 Music I Can... Rhythm I can show that beats may be
... I can tell that an interval is the space between two sounds. • I know that an interval may be changed by an accidental. • I can tell that intervals can give shape or contour to a melody I can tell the melody is based on the C major scale. Harmony I can tell the IV and V chords are used to accompany ...
... I can tell that an interval is the space between two sounds. • I know that an interval may be changed by an accidental. • I can tell that intervals can give shape or contour to a melody I can tell the melody is based on the C major scale. Harmony I can tell the IV and V chords are used to accompany ...
Psychology of Music Learning
... Notation - tempo, duration events/silences, groupings, meter Also grouping – pitch, timbre, dynamic Also metrical – tension and release Also interpretive – notated duration vs. resulting duration after articulation style is applied ...
... Notation - tempo, duration events/silences, groupings, meter Also grouping – pitch, timbre, dynamic Also metrical – tension and release Also interpretive – notated duration vs. resulting duration after articulation style is applied ...
Expanded Tonality in Quartal Space: Back to Debussy`s
... (1915), we attempt to locate and apply a fourth-based system that could fit the actual chord content of the piece. Moreover, one might expect that Debussy may have hidden in the piece pseudo or expanded tonal functions behind a colorful, exotic-sounding (since non-triadic) harmony, which will also g ...
... (1915), we attempt to locate and apply a fourth-based system that could fit the actual chord content of the piece. Moreover, one might expect that Debussy may have hidden in the piece pseudo or expanded tonal functions behind a colorful, exotic-sounding (since non-triadic) harmony, which will also g ...
Lesson SSS - Diatonic Sequences
... Beginning with the vi chord on the anacrusis to m. 14, a series of arpeggios in the left hand outline a descending fifth sequence through the remainder of that measure. In m. 15, the descending-fifth harmonic pattern set into motion by the sequence continues through V, I, and IV, despite the altere ...
... Beginning with the vi chord on the anacrusis to m. 14, a series of arpeggios in the left hand outline a descending fifth sequence through the remainder of that measure. In m. 15, the descending-fifth harmonic pattern set into motion by the sequence continues through V, I, and IV, despite the altere ...
Two By Three - Michael Dellaira
... color: her instruments tend to gather in the same registers, the effect of which makes her tunes, which are otherwise well-wrought and fetching, appear tired out. Her particular way of doing things does give her music personality; it’s just that she does them twice too often, and the more active (or ...
... color: her instruments tend to gather in the same registers, the effect of which makes her tunes, which are otherwise well-wrought and fetching, appear tired out. Her particular way of doing things does give her music personality; it’s just that she does them twice too often, and the more active (or ...
Tonality

Tonality is a musical system in which pitches or chords are arranged so as to induce a hierarchy of perceived relations, stabilities, and attractions. The pitch or chord with the greatest stability is called the tonic. The most common use of the term ""is to designate the arrangement of musical phenomena around a referential tonic in European music from about 1600 to about 1910"" (Hyer 2001). While today classical musics may practice or avoid any sort of tonality, harmony in popular musics remains tonal in some sense, and harmony in folk and jazz musics include many, if not all, modal or tonal characteristics, while having different properties from common-practice classical music.""All harmonic idioms in popular music are tonal, and none is without function"" (Tagg 2003, 534).""Tonality is an organized system of tones (e.g., the tones of a major or minor scale) in which one tone (the tonic) becomes the central point to which the remaining tones are related. In tonality, the tonic (tonal center) is the tone of complete relaxation, the target toward which other tones lead"" (Benward & Saker 2003, 36).""Tonal music is music that is unified and dimensional. Music is unified if it is exhaustively referable to a precompositional system generated by a single constructive principle derived from a basic scale-type; it is dimensional if it can nonetheless be distinguished from that precompositional ordering"" (Pitt 1995, 299).The term tonalité originated with Alexandre-Étienne Choron (1810) and was borrowed by François-Joseph Fétis in 1840 (Reti 1958,; Simms 1975, 119; Judd 1998a, 5; Heyer 2001; Brown 2005, xiii). According to Carl Dahlhaus, however, the term tonalité was only coined by Castil-Blaze in 1821 (Dahlhaus 1967, 960; Dahlhaus 1980, 51).Although Fétis used it as a general term for a system of musical organization and spoke of types de tonalités rather than a single system, today the term is most often used to refer to major–minor tonality, the system of musical organization of the common practice period. Major-minor tonality is also called harmonic tonality, diatonic tonality, common practice tonality, functional tonality, or just tonality.