From Pythagoras to Johann Sebastian Bach: An
... that allows humans to reach ultimate happiness, not a spiritual relationship with God. This return to ancient worldviews is echoed in the construction of the forty-eight preludes and fugues of Bach’s Well-Tempered Clavier. In comparison, Bach’s First Invention, BWV 772, is much like the consistency ...
... that allows humans to reach ultimate happiness, not a spiritual relationship with God. This return to ancient worldviews is echoed in the construction of the forty-eight preludes and fugues of Bach’s Well-Tempered Clavier. In comparison, Bach’s First Invention, BWV 772, is much like the consistency ...
Non-Chord Tones
... by step in the same direction. • Neighboring tone (n)- Approached by step and left by step in the opposite direction. • Suspension (s)- Approached by same tone and left by a step down. • Retardation (r)- Approached by the same tone and left by a step up. ...
... by step in the same direction. • Neighboring tone (n)- Approached by step and left by step in the opposite direction. • Suspension (s)- Approached by same tone and left by a step down. • Retardation (r)- Approached by the same tone and left by a step up. ...
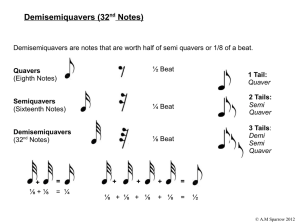
Demisemiquavers (32nd Notes)
... Do not be afraid of notes on ledger lines as all you need to do is count up or down Them like climbing a ladder. Just count the lines and spaces. Middle C is always easy to recognise and all you need to do to find the note next to Middle C In this example is count backwards through the 'Musical Alph ...
... Do not be afraid of notes on ledger lines as all you need to do is count up or down Them like climbing a ladder. Just count the lines and spaces. Middle C is always easy to recognise and all you need to do to find the note next to Middle C In this example is count backwards through the 'Musical Alph ...
`The Minóre Dhrómos [Popular Mode] in the Songs of Vasilis
... may be a melody set only in the lower pentachord, that is, D to A, which is identical for both Minóres. Therefore, one cannot suggest that this particular melody belongs in the sphere of Armonikó, nor of Natural. Thus, a fifth major chord could play the determining role in this case, for it includes ...
... may be a melody set only in the lower pentachord, that is, D to A, which is identical for both Minóres. Therefore, one cannot suggest that this particular melody belongs in the sphere of Armonikó, nor of Natural. Thus, a fifth major chord could play the determining role in this case, for it includes ...
arranging for strings i
... slur, when and where to shift positions, and whether to use an open string or the fourth finger. Isaac goes on to say that, the first violin part should remain in first position most of the time, except for an occasional shift to third position. The cellos shouldn’t include a tenor clef, and the sec ...
... slur, when and where to shift positions, and whether to use an open string or the fourth finger. Isaac goes on to say that, the first violin part should remain in first position most of the time, except for an occasional shift to third position. The cellos shouldn’t include a tenor clef, and the sec ...
Course: Music Theory II
... (4 part form A-A-B-A)), exposition, development, recapitulation, rondo form (five part A-B-A-C-A) Produce Quality Work ...
... (4 part form A-A-B-A)), exposition, development, recapitulation, rondo form (five part A-B-A-C-A) Produce Quality Work ...
Test Review - The OCD Musician
... 40. The term musical ______________ (or musical architecture) refers to the overall structure or plan of a piece of music, and it describes the layout of a composition as divided into sections, "a series of strategies designed to find a successful mean between the opposite extremes of unrelieved rep ...
... 40. The term musical ______________ (or musical architecture) refers to the overall structure or plan of a piece of music, and it describes the layout of a composition as divided into sections, "a series of strategies designed to find a successful mean between the opposite extremes of unrelieved rep ...
Stephanie Reusch Paper 2 Composers use several types of non
... In the C section of the exposition at measure 44, Mozart reminds the listener of the presentation of P by imitating the initial motive again. However, though he reminds the listener of stability by doing this, he also reminds the listener of the instable bass line of running 16th notes, this time s ...
... In the C section of the exposition at measure 44, Mozart reminds the listener of the presentation of P by imitating the initial motive again. However, though he reminds the listener of stability by doing this, he also reminds the listener of the instable bass line of running 16th notes, this time s ...
Friday, March 13, 2015 at 8pm NEC`s Jordan Hall Daniil Trifonov
... On January 13, 1822, less than a month after completing Opus 110, Beethoven put the finishing touches on his last piano sonata. The fact that it has only two movements—rare, though not unprecedented in Beethoven’s sonata output—aroused some question as to whether it was in fact complete. The publish ...
... On January 13, 1822, less than a month after completing Opus 110, Beethoven put the finishing touches on his last piano sonata. The fact that it has only two movements—rare, though not unprecedented in Beethoven’s sonata output—aroused some question as to whether it was in fact complete. The publish ...
Elements_lecs_Chs1-6_musmaj
... scale?] Balinese “pentatonic scales” (p. 51): OMI 10 (slendro and 5-tone pelog) India: 22 microtones per octave; Arab music: 24 quarter tones per octave. OMI 11 (quarter tone scale, one octave) [If time, CD ex. 1-27, Egyptian quartertone accordion]. Also ornamentation, articulation. Scale vs. ...
... scale?] Balinese “pentatonic scales” (p. 51): OMI 10 (slendro and 5-tone pelog) India: 22 microtones per octave; Arab music: 24 quarter tones per octave. OMI 11 (quarter tone scale, one octave) [If time, CD ex. 1-27, Egyptian quartertone accordion]. Also ornamentation, articulation. Scale vs. ...
Listening To Music
... • The part of the music you tap your feet or dance to • Quantifies duration of musical sound: how long or how short ...
... • The part of the music you tap your feet or dance to • Quantifies duration of musical sound: how long or how short ...
6-Many Streams Flowing
... Imagine the body of Western concert art music at the end of the 19th‐century as a huge river flowing. One way to look at what was happening at the start of the 20th‐ century is a bifurcation, or splitting off, of this river into two smaller streams. The divide was because of an approach to tonal ...
... Imagine the body of Western concert art music at the end of the 19th‐century as a huge river flowing. One way to look at what was happening at the start of the 20th‐ century is a bifurcation, or splitting off, of this river into two smaller streams. The divide was because of an approach to tonal ...
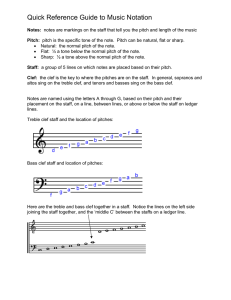
Quick Reference Guide to Music Notation
... beats. Similarly, rests have duration. Rests indicate space in the music where there is no note being sung or played. All this counting and measuring is called the metre of the music. Music is very mathematical in nature. Here are the durations of notes and rests. Whenever you see a dot ( · ) after ...
... beats. Similarly, rests have duration. Rests indicate space in the music where there is no note being sung or played. All this counting and measuring is called the metre of the music. Music is very mathematical in nature. Here are the durations of notes and rests. Whenever you see a dot ( · ) after ...
File
... Sharp: Raised in pitch by a semitone / Being above the proper pitch Staccato: Cut short crisply; detached Staff/Staves: Five parallel lines on which music is traditionally written. Support: To hold in position so as to keep from falling, sinking, or slipping. System/Score: A notation showing all the ...
... Sharp: Raised in pitch by a semitone / Being above the proper pitch Staccato: Cut short crisply; detached Staff/Staves: Five parallel lines on which music is traditionally written. Support: To hold in position so as to keep from falling, sinking, or slipping. System/Score: A notation showing all the ...
Three Conceptions of Musical Distance
... G} and {Cs, Fs} can be linked by semitonal voice leading, but are fairly far apart on the Tonnetz. Slightly more subtle, but more musically pertinent, is the following example: on the Tonnetz, C major is two units away from F major but three units from F minor (Figure 10). (Here I measure distance i ...
... G} and {Cs, Fs} can be linked by semitonal voice leading, but are fairly far apart on the Tonnetz. Slightly more subtle, but more musically pertinent, is the following example: on the Tonnetz, C major is two units away from F major but three units from F minor (Figure 10). (Here I measure distance i ...
The Pythagorean Comma The Spiral of Fifths and Equal Temperament
... Three Native American women are sitting and talking. The first is sitting on a deerskin and she says, “I have a son who weighs 130 pounds.” The second one is sitting on a bearskin and says, “I have a son who weighs 170 pounds.” The third one is sitting on a hippopotamus skin and she says, “Well, I m ...
... Three Native American women are sitting and talking. The first is sitting on a deerskin and she says, “I have a son who weighs 130 pounds.” The second one is sitting on a bearskin and says, “I have a son who weighs 170 pounds.” The third one is sitting on a hippopotamus skin and she says, “Well, I m ...
2009 HSC Music 1 Aural Skills Sample Answers
... • Use of falsetto with voice as an effect that is used to build tension and therefore musical interest. • Jungle type sounds from lower drums (Toms) at the beginning provides a driving intensity and introduction that gives an aural hint as to the musical content and music intent • Call and respon ...
... • Use of falsetto with voice as an effect that is used to build tension and therefore musical interest. • Jungle type sounds from lower drums (Toms) at the beginning provides a driving intensity and introduction that gives an aural hint as to the musical content and music intent • Call and respon ...
MUSICAL NOTATION Music is notated on a staff
... lines and spaces represent other notes and always follow in order of the alphabet using only the first seven letters (and then repeating them). For example, in treble clef, we have: ...
... lines and spaces represent other notes and always follow in order of the alphabet using only the first seven letters (and then repeating them). For example, in treble clef, we have: ...
Modal Jazz and Miles Davis: George Russell`s Influence and the
... Russell’s discovery of the Lydian mode’s relationship to its tonic triad was crucial to his Concept, for he had found a scale that truly captured the sound of the major chord. When the Lydian scale is played over its tonic triad, none of the notes sound significantly more conclusive than the others, ...
... Russell’s discovery of the Lydian mode’s relationship to its tonic triad was crucial to his Concept, for he had found a scale that truly captured the sound of the major chord. When the Lydian scale is played over its tonic triad, none of the notes sound significantly more conclusive than the others, ...
Jennifer Lancaster
... • Music has a key and tonal center For instance: C major C-D-E-F-G-A-B-C • The tonic of this scale is C • When this scale is played or a tone from it is given as a reference, people with RP can identify pitches from it ...
... • Music has a key and tonal center For instance: C major C-D-E-F-G-A-B-C • The tonic of this scale is C • When this scale is played or a tone from it is given as a reference, people with RP can identify pitches from it ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.

![`The Minóre Dhrómos [Popular Mode] in the Songs of Vasilis](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007753900_1-d4a47c601d6a2de9c01d03e9090ab75c-300x300.png)