Psychology of Music Learning
... R & B - Melody Structure • Perceptual organization: psychological factors influence apprehension of tonal sequence as a melody • Gestalt Laws • Proximity: close in time and auditory space as a melodic unit • Similarity: repeated tones as a unit • Common direction: moving in a common direction towar ...
... R & B - Melody Structure • Perceptual organization: psychological factors influence apprehension of tonal sequence as a melody • Gestalt Laws • Proximity: close in time and auditory space as a melodic unit • Similarity: repeated tones as a unit • Common direction: moving in a common direction towar ...
powerpoint - davenantperformingarts
... 63, the long notes appear on muted trumpet which also plays the rapid three-note figure returns much as it occurred first, but now on the trumpet as well (Bar 64-5). ...
... 63, the long notes appear on muted trumpet which also plays the rapid three-note figure returns much as it occurred first, but now on the trumpet as well (Bar 64-5). ...
Music Dictionary - Nitschmann Middle School Instrumental Music
... Very quick; faster than Allegro ...
... Very quick; faster than Allegro ...
AP Music Theory
... represented by two notes on the staff or two keys on the keyboard. Half Step – two pitches as close together as possible. *Half steps between E and F and between B and C *Half step between any white key and an adjacent black key Whole Step make up of two half steps. *Each pair of adjacent white keys ...
... represented by two notes on the staff or two keys on the keyboard. Half Step – two pitches as close together as possible. *Half steps between E and F and between B and C *Half step between any white key and an adjacent black key Whole Step make up of two half steps. *Each pair of adjacent white keys ...
PDF - UNT Digital Library
... only the beginning and end of a work as indicative of its central key offered a similar lack of explanation of the status and function of so-called modulatory sections. 1 9 He realized the need for a broader concept of tonality-one which would differentiate between chord grammar and chord significan ...
... only the beginning and end of a work as indicative of its central key offered a similar lack of explanation of the status and function of so-called modulatory sections. 1 9 He realized the need for a broader concept of tonality-one which would differentiate between chord grammar and chord significan ...
Music Theory Combination Tones
... I did this work at the piano) Secondly, using cycles per second values corresponding to equal tempered pitches, first , second, and third order combination tones were listed in spreadsheet form, and also transferred to musical notation. This in itself is of some interest, as it present a kind of fac ...
... I did this work at the piano) Secondly, using cycles per second values corresponding to equal tempered pitches, first , second, and third order combination tones were listed in spreadsheet form, and also transferred to musical notation. This in itself is of some interest, as it present a kind of fac ...
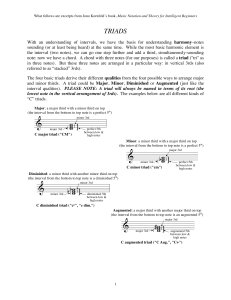
Triads, 7th chords, the roman numeral harmony system, inversions
... In recalling the issues of continuity and cohesion, it is worth noting that a big point has been made to understand triads as chords in a diatonic system, meaning that a particular group of triads can all be related to a single scale. Since a scale can be heard to represent a type of melodic continu ...
... In recalling the issues of continuity and cohesion, it is worth noting that a big point has been made to understand triads as chords in a diatonic system, meaning that a particular group of triads can all be related to a single scale. Since a scale can be heard to represent a type of melodic continu ...
A Comparison between Genetic and Memetic Algorithm
... Pitches can be adjusted but it will keep the rhythm as its characteristic. A great example of using motif is Beethoven’s Symphony No.5. ...
... Pitches can be adjusted but it will keep the rhythm as its characteristic. A great example of using motif is Beethoven’s Symphony No.5. ...
Seeing Music, Hearing Waves - Illuminations
... Musical pitches (notes) are determined by their frequency, which is measured in vibrations per second, or Hertz (Hz). The notes on a piano keyboard form a chromatic scale. A chromatic scale divides the octave into its semitones. There are twelve semitones, or half steps, to an octave in the chromati ...
... Musical pitches (notes) are determined by their frequency, which is measured in vibrations per second, or Hertz (Hz). The notes on a piano keyboard form a chromatic scale. A chromatic scale divides the octave into its semitones. There are twelve semitones, or half steps, to an octave in the chromati ...
A Derivation of the Rules of Voice-leading from Perceptual Principles
... In other words, tonal fusion is most salient when co-modulation is precise with respect to log-frequency and the frequencies of the two tones are harmonically related. Tonal fusion is next most salient when co-modulation is precise with respect to logfrequency and the frequencies of the two tones ar ...
... In other words, tonal fusion is most salient when co-modulation is precise with respect to log-frequency and the frequencies of the two tones are harmonically related. Tonal fusion is next most salient when co-modulation is precise with respect to logfrequency and the frequencies of the two tones ar ...
Pitch Perception
... the same and the second one can be varied in pitch: 1. When second pitch is close, most people think the resultant sound is “consonant” 2. As second sound gets farther away, very few people think sound is consonant 3. After two sounds get to around the distance of a minor third, most people again th ...
... the same and the second one can be varied in pitch: 1. When second pitch is close, most people think the resultant sound is “consonant” 2. As second sound gets farther away, very few people think sound is consonant 3. After two sounds get to around the distance of a minor third, most people again th ...
Georgian Court University © 2006 The McGraw
... a particular frequency, or rate of speed, and are… Relatively high or low in pitch = highness or lowness of sound Tones have letter names, A through G Interval = The distance between two tones Octave = The interval of an eighth; the most basic interval, where two tones share the same letter ...
... a particular frequency, or rate of speed, and are… Relatively high or low in pitch = highness or lowness of sound Tones have letter names, A through G Interval = The distance between two tones Octave = The interval of an eighth; the most basic interval, where two tones share the same letter ...
Walter Piston, Practical Theorist
... Harmony he wrote about a Bach chorale: "The last chord in the second measure from the end, F minor, is obviously here II of IV rather than V of B flat, so that its dominant before it has been given the somewhat awkward but nonetheless accurate designation as V of II of IV." (p. 332) In the summer of ...
... Harmony he wrote about a Bach chorale: "The last chord in the second measure from the end, F minor, is obviously here II of IV rather than V of B flat, so that its dominant before it has been given the somewhat awkward but nonetheless accurate designation as V of II of IV." (p. 332) In the summer of ...
9.2-jacobs
... concluded by previous note is a candidate for three operations: 2) Pattern Class Extension - If previous condition does not occur, check eventual extension of PO with current note. - Extension should not already be ...
... concluded by previous note is a candidate for three operations: 2) Pattern Class Extension - If previous condition does not occur, check eventual extension of PO with current note. - Extension should not already be ...
File
... regulated) by manipulating the tension of the membrane (Tympani, Kettledrums). Other instruments do not have a fixed pitch (Snare Drums, Bongos, etc). ...
... regulated) by manipulating the tension of the membrane (Tympani, Kettledrums). Other instruments do not have a fixed pitch (Snare Drums, Bongos, etc). ...
midterm review test
... 1. The Baritone is a member of what instrument family in the band? a. Woodwinds b. Brass c. Percussion d. Strings 2. The musical term Andante is a/n a. Articulation marking b. Dynamic marking c. Tempo marking d. How loud the song is 3. The musical term Crescendo means to a. Gradually get louder b. S ...
... 1. The Baritone is a member of what instrument family in the band? a. Woodwinds b. Brass c. Percussion d. Strings 2. The musical term Andante is a/n a. Articulation marking b. Dynamic marking c. Tempo marking d. How loud the song is 3. The musical term Crescendo means to a. Gradually get louder b. S ...
Hexatonic Experiments (watermarked)
... V. The Chromatic Mediant Experiment (with added tone) – This movement utilizes a scale of my own invention. The scale is derived from the juxtaposition of two chords which exhibit a chromatic mediant relationship (that is, their roots are a third apart and they have only one common tone) and an adde ...
... V. The Chromatic Mediant Experiment (with added tone) – This movement utilizes a scale of my own invention. The scale is derived from the juxtaposition of two chords which exhibit a chromatic mediant relationship (that is, their roots are a third apart and they have only one common tone) and an adde ...
presentation source
... the time of the original rhythm. In order to keep the musicality, I did change the pitches of the second phrase by beginning the same interval pattern on the 4th note of the first 6-note phrase. Also, the melody is moved up an octave in order to maintain the harmonic undertones. ...
... the time of the original rhythm. In order to keep the musicality, I did change the pitches of the second phrase by beginning the same interval pattern on the 4th note of the first 6-note phrase. Also, the melody is moved up an octave in order to maintain the harmonic undertones. ...
Year-9-Music
... Minimalism is a style of music using short musical ideas known as motifs or cells. These musical ideas are repeated many times creating ostinatos (repeating patterns). These patterns can be layered, to create contrapuntal (layered) textures. In minimalist pieces, complex, syncopated rhythms are comm ...
... Minimalism is a style of music using short musical ideas known as motifs or cells. These musical ideas are repeated many times creating ostinatos (repeating patterns). These patterns can be layered, to create contrapuntal (layered) textures. In minimalist pieces, complex, syncopated rhythms are comm ...
Physics 193 Physics of Music
... Is this solely the explanation for why our brains have separate processing for discriminating between these two types of sounds, experiencing pleasure for {human-like} consonant sounds vs. displeasure {non-humanlike} dissonant sounds? Note that dissonant sounds – complex sound waveforms with non-int ...
... Is this solely the explanation for why our brains have separate processing for discriminating between these two types of sounds, experiencing pleasure for {human-like} consonant sounds vs. displeasure {non-humanlike} dissonant sounds? Note that dissonant sounds – complex sound waveforms with non-int ...
Western music history, pitch salience, key profiles, and the origins of
... Major-minor tonality (MmT) 1. Major and minor scales 2. Major and minor tonic triads 3. Harmonic functions (S, D, T) ...
... Major-minor tonality (MmT) 1. Major and minor scales 2. Major and minor tonic triads 3. Harmonic functions (S, D, T) ...
Phrase Painting and Goal Orientation In Two Late Gesualdo Madrigals
... of the "Lower-Leading Tone"-the third of a major triad-upward by half-step to any tone of the following chord."2 This latter type of progression does not usually result in chromatic-third movement, so that it bears less significance to the study of Gesualdo's chromaticism. The importance of Clough's ...
... of the "Lower-Leading Tone"-the third of a major triad-upward by half-step to any tone of the following chord."2 This latter type of progression does not usually result in chromatic-third movement, so that it bears less significance to the study of Gesualdo's chromaticism. The importance of Clough's ...
Just Intonation Explained
... 1984, I would tune a synthesizer to the intervals I wanted to learn - I started out contrasting 10/9 and 9/8 - and then let the intervals run in a loop on tape (later computersequenced) as I was going about my daily business, letting myself pick up the differences in character with my peripheral hea ...
... 1984, I would tune a synthesizer to the intervals I wanted to learn - I started out contrasting 10/9 and 9/8 - and then let the intervals run in a loop on tape (later computersequenced) as I was going about my daily business, letting myself pick up the differences in character with my peripheral hea ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.