Grunge Music In Bloom: Musical Analysis of Nirvana`s Hit
... ambiguous cases or when discussing the guitar playing in particular, I will rather use the X5 notation, or solely the root letter, as the latter reflects the linear-contrapuntal thought process of many Nirvana's bass lines. In discussing note alterations, I will use the common notation from common-p ...
... ambiguous cases or when discussing the guitar playing in particular, I will rather use the X5 notation, or solely the root letter, as the latter reflects the linear-contrapuntal thought process of many Nirvana's bass lines. In discussing note alterations, I will use the common notation from common-p ...
MUSIC THEORY BASIC Jonathan Harnum HOW TO READ, WRITE, AND
... root, minor third, diminished fifth, and diminished seventh. diminished triad: A triad with root, minor third, and diminished fifth. diminuendo (It): Growing gradually softer. diminution: Shortening the length of notes in a theme. discord: Dissonant sounds or sounds unpleasant to the ear. disjunct: ...
... root, minor third, diminished fifth, and diminished seventh. diminished triad: A triad with root, minor third, and diminished fifth. diminuendo (It): Growing gradually softer. diminution: Shortening the length of notes in a theme. discord: Dissonant sounds or sounds unpleasant to the ear. disjunct: ...
Artistic Song Leading (Lesson 7)
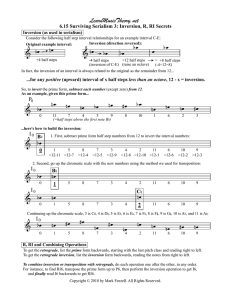
... The major scale consists of seven different pitches. There are half steps between the third and fourth and seventh and eighth scale degrees; whole steps exist between all other steps. Below is the C major scale. The pattern of whole and half steps is the same for all major scales. The Shape of the n ...
... The major scale consists of seven different pitches. There are half steps between the third and fourth and seventh and eighth scale degrees; whole steps exist between all other steps. Below is the C major scale. The pattern of whole and half steps is the same for all major scales. The Shape of the n ...
image by Hans-Christoph Steiner based on Grey, JM 1979, JASA
... The time envelope in terms of rise, duration, and decay. The changes both of spectral envelope (formant-glide) and fundamental frequency (micro-intonation). 5. The prefix, an onset of a sound quite dissimilar to the ...
... The time envelope in terms of rise, duration, and decay. The changes both of spectral envelope (formant-glide) and fundamental frequency (micro-intonation). 5. The prefix, an onset of a sound quite dissimilar to the ...
Mr Allen`s Final Review
... Tempo- speed of music. How fast or slow a piece should be played. Andante Slow), Moderato, (Moderate) Allegro (Fast), Presto (Very Fast) ½ Step - is the smallest written musical interval (minor 2nd), on a piano, notes a ½ Step apart have no other pitches between them. These are often ‘accidentals’ b ...
... Tempo- speed of music. How fast or slow a piece should be played. Andante Slow), Moderato, (Moderate) Allegro (Fast), Presto (Very Fast) ½ Step - is the smallest written musical interval (minor 2nd), on a piano, notes a ½ Step apart have no other pitches between them. These are often ‘accidentals’ b ...
Vivaldi: Concerto in D minor, Op. 3 No. 11 (for component 3
... The music modulates briefly to closely related keys such as G minor (subdominant) and A minor (dominant). There are also occasional passages in more remote keys, such as F minor in the third movement. The music uses what is called functional tonality (where key relationships are built on a carefully ...
... The music modulates briefly to closely related keys such as G minor (subdominant) and A minor (dominant). There are also occasional passages in more remote keys, such as F minor in the third movement. The music uses what is called functional tonality (where key relationships are built on a carefully ...
MT Test 1140 sample questions
... 24. The “tone” center or tonal center of a musical work or section of music, also the key note in a Major or minor scale. ____ A. Dominant B. Tonic C. Subdominant D. Supertonic E. Subtonic PART II. THE CLASSICAL PERIOD: MULTIPLE-CHOICE (25-39) 25. A polyphonic composition for a fixed number of instr ...
... 24. The “tone” center or tonal center of a musical work or section of music, also the key note in a Major or minor scale. ____ A. Dominant B. Tonic C. Subdominant D. Supertonic E. Subtonic PART II. THE CLASSICAL PERIOD: MULTIPLE-CHOICE (25-39) 25. A polyphonic composition for a fixed number of instr ...
elements of music
... piece to an audience. If one instrument is performing on whole notes while the other is playing the main melody there will be harmony. ...
... piece to an audience. If one instrument is performing on whole notes while the other is playing the main melody there will be harmony. ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 11 Non Chord Tones 1
... 9-8 suspension is a special kind of suspension because the note of resolution should NOT be present anywhere in the texture when a suspension occurs 11-10 suspensions is actually a 4-3 suspension 9-8 suspension is NOT labeled as a 2-1 suspension because 2-1suspension if found much less frequen ...
... 9-8 suspension is a special kind of suspension because the note of resolution should NOT be present anywhere in the texture when a suspension occurs 11-10 suspensions is actually a 4-3 suspension 9-8 suspension is NOT labeled as a 2-1 suspension because 2-1suspension if found much less frequen ...
Music Lettering Test
... a minor scale or a major scale. A few of the things that may help to determine whether the piece is in major or minor are the following: 1. What does the piece sound like? Is it major sounding or minor? 2. Are there a lot of accidentals in the piece? If there are this could be a good sign that it ma ...
... a minor scale or a major scale. A few of the things that may help to determine whether the piece is in major or minor are the following: 1. What does the piece sound like? Is it major sounding or minor? 2. Are there a lot of accidentals in the piece? If there are this could be a good sign that it ma ...
Tones and Semitones
... In the "C major" scale, both the first and the last notes are Cs- but how do we know what the inbetween notes are? On the piano, a C major scale uses all the white notes (so it doesn't have any sharps or flats), but on other instruments, we don't have white notes, so how do we know which notes to us ...
... In the "C major" scale, both the first and the last notes are Cs- but how do we know what the inbetween notes are? On the piano, a C major scale uses all the white notes (so it doesn't have any sharps or flats), but on other instruments, we don't have white notes, so how do we know which notes to us ...
Programme music is music where the composer
... What image does the combined timbre of violins and triangle bring to mind? There is no particular ‘right’ answer. One image that comes to mind is Anitra waving a scarf. What note values are used most for the melody? Quavers A feminine sound is created by the predominantly high pitch that is used. Th ...
... What image does the combined timbre of violins and triangle bring to mind? There is no particular ‘right’ answer. One image that comes to mind is Anitra waving a scarf. What note values are used most for the melody? Quavers A feminine sound is created by the predominantly high pitch that is used. Th ...
Full CD Booklet
... the main harmonic unit of the Etude, which also makes melodic use of the division of an octave into five equal parts. 19 notes: This tuning contains diatonic scales in which the major second spans three chromatic degrees, and the minor second two. Triads are smooth, but the scale sounds slightly out ...
... the main harmonic unit of the Etude, which also makes melodic use of the division of an octave into five equal parts. 19 notes: This tuning contains diatonic scales in which the major second spans three chromatic degrees, and the minor second two. Triads are smooth, but the scale sounds slightly out ...
important overtones are higher
... the same and the second one can be varied in pitch: 1. When second pitch is close, most people think the resultant sound is “consonant” 2. As second sound gets farther away, very few people think sound is consonant 3. After two sounds get to around the distance of a minor third, most people again th ...
... the same and the second one can be varied in pitch: 1. When second pitch is close, most people think the resultant sound is “consonant” 2. As second sound gets farther away, very few people think sound is consonant 3. After two sounds get to around the distance of a minor third, most people again th ...
Advanced - Georgia Standards
... arts throughout the major historical periods for western art (e.g., “classical”) music, from antiquity to contemporary. MHSAMTh.7 – Understanding relationships between music and other disciplines outside the fine arts a. Articulate how music is based upon mathematic and scientific principles. (This ...
... arts throughout the major historical periods for western art (e.g., “classical”) music, from antiquity to contemporary. MHSAMTh.7 – Understanding relationships between music and other disciplines outside the fine arts a. Articulate how music is based upon mathematic and scientific principles. (This ...
Tonal Music
... Although they may not know the correct title, most people regardless of musical background have heard Beethoven’s Symphony #5 in C Minor. In addition to being very popular at symphonic concerts this compositions has been used as background music in everything from the dramatic plays to Warner Bros. ...
... Although they may not know the correct title, most people regardless of musical background have heard Beethoven’s Symphony #5 in C Minor. In addition to being very popular at symphonic concerts this compositions has been used as background music in everything from the dramatic plays to Warner Bros. ...
Beautiful city
... Each page is between 2 and 3 minutes long, with durations matching the relative positions of the notes in the score. Tones sustain until the next dotted barline (except when tied into the next measure). When more than one tone is indicated within a single bar, the notes should be sustained simultane ...
... Each page is between 2 and 3 minutes long, with durations matching the relative positions of the notes in the score. Tones sustain until the next dotted barline (except when tied into the next measure). When more than one tone is indicated within a single bar, the notes should be sustained simultane ...
How to Represent Texture of a Musical
... music might be thick or thin, or it may have many or few layers. It might be made up of rhythm only, or of a melody line with chordal accompaniment, or many interweaving melodies. Below you will find some of the formal terms musicians use to describe texture, and also some suggestions for introducin ...
... music might be thick or thin, or it may have many or few layers. It might be made up of rhythm only, or of a melody line with chordal accompaniment, or many interweaving melodies. Below you will find some of the formal terms musicians use to describe texture, and also some suggestions for introducin ...
Octave - Philip Tagg
... as ‘the same note’. For example, men are understood to be singing the same tune as women and children if both parties follow the same pitch contour at the same time in parallel octaves. The octave’s property of ‘unison at another pitch’ is also illustrated by the fact that: (i) a common chord consis ...
... as ‘the same note’. For example, men are understood to be singing the same tune as women and children if both parties follow the same pitch contour at the same time in parallel octaves. The octave’s property of ‘unison at another pitch’ is also illustrated by the fact that: (i) a common chord consis ...
AP® Music Theory 2012 Scoring Guidelines
... 5. A chordal seventh approached by a descending leap. D. Award 0 points for voice leading between two correctly realized chords (as defined in II.A.) if any one of the following statements is true: 1. Parallel octaves, fifths, or unisons occur (immediately successive or on successive beats), includi ...
... 5. A chordal seventh approached by a descending leap. D. Award 0 points for voice leading between two correctly realized chords (as defined in II.A.) if any one of the following statements is true: 1. Parallel octaves, fifths, or unisons occur (immediately successive or on successive beats), includi ...
vocabulary 1
... that those notes should be performed one octave higher than written. 8vb - ottava bassa or "at the octave below." This indication is found below specific notes on a staff and indicates that those notes should be performed one octave lower than written. A tempo - return to the original tempo after a ...
... that those notes should be performed one octave higher than written. 8vb - ottava bassa or "at the octave below." This indication is found below specific notes on a staff and indicates that those notes should be performed one octave lower than written. A tempo - return to the original tempo after a ...
BASIC MATHEMATICAL AND MUSICAL CONCEPTS Sets and
... Note that it is possible for a sequence to be a non-trivial cyclic permutation of itself. For example, if we permute the sequence 3, 5, 3, 3, 5, 3 using i = 3, we get the same sequence. Modality. We have designated the standard scale, in a given key, as a sequence of notes: in C is is the sequence C ...
... Note that it is possible for a sequence to be a non-trivial cyclic permutation of itself. For example, if we permute the sequence 3, 5, 3, 3, 5, 3 using i = 3, we get the same sequence. Modality. We have designated the standard scale, in a given key, as a sequence of notes: in C is is the sequence C ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.