Biology Chapter 5, Lesson 1 Notes
... Phospholipids are lipid molecules that have a head and a tail. The tail or fatty acid end of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophobic (water hating) and carries a neutral charge and is nonpolar. The tails keep water from rushing into the cell, that could cause the cell to burst. The head of a ph ...
... Phospholipids are lipid molecules that have a head and a tail. The tail or fatty acid end of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophobic (water hating) and carries a neutral charge and is nonpolar. The tails keep water from rushing into the cell, that could cause the cell to burst. The head of a ph ...
Slide 1
... Energy stored in NADH & FADH2 as electrons from the metabolic pathways is used for ATP synthesis by the process of oxidative phosphorylation When NADH and FADH2 are re-oxidized to NAD+ and FAD, the electrons released from them are transferred through a chain of electron carrier complexes (redox pro ...
... Energy stored in NADH & FADH2 as electrons from the metabolic pathways is used for ATP synthesis by the process of oxidative phosphorylation When NADH and FADH2 are re-oxidized to NAD+ and FAD, the electrons released from them are transferred through a chain of electron carrier complexes (redox pro ...
Cell Energetics - Practice Test - Biology
... a. It stores energy as glucose. b. It transfers energy to cell processes. c. It releases energy when it gains a phosphate group. d. It converts sunlight into chemical energy. ____ 19. Which of the following is the site of the photosystems in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis? a. stroma ...
... a. It stores energy as glucose. b. It transfers energy to cell processes. c. It releases energy when it gains a phosphate group. d. It converts sunlight into chemical energy. ____ 19. Which of the following is the site of the photosystems in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis? a. stroma ...
LB145-lecture4
... a. Chemical reactions are more efficient because substrates are more easily maintained at high concentrations within organelles. b. Chemical reactions that are incompatible can be segregated in different organelles. c. DNA is transcribed and translated at significantly higher rates because all of th ...
... a. Chemical reactions are more efficient because substrates are more easily maintained at high concentrations within organelles. b. Chemical reactions that are incompatible can be segregated in different organelles. c. DNA is transcribed and translated at significantly higher rates because all of th ...
Plasma Membrane
... cell membrane. Some integral proteins cross the membrane and act as pathways for ions and molecules. Some of the ion movement may not require work (passive transport), but other processes require lot of energy and pumping action (active transport). When you look at the whole membrane, there are very ...
... cell membrane. Some integral proteins cross the membrane and act as pathways for ions and molecules. Some of the ion movement may not require work (passive transport), but other processes require lot of energy and pumping action (active transport). When you look at the whole membrane, there are very ...
protein targeting
... Membrane and soluble secretory proteins synthesized on the rough ER undergo four principal modifications: 1. Covalent addition and processing of carbohydrates (glycosylation) in the ER and Golgi 2. Formation of disulfide bonds in the ER, 3. Proper folding of polypeptide chains and assembly of multis ...
... Membrane and soluble secretory proteins synthesized on the rough ER undergo four principal modifications: 1. Covalent addition and processing of carbohydrates (glycosylation) in the ER and Golgi 2. Formation of disulfide bonds in the ER, 3. Proper folding of polypeptide chains and assembly of multis ...
The Proton Motive Force
... Uses electron transport chain and proton motive force Autotrophic; uses CO2 as carbon source Phototrophy: uses light as energy source Photophosphorylation: light-mediated ATP synthesis Photoautotrophs: use ATP for assimilation of CO2 for biosynthesis Photoheterotrophs: use ATP for assimilation of or ...
... Uses electron transport chain and proton motive force Autotrophic; uses CO2 as carbon source Phototrophy: uses light as energy source Photophosphorylation: light-mediated ATP synthesis Photoautotrophs: use ATP for assimilation of CO2 for biosynthesis Photoheterotrophs: use ATP for assimilation of or ...
p134
... (b) An electrochemical gradient is created during electron transport as the enzyme complexes move protons from NADH and FADH2 into the intermembrane space. The intermembrane space becomes an H+ reservoir because the membrane is almost impermeable to protons. There is, therefore, a much higher conce ...
... (b) An electrochemical gradient is created during electron transport as the enzyme complexes move protons from NADH and FADH2 into the intermembrane space. The intermembrane space becomes an H+ reservoir because the membrane is almost impermeable to protons. There is, therefore, a much higher conce ...
1. What does it mean to be a selective person? 2. Which organelle
... http://ourphysiologygroup.wikispaces.com/03+Cells+Interaction+with+Environment ...
... http://ourphysiologygroup.wikispaces.com/03+Cells+Interaction+with+Environment ...
Beats rhythmically to move fluids across cell surface
... Cells are the smallest units that perform all vital physiological functions Each cell maintains homeostasis at the cellular level ...
... Cells are the smallest units that perform all vital physiological functions Each cell maintains homeostasis at the cellular level ...
بسم الله الرحمن الرحیم The Plasma Membrane Membrane Functions
... NOTE: this model is not correct but shows the progression of the current model Lipid bilayer composed of phospholipids Hydrophobic tails inside Hydrophilic heads outside This forms two separate water-interacting surfaces Proteins coat outer surface This forms a protein-lipid sandwich Proteins do no ...
... NOTE: this model is not correct but shows the progression of the current model Lipid bilayer composed of phospholipids Hydrophobic tails inside Hydrophilic heads outside This forms two separate water-interacting surfaces Proteins coat outer surface This forms a protein-lipid sandwich Proteins do no ...
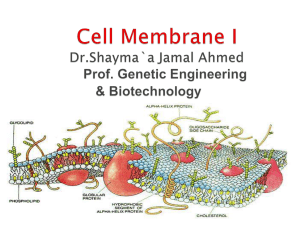
Plasma membrane Dr.Shayma`a Jamal Ahmed
... embedded in a supporting structure 1. membrane lipids form the supporting structure 2. membrane proteins provide the bits and pieces 3. both lipids and proteins may be mobile or 'fluid' B. Membrane lipids: the supporting structure 1. phospholipids 2. glycolipids 3. cholesterol C. Membrane proteins: ...
... embedded in a supporting structure 1. membrane lipids form the supporting structure 2. membrane proteins provide the bits and pieces 3. both lipids and proteins may be mobile or 'fluid' B. Membrane lipids: the supporting structure 1. phospholipids 2. glycolipids 3. cholesterol C. Membrane proteins: ...
Name____________________________________________
... The diagram below shows which areas on the surface of a protein are composed of hydrophobic amino acids and which areas of hydrophilic amino acids. ...
... The diagram below shows which areas on the surface of a protein are composed of hydrophobic amino acids and which areas of hydrophilic amino acids. ...
Membrane Transport
... • Inhibit growth of other bacteria (even other strains of E. coli) • Single colicin molecule can kill a host! ...
... • Inhibit growth of other bacteria (even other strains of E. coli) • Single colicin molecule can kill a host! ...
Introduction to the study of cell biology
... The electrochemical gradient resulting from transport of protons links to oxidative phosphorylation. When electrons are transported along the chain, the H+ is translocated across the inner membrane. The mitochondrial inner membrane is impermeable to H+ . When protons flow in the reverse directio ...
... The electrochemical gradient resulting from transport of protons links to oxidative phosphorylation. When electrons are transported along the chain, the H+ is translocated across the inner membrane. The mitochondrial inner membrane is impermeable to H+ . When protons flow in the reverse directio ...
Why does a drop of food coloring diffuse more rapidly in
... and must be synthesized within the cell are enzymatically converted to nonpolar forms before crossing the membrane cross membranes by interacting with membrane transport proteins pass between the hydrophobic heads and dissolve through the hydrophilic tails of the phospholipid ...
... and must be synthesized within the cell are enzymatically converted to nonpolar forms before crossing the membrane cross membranes by interacting with membrane transport proteins pass between the hydrophobic heads and dissolve through the hydrophilic tails of the phospholipid ...
Membranes
... some penetrate only part of the way through, while others penetrate all the way through (b) ...
... some penetrate only part of the way through, while others penetrate all the way through (b) ...
You Gotta Know
... break down proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. They are important in processing the contents of vesicles taken in from outside the cell. It is crucial to maintain the integrity of the lysosomal membranes because the enzymes they contain can digest cellular components as well. 7. Chlo ...
... break down proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. They are important in processing the contents of vesicles taken in from outside the cell. It is crucial to maintain the integrity of the lysosomal membranes because the enzymes they contain can digest cellular components as well. 7. Chlo ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... Previously Bio308 Hypotheses for molecular basis of bipolar disorder •Suggest problem lies in protein targeting How are proteins targeted and delivered? ...
... Previously Bio308 Hypotheses for molecular basis of bipolar disorder •Suggest problem lies in protein targeting How are proteins targeted and delivered? ...
Andrew Tibbits
... substantial improvements in thermal and alkaline stability, hydroxide conductivity, mechanical flexibility, and processing are needed to create a competitive membrane for HEMFC applications. Regardless of the type of membrane, the high water uptake that is typically associated with increased ionic c ...
... substantial improvements in thermal and alkaline stability, hydroxide conductivity, mechanical flexibility, and processing are needed to create a competitive membrane for HEMFC applications. Regardless of the type of membrane, the high water uptake that is typically associated with increased ionic c ...
Biology 123 SI- Dr. Raut`s Class Session 11
... 1. Why is the amount of ATP formed so variable? (Several answers. List them all) Pyruvate actually requires active transport to get into the mitochondria which means it uses some ATP. NADH that is produced in glycolysis cannot cross the mitochondria’s membrane and must use a shuttle system and give ...
... 1. Why is the amount of ATP formed so variable? (Several answers. List them all) Pyruvate actually requires active transport to get into the mitochondria which means it uses some ATP. NADH that is produced in glycolysis cannot cross the mitochondria’s membrane and must use a shuttle system and give ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.