Neural Phys
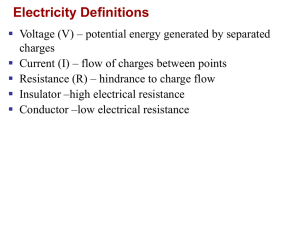
... Flow of ions rather than electrons Generated by different [Na+], [ K+], [ Cl], [anionic proteins] and charged phospholipids Ion gradients Differential permeability to Na+ and K+ Sodium-potassium pump ...
... Flow of ions rather than electrons Generated by different [Na+], [ K+], [ Cl], [anionic proteins] and charged phospholipids Ion gradients Differential permeability to Na+ and K+ Sodium-potassium pump ...
solute - Life Science Academy
... Have a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails Are the main structural ...
... Have a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails Are the main structural ...
Expression of KCNA10, a Voltage-Gated K Channel, in Glomerular
... The specificity of the antibody was tested further in competition studies with the peptide used to generate anti-KCNA10. As shown in Figure 1b, the signal obtained with anti-KCNa10 was nearly completely abolished by the addition of the peptide. KCNA10 is the only Kv channel gene that is more abundan ...
... The specificity of the antibody was tested further in competition studies with the peptide used to generate anti-KCNA10. As shown in Figure 1b, the signal obtained with anti-KCNa10 was nearly completely abolished by the addition of the peptide. KCNA10 is the only Kv channel gene that is more abundan ...
Growth of Pseudomonas oleovorans in Two Liquid Phase
... expansion and fluidization of the membrane, which allowed the periplasmic isomerase to access fatty acid double bonds and to change the configuration of the double bonds from cis to trans. Given these results, we expect that the isomerisation will be facilitated and the cis/trans isomerization will ...
... expansion and fluidization of the membrane, which allowed the periplasmic isomerase to access fatty acid double bonds and to change the configuration of the double bonds from cis to trans. Given these results, we expect that the isomerisation will be facilitated and the cis/trans isomerization will ...
TRANSPORT PROCESSES
... 1b. moving proteins into membranes and organelles SLIDE 1 A typical mammalian cell contains up to 10,000 different kinds of proteins. The vast majority of these proteins are synthesized by cytosolic ribosomes, and many remain within the cytosol. However, as many as half the different kinds of protei ...
... 1b. moving proteins into membranes and organelles SLIDE 1 A typical mammalian cell contains up to 10,000 different kinds of proteins. The vast majority of these proteins are synthesized by cytosolic ribosomes, and many remain within the cytosol. However, as many as half the different kinds of protei ...
No Slide Title
... Which process is best represented by the following chemical equation? sugars + oxygen carbon dioxide + water ...
... Which process is best represented by the following chemical equation? sugars + oxygen carbon dioxide + water ...
2) Where
... 1) Glycolysis -‐ spli[ng of glucose (2 ATP) (anaerobic -‐ no O2 needed) 2) Citric Acid (Kreb’s) cycle (2 ATP) (aerobic -‐ O2 needed) 3) Electron transport chain (32-‐34 ATP) ...
... 1) Glycolysis -‐ spli[ng of glucose (2 ATP) (anaerobic -‐ no O2 needed) 2) Citric Acid (Kreb’s) cycle (2 ATP) (aerobic -‐ O2 needed) 3) Electron transport chain (32-‐34 ATP) ...
食物的吸收
... magnitude of the Na absorptive flux through this pathway. B, Electroneutral Na-H exchange at the apical membrane, in the absence of Cl-HCO exchange, is stimulated by the high pH of the HCO -rich luminal contents. C, Na-H and Cl-HCO exchange is coupled by a change in intracellular pH that results in ...
... magnitude of the Na absorptive flux through this pathway. B, Electroneutral Na-H exchange at the apical membrane, in the absence of Cl-HCO exchange, is stimulated by the high pH of the HCO -rich luminal contents. C, Na-H and Cl-HCO exchange is coupled by a change in intracellular pH that results in ...
In silico Study of Target Proteins for Mycobacterium
... The completion of the genome of pathogens and the human has provided data that can be utilized to design vaccines and drug targets. One of the recently adopted strategies for drug designing is based on comparative genomics approach, it gives a set of genes that are likely to be essential to the path ...
... The completion of the genome of pathogens and the human has provided data that can be utilized to design vaccines and drug targets. One of the recently adopted strategies for drug designing is based on comparative genomics approach, it gives a set of genes that are likely to be essential to the path ...
ATP-driven Pumps
... Comparing this structure with that in Ca2+- free (E2) state…… 1. Kinase activity unleashes N domain from P domain 2. A domain associates with N & P domains, exerts downward push on M3/M4, opening luminal pathway for ...
... Comparing this structure with that in Ca2+- free (E2) state…… 1. Kinase activity unleashes N domain from P domain 2. A domain associates with N & P domains, exerts downward push on M3/M4, opening luminal pathway for ...
An abundant TIP expressed in mature highly vacuolated cells
... To discern the expression pattern of So-dTIP in more detail, immunolocalization experiments were performed using ultrathin sections of leaves, petioles and roots. Antibody labelling of So-dTIP was visualized by electron and light microscopy using gold-conjugated secondary antibodies followed by silv ...
... To discern the expression pattern of So-dTIP in more detail, immunolocalization experiments were performed using ultrathin sections of leaves, petioles and roots. Antibody labelling of So-dTIP was visualized by electron and light microscopy using gold-conjugated secondary antibodies followed by silv ...
2 ATP`s - Madeira City Schools
... 2. The flow of electrons through the chain produces energy that is used to pump H+ ions across the membrane (from matrix to intermembrane space). a. When certain carriers within the chain transfer electrons, H+ ions are also taken up and released back into the surrounding solution. b. The carriers a ...
... 2. The flow of electrons through the chain produces energy that is used to pump H+ ions across the membrane (from matrix to intermembrane space). a. When certain carriers within the chain transfer electrons, H+ ions are also taken up and released back into the surrounding solution. b. The carriers a ...
VI. LIGHT REACTION OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS, cont
... Collection of molecules, each more electronegative than the one before it Molecules are reduced, then oxidized as electrons are passed down the chain Oxygen is ultimate electron acceptor Purpose is to establish H+ gradient on two sides of inner mitochondrial membrane Energy from “falling e ...
... Collection of molecules, each more electronegative than the one before it Molecules are reduced, then oxidized as electrons are passed down the chain Oxygen is ultimate electron acceptor Purpose is to establish H+ gradient on two sides of inner mitochondrial membrane Energy from “falling e ...
Cellular Respiration Explained
... ❋GLYCOLYSIS means the “splitting of sugar,” and takes place in the cytoplasm! The overall process is just that: Glucose, a six carbon sugar is split into two separate three carbon molecules. These are then changed into another type of molecule called pyruvate, AKA pyruvic acid. But pyruvate is not t ...
... ❋GLYCOLYSIS means the “splitting of sugar,” and takes place in the cytoplasm! The overall process is just that: Glucose, a six carbon sugar is split into two separate three carbon molecules. These are then changed into another type of molecule called pyruvate, AKA pyruvic acid. But pyruvate is not t ...
ATP Production
... Cellular Respiration (anaerobic) What happens when cells don’t have enough oxygen? Some organisms live in an oxygen-free environment. The Kreb’s Cycle and Electron Transport How do they get their energy? ...
... Cellular Respiration (anaerobic) What happens when cells don’t have enough oxygen? Some organisms live in an oxygen-free environment. The Kreb’s Cycle and Electron Transport How do they get their energy? ...
Transport. Active and Passive
... • Get into your groups (no larger than 4) or work independently to complete packet. • When complete, check in with me. • Take a few minutes to organize your notebooks. – There may be a notebook check next week… ...
... • Get into your groups (no larger than 4) or work independently to complete packet. • When complete, check in with me. • Take a few minutes to organize your notebooks. – There may be a notebook check next week… ...
File
... •Oxygen = “terminal electron acceptor” •Oxygen accepts electrons at the end of the ETC and H+ ions to form water as a byproduct of aerobic respiration ...
... •Oxygen = “terminal electron acceptor” •Oxygen accepts electrons at the end of the ETC and H+ ions to form water as a byproduct of aerobic respiration ...
The action potential and the synapses
... Bundling neuropeptide in small vesicles that bud from it. Thanks to the axonal flow vesicles are transported to the ends of the nerve endings, ready to be released into the nerve terminal with the arrival of an action potential. Typically the neuropeptides are released in much smaller quantities tha ...
... Bundling neuropeptide in small vesicles that bud from it. Thanks to the axonal flow vesicles are transported to the ends of the nerve endings, ready to be released into the nerve terminal with the arrival of an action potential. Typically the neuropeptides are released in much smaller quantities tha ...
Tutorial 9: Excitatory Postsynaptic Potentials
... takes place at the postsynaptic membrane, or along the membrane of a neuron's dendrites and cell body. This is where information converges from the terminal endings of axons from other neurons. As described previously, the direction of information as it flows along a neuron is from dendrite to cell ...
... takes place at the postsynaptic membrane, or along the membrane of a neuron's dendrites and cell body. This is where information converges from the terminal endings of axons from other neurons. As described previously, the direction of information as it flows along a neuron is from dendrite to cell ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.