Truncated Photosystem Chlorophyll Antenna Size in the Green
... Some figures in this article are displayed in color online but in black and white in the print edition. [W] The online version of this article contains Web-only data. [OA] Open Access articles can be viewed online without a subscription. www.plantphysiol.org/cgi/doi/10.1104/pp.112.206672 ...
... Some figures in this article are displayed in color online but in black and white in the print edition. [W] The online version of this article contains Web-only data. [OA] Open Access articles can be viewed online without a subscription. www.plantphysiol.org/cgi/doi/10.1104/pp.112.206672 ...
No Slide Title
... too large for vesicles traverse the Golgi stack. No evidence for a megavesicle. Rate of aggregate movement much slower than for normal proteins. Model - cisternae “progress” or mature. Cis Golgi becomes medial becomes trans. Golgi enzymes are moved back by retrograde transport. ...
... too large for vesicles traverse the Golgi stack. No evidence for a megavesicle. Rate of aggregate movement much slower than for normal proteins. Model - cisternae “progress” or mature. Cis Golgi becomes medial becomes trans. Golgi enzymes are moved back by retrograde transport. ...
Glycolysis
... tricarboxylic acids •Carbons from glucose are shown in red •Carbons from glucose are lost as CO2 (decarboxylation) •Several NADH + H+ are generated via oxidation of intermediates •One high energy phosphate compound (GTP)is produced ...
... tricarboxylic acids •Carbons from glucose are shown in red •Carbons from glucose are lost as CO2 (decarboxylation) •Several NADH + H+ are generated via oxidation of intermediates •One high energy phosphate compound (GTP)is produced ...
I. Cellular Energy • ATP: a) When the terminal phosphate is removed
... a) Liver, kidney, & heart cells: shuttle system transfers the electrons from NADH through the inner mitochondrial membrane to an NAD+ in the matrix. These electrons are transferred to the electron transport chain to yield 3 ATP/electron pair (38 ATP’s/glucose molecule). b) Skeletal muscle, brain cel ...
... a) Liver, kidney, & heart cells: shuttle system transfers the electrons from NADH through the inner mitochondrial membrane to an NAD+ in the matrix. These electrons are transferred to the electron transport chain to yield 3 ATP/electron pair (38 ATP’s/glucose molecule). b) Skeletal muscle, brain cel ...
Metabolism - College of the Canyons
... • electrons travel in pairs (2 e-) along the transport chain • each electron carrier becomes reduced when it receives an electron pair and oxidized again when it passes the electrons along to the next carrier • oxygen is the final electron acceptor – each oxygen atom accepts two electrons from cytoc ...
... • electrons travel in pairs (2 e-) along the transport chain • each electron carrier becomes reduced when it receives an electron pair and oxidized again when it passes the electrons along to the next carrier • oxygen is the final electron acceptor – each oxygen atom accepts two electrons from cytoc ...
MITOCHONDRIA
... numerous electrons are liberated and passed down the electron transport chain of proteins. This is accompanied by a flow of protons from the matrix into the intermembranous space, ...
... numerous electrons are liberated and passed down the electron transport chain of proteins. This is accompanied by a flow of protons from the matrix into the intermembranous space, ...
Intracellular Respiration
... electronegative oxygen) a. in respiration Glucose is oxidized, releasing energy b. Oxygen, in turn, is reduced 2.reduction the addition of electrons 3. hydrocarbons, and molecules that have a lot of Hydrogen(sugars, fats) are sources of electrons that can be pulled by Oxygen ...
... electronegative oxygen) a. in respiration Glucose is oxidized, releasing energy b. Oxygen, in turn, is reduced 2.reduction the addition of electrons 3. hydrocarbons, and molecules that have a lot of Hydrogen(sugars, fats) are sources of electrons that can be pulled by Oxygen ...
Tuesday 11/15/05
... AIM: how does the structure of the cell membrane relate to its function? DO NOW: What do you think would happen to a fresh water fish if you put it in salt water and explain why you think that HOMEWORK: Text page 183 questions 13 ...
... AIM: how does the structure of the cell membrane relate to its function? DO NOW: What do you think would happen to a fresh water fish if you put it in salt water and explain why you think that HOMEWORK: Text page 183 questions 13 ...
Side-chain hydrophobicity scale derived from transmembrane
... We used the outer membrane phospholipase A (OmpLA) as a transmembrane scaffold on which to introduce amino acid side chains of our choice at various membrane depths. We selected OmpLA because it: (a) spontaneously folds and inserts into lipid membranes from a solubilized unfolded state (14), (b) has ...
... We used the outer membrane phospholipase A (OmpLA) as a transmembrane scaffold on which to introduce amino acid side chains of our choice at various membrane depths. We selected OmpLA because it: (a) spontaneously folds and inserts into lipid membranes from a solubilized unfolded state (14), (b) has ...
Cell Transport webquest
... 2. Most of the cell membrane is made up of ______________________________________ ...
... 2. Most of the cell membrane is made up of ______________________________________ ...
Summary - University of Amsterdam
... possiblee presence of transporters for these metabolites, the ability of proteoliposomes containing peroxisomall membrane protein to take up various radiolabeled substrates was investigated, as describedd in chapter 5. It was observed that the peroxisomal membrane contains one or more proteinss that ...
... possiblee presence of transporters for these metabolites, the ability of proteoliposomes containing peroxisomall membrane protein to take up various radiolabeled substrates was investigated, as describedd in chapter 5. It was observed that the peroxisomal membrane contains one or more proteinss that ...
Cellular Respiration Notes - 2016 2017
... 7) What happens during the electron transport chain (i.e. the third step of aerobic cellular respiration)? a. The electron transport chain occurs in the folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Folding the membrane creates more membrane surface area to fit more electron transport chain protein com ...
... 7) What happens during the electron transport chain (i.e. the third step of aerobic cellular respiration)? a. The electron transport chain occurs in the folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Folding the membrane creates more membrane surface area to fit more electron transport chain protein com ...
Cell Respiration SAT II Review
... • NADH and FADH2 release electrons to carriers/proteins embedded in the membrane of the cristae. • NADH and FADH2(less energy) both hand over the electrons to ETC, but at different levels. • As the electrons are transferred, H+ ions are pumped from the matrix to the intermembrane space up the concen ...
... • NADH and FADH2 release electrons to carriers/proteins embedded in the membrane of the cristae. • NADH and FADH2(less energy) both hand over the electrons to ETC, but at different levels. • As the electrons are transferred, H+ ions are pumped from the matrix to the intermembrane space up the concen ...
Überschrift – Thema, Arial 80 pt fett schwarz oder KIT-Grün
... The reason for the recalcitrance of these biofilms are so-called persister cells. Persisters are dormant variants of regular cells that form stochastically in microbial populations and are highly tolerant against modern antibiotics [1]. It is known that one protein plays a major role in persister ce ...
... The reason for the recalcitrance of these biofilms are so-called persister cells. Persisters are dormant variants of regular cells that form stochastically in microbial populations and are highly tolerant against modern antibiotics [1]. It is known that one protein plays a major role in persister ce ...
Toxicant Disposition and Metabolism
... • Enzyme family, with broad substrate specificities. • Most significant of all toxicant oxidation reactions. • Adds one atom of molecular oxygen to substrate, other atom becomes a reactive oxygen species (with potential for oxidative damage within the cell). • Very important in detoxication of many ...
... • Enzyme family, with broad substrate specificities. • Most significant of all toxicant oxidation reactions. • Adds one atom of molecular oxygen to substrate, other atom becomes a reactive oxygen species (with potential for oxidative damage within the cell). • Very important in detoxication of many ...
Nerves and Muscles
... • There is a slow Na+ leak inward • There is also a slow K+ leak outward. ...
... • There is a slow Na+ leak inward • There is also a slow K+ leak outward. ...
Chapter_9_ppt_FINAL_FINAL_AP_BIO
... • Electron transport & oxidative phosphorylation: 2 NADH (glycolysis) → 6ATP 2 NADH (acetyl CoA) →6ATP 6 NADH (Kreb’s) → 18 ATP 2 FADH2 (Kreb’s) → 4 ATP 38 TOTAL ATP from 1 molecule of glucose (-2 ATP to transport 2 pyruvate into mitochondria) NET of 36 ATP ...
... • Electron transport & oxidative phosphorylation: 2 NADH (glycolysis) → 6ATP 2 NADH (acetyl CoA) →6ATP 6 NADH (Kreb’s) → 18 ATP 2 FADH2 (Kreb’s) → 4 ATP 38 TOTAL ATP from 1 molecule of glucose (-2 ATP to transport 2 pyruvate into mitochondria) NET of 36 ATP ...
Exam 2
... (b) (2 pts) A b-specific nuclease catalyzes the hydrolysis of pApGpCpTp between the C and T residues. Write the products of this cleavage reaction using the same nomenclature. (c) (2 pts) What two amino acid residues are somewhat more likely to be part of a tight beta turn in a protein structure? (d ...
... (b) (2 pts) A b-specific nuclease catalyzes the hydrolysis of pApGpCpTp between the C and T residues. Write the products of this cleavage reaction using the same nomenclature. (c) (2 pts) What two amino acid residues are somewhat more likely to be part of a tight beta turn in a protein structure? (d ...
Cellular Respiration Chapter 7- Cfe Higher Human Biology
... PROTEINS AS RESPIRATORY SUBSTRATES Proteins in the diet are broken down to their component amino acids by the action of digestive enzymes. Amino acids in excess of the body’s requirements for protein synthesis undergo deamination, forming urea and respiratory pathway intermediates as shown opposite ...
... PROTEINS AS RESPIRATORY SUBSTRATES Proteins in the diet are broken down to their component amino acids by the action of digestive enzymes. Amino acids in excess of the body’s requirements for protein synthesis undergo deamination, forming urea and respiratory pathway intermediates as shown opposite ...
Harvesting Energy
... The initial reactions in the conversion of glucose to energy are called glycolysis. We will look at the overall process in terms of energy yield and final products. It may seem strange, but to get energy in the form of ATP from glucose, we first have to expend energy in the form of ATP. During this ...
... The initial reactions in the conversion of glucose to energy are called glycolysis. We will look at the overall process in terms of energy yield and final products. It may seem strange, but to get energy in the form of ATP from glucose, we first have to expend energy in the form of ATP. During this ...
Photosynthesis
... channel proteins (ATP synthase) in the cristae generate energy to drive the formation of ATP’s by allowing the protons to flow back into the matrix from the cristae. The process in which ATP is produced by the flow of protons across the channel is called oxidative phosphorylation. - NADH produces 3 ...
... channel proteins (ATP synthase) in the cristae generate energy to drive the formation of ATP’s by allowing the protons to flow back into the matrix from the cristae. The process in which ATP is produced by the flow of protons across the channel is called oxidative phosphorylation. - NADH produces 3 ...
Lecture 8 - People Server at UNCW
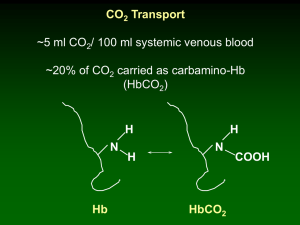
... Reverse chloride shift HCO3- / Cl- exchanger moves Cl- out of RBC and HCO3- in. ...
... Reverse chloride shift HCO3- / Cl- exchanger moves Cl- out of RBC and HCO3- in. ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.