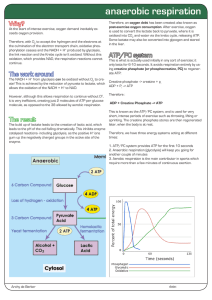
anaerobic respiration
... The NADH + H+ from glycolysis can be oxidized without O2 to create! This is achieved by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate, which allows the oxidation of the NADH + H+ to NAD. However, although this allows respiration to continue without O2, it is very inefficient, creating just 2 molecules of ATP ...
... The NADH + H+ from glycolysis can be oxidized without O2 to create! This is achieved by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate, which allows the oxidation of the NADH + H+ to NAD. However, although this allows respiration to continue without O2, it is very inefficient, creating just 2 molecules of ATP ...
I. Metabolism
... Many other carbon sources can be utilized by the specific enzyme systems in the microorganisms. Thus special microorganisms can be applied as “waste disposal units”, forming the basis of environmental biotechnology. Ex: microbial degradation of oils and fatty acids. ...
... Many other carbon sources can be utilized by the specific enzyme systems in the microorganisms. Thus special microorganisms can be applied as “waste disposal units”, forming the basis of environmental biotechnology. Ex: microbial degradation of oils and fatty acids. ...
hapter 11
... – e.g., carotenoids and phycobiliproteins – accessory pigments absorb different wavelengths of light than chlorophylls ...
... – e.g., carotenoids and phycobiliproteins – accessory pigments absorb different wavelengths of light than chlorophylls ...
Cell Shapes
... result of their constant, random motion • Net diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (down or with the concentration ...
... result of their constant, random motion • Net diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (down or with the concentration ...
A Rice Plastidial Nucleotide Sugar Epimerase Is Involved in
... novel chloroplast-localized UDP-glucose epimerase (UGE), which is conserved in the plant kingdom. The chloroplast localization of PHD1 was confirmed by immunoblots, immunocytochemistry, and UGE activity in isolated chloroplasts, which was approximately 50% lower in the phd1-1 mutant than in the wild ...
... novel chloroplast-localized UDP-glucose epimerase (UGE), which is conserved in the plant kingdom. The chloroplast localization of PHD1 was confirmed by immunoblots, immunocytochemistry, and UGE activity in isolated chloroplasts, which was approximately 50% lower in the phd1-1 mutant than in the wild ...
Cellular Respiration
... • If no oxygen is available- the process stops. • If oxygen becomes available, the process moves onto oxidative reduction & the kreb’s cycle. • Possible for 36 ATP to be made. ...
... • If no oxygen is available- the process stops. • If oxygen becomes available, the process moves onto oxidative reduction & the kreb’s cycle. • Possible for 36 ATP to be made. ...
Mass Spectrometry of Peptides
... Describe the steps of a typical peptide analysis by MS (proteomic experiment) Explain peptide ionization, fragmentation, identification ...
... Describe the steps of a typical peptide analysis by MS (proteomic experiment) Explain peptide ionization, fragmentation, identification ...
Substrate Level Phosphorylation Substrate level phosphorylation
... electrons allows for more bonds • Glucose oxidation transfers electrons (of hydrogen) to a lower energy state as it bonds with oxygen – Energy released is used in ATP regeneration ...
... electrons allows for more bonds • Glucose oxidation transfers electrons (of hydrogen) to a lower energy state as it bonds with oxygen – Energy released is used in ATP regeneration ...
Cellular Respiration www.AssignmentPoint.com Cellular respiration
... The potential of NADH and FADH2 is converted to more ATP through an electron transport chain with oxygen as the "terminal electron acceptor". Most of the ATP produced by aerobic cellular respiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation. This works by the energy released in the consumption of pyruvat ...
... The potential of NADH and FADH2 is converted to more ATP through an electron transport chain with oxygen as the "terminal electron acceptor". Most of the ATP produced by aerobic cellular respiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation. This works by the energy released in the consumption of pyruvat ...
How Cell Harvest Energy
... 25. What happens to most of the energy released during cell respiration? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 26. What is the theoretical ATP yield of aerobic respiration? …the actual yie ...
... 25. What happens to most of the energy released during cell respiration? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 26. What is the theoretical ATP yield of aerobic respiration? …the actual yie ...
tethering redox proteins to the outer membrane in Neisseria and
... Parts of bacterial respiratory chains are, by necessity, embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane in order to allow generation of ion gradients to drive the synthesis of ATP. In Gram-negative bacteria, it is typical to also find redoxcofactor-containing respiratory proteins within the periplasm where th ...
... Parts of bacterial respiratory chains are, by necessity, embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane in order to allow generation of ion gradients to drive the synthesis of ATP. In Gram-negative bacteria, it is typical to also find redoxcofactor-containing respiratory proteins within the periplasm where th ...
Citrate transporters of Bacillus subtilis Krom, Bastiaan Philip
... transduction. The hydrophobic nature of the membrane prevents hydrophilic solutes to cross the membrane. Specific transport of solutes across the membrane is catalyzed by designated transport proteins that are embedded in the membrane. The importance of transport proteins is illustrated by the fact ...
... transduction. The hydrophobic nature of the membrane prevents hydrophilic solutes to cross the membrane. Specific transport of solutes across the membrane is catalyzed by designated transport proteins that are embedded in the membrane. The importance of transport proteins is illustrated by the fact ...
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane
... concentration gradient, independent of concentration gradients of other ...
... concentration gradient, independent of concentration gradients of other ...
Cellular Respiration
... • Examples: plants, algae, some bacteria – Heterotrophs or Consumers • Cannot make their own food • Take in food by eating • Examples: animals, protists, fungi, most bacteria ...
... • Examples: plants, algae, some bacteria – Heterotrophs or Consumers • Cannot make their own food • Take in food by eating • Examples: animals, protists, fungi, most bacteria ...
Cell Metabolism - U of L Class Index
... These reactions are catalyzed by enzymes called dehydrogenases, which: Remove a pair of hydrogen atoms (two electrons and two protons) from susbstrate Deliver the two electrons and one proton to NAD+ Release the remaining proton into the surrounding solution The high energy electrons transferred fro ...
... These reactions are catalyzed by enzymes called dehydrogenases, which: Remove a pair of hydrogen atoms (two electrons and two protons) from susbstrate Deliver the two electrons and one proton to NAD+ Release the remaining proton into the surrounding solution The high energy electrons transferred fro ...
Lecture 6 (ADP/ATP carrier) []
... integral membrane proteins called porins, which feature relatively large internal channels (about 2-3 nm) that are permeable to molecules of ~5,000 Da or less. In contrast, larger molecules, for example most proteins, can only traverse the outer membrane by active transport. ...
... integral membrane proteins called porins, which feature relatively large internal channels (about 2-3 nm) that are permeable to molecules of ~5,000 Da or less. In contrast, larger molecules, for example most proteins, can only traverse the outer membrane by active transport. ...
Chapter 3: Cellular Form and Function
... Principles of Modern Cell Theory • All organisms composed of cells and cell products. • A cell is the simplest structural and functional unit of life. There are no smaller subdivisions of a cell or organism that, in themselves, are alive. • An organism’s structure and all of its functions are ultima ...
... Principles of Modern Cell Theory • All organisms composed of cells and cell products. • A cell is the simplest structural and functional unit of life. There are no smaller subdivisions of a cell or organism that, in themselves, are alive. • An organism’s structure and all of its functions are ultima ...
Questions for exam #1
... B-1. If you carry out expt. 1 with cells from patients with mutant membrin, which antibodies should be found in an ‘intracellular vesicular staining pattern?’ (Ab 1) (Ab 2) or (both) (neither) (one or the other but not both). B-2. For this experiment, the secondary antibodies used to detect Ab 1 and ...
... B-1. If you carry out expt. 1 with cells from patients with mutant membrin, which antibodies should be found in an ‘intracellular vesicular staining pattern?’ (Ab 1) (Ab 2) or (both) (neither) (one or the other but not both). B-2. For this experiment, the secondary antibodies used to detect Ab 1 and ...
Document
... substrate level phosphorylation. How is the proton motive force made? Where does photosynthesis occur in eukaryotes? 3. What is the role of water in oxygenic photosynthesis? Does water play the same role in anoxygenic photosynthesis? 4. Define autotroph. What is the purpose of the Calvin cycle? What ...
... substrate level phosphorylation. How is the proton motive force made? Where does photosynthesis occur in eukaryotes? 3. What is the role of water in oxygenic photosynthesis? Does water play the same role in anoxygenic photosynthesis? 4. Define autotroph. What is the purpose of the Calvin cycle? What ...
Cell Energy
... reactions results in the formation of ATP, NADPH, and O2 • How chemiosmosis generates ATP in the light reactions ...
... reactions results in the formation of ATP, NADPH, and O2 • How chemiosmosis generates ATP in the light reactions ...
The Cell Membrane
... fluidity of the cellular membrane. As membrane fluidity in creases, there is a rise in membrane permeability to water and small hydrophilic solutes. The fluidity of a cell membrane de pends on the lipid composition of the membrane, the density of integral proteins, and the temperature. Role of fa ...
... fluidity of the cellular membrane. As membrane fluidity in creases, there is a rise in membrane permeability to water and small hydrophilic solutes. The fluidity of a cell membrane de pends on the lipid composition of the membrane, the density of integral proteins, and the temperature. Role of fa ...
Approaches Expectations
... it belongs there. (Cellular Transport, n.d.) The membrane is called a fluid mosaic model due to all the components that make it up. (Cellular Transport, n.d.) Part of the cell membrane is the way molecules get transported across of it through forms of passive and active transport. There are two typ ...
... it belongs there. (Cellular Transport, n.d.) The membrane is called a fluid mosaic model due to all the components that make it up. (Cellular Transport, n.d.) Part of the cell membrane is the way molecules get transported across of it through forms of passive and active transport. There are two typ ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.
















![Lecture 6 (ADP/ATP carrier) []](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000909663_1-dac6ef69248cb11cfa508c989c7d6804-300x300.png)





