
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 7, Part 2 Notes: The Nervous
... reference microelectrode placed outside the cell, and a voltmeter (voltage meter). ...
... reference microelectrode placed outside the cell, and a voltmeter (voltage meter). ...
For electrical signaling
... At gap junctions, cells approach within about 3.5 nm of each other, rather than the 20 to 40 nm distance that separates cells at chemical synapses Postsynaptic potential in electrical synapses is not caused by the opening of ion channels by chemical transmitters, but by direct electrical coupling be ...
... At gap junctions, cells approach within about 3.5 nm of each other, rather than the 20 to 40 nm distance that separates cells at chemical synapses Postsynaptic potential in electrical synapses is not caused by the opening of ion channels by chemical transmitters, but by direct electrical coupling be ...
Synapses
... the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
Biology 3201 - s3.amazonaws.com
... abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This further creates a charge difference!! ...
... abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This further creates a charge difference!! ...
Na+ - cloudfront.net
... Na+ channels open and Na+ rushes inside K+ channels open to let K+ out Causes other Na+ channels to open, like a chain ...
... Na+ channels open and Na+ rushes inside K+ channels open to let K+ out Causes other Na+ channels to open, like a chain ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
... to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology 3rd Nine Weeks Study Guide
... Smooth muscle has rhythmicity…they contract in a pattern called peristalsis ...
... Smooth muscle has rhythmicity…they contract in a pattern called peristalsis ...
Neurons
... polarity of the electrical charge across the cell membrane. The membrane then alters its permeability to the charged ions, and the charge across the cell membrane becomes briefly less positive or negative. Action potentials result in the positively charged sodium ions flow rapidly into the neuron. T ...
... polarity of the electrical charge across the cell membrane. The membrane then alters its permeability to the charged ions, and the charge across the cell membrane becomes briefly less positive or negative. Action potentials result in the positively charged sodium ions flow rapidly into the neuron. T ...
Document
... The Neuromuscular Junction • end of neuron (synaptic terminal or axon bulb) is in very close association with the muscle fiber • distance between the bulb and the folded sarcolemma = synaptic cleft • nerve impulse leads to release of neurotransmitter (acetylcholine) • N.T. binds to receptors on myo ...
... The Neuromuscular Junction • end of neuron (synaptic terminal or axon bulb) is in very close association with the muscle fiber • distance between the bulb and the folded sarcolemma = synaptic cleft • nerve impulse leads to release of neurotransmitter (acetylcholine) • N.T. binds to receptors on myo ...
6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis part 1
... of ions across their membranes. Sodium ions are pumped out and potassium ions are pumped in. There are chloride ions, DNA and other negatively charged ions inside the neuron that are fairly large and have a tendency to stay inside which creates a net negative charge inside the neuron as compared wit ...
... of ions across their membranes. Sodium ions are pumped out and potassium ions are pumped in. There are chloride ions, DNA and other negatively charged ions inside the neuron that are fairly large and have a tendency to stay inside which creates a net negative charge inside the neuron as compared wit ...
Chapter 11 Marieb
... 1. Action potential reaches axon terminal, causing the voltageAll cells pump calcium gated calcium channels to open, so… out of the cell! 2. Calcium rushes in! 3. Calcium influx stimulates exocytosis of vesicles containing neurotransmitter. This mechanism is not clear. 4. Neurotransmitter is release ...
... 1. Action potential reaches axon terminal, causing the voltageAll cells pump calcium gated calcium channels to open, so… out of the cell! 2. Calcium rushes in! 3. Calcium influx stimulates exocytosis of vesicles containing neurotransmitter. This mechanism is not clear. 4. Neurotransmitter is release ...
31.1 The Neuron
... your senses. In your notes write out the path it would take from outside the body and through the aspects of the nervous system. ...
... your senses. In your notes write out the path it would take from outside the body and through the aspects of the nervous system. ...
File - Mr. Haan`s Science
... conc. of K+ inside membrane c. Na+K+ pump works d. K+ diffuses out quickly causing the outside to be + and inside to be – in comparison e. Resting potential = difference in charges ...
... conc. of K+ inside membrane c. Na+K+ pump works d. K+ diffuses out quickly causing the outside to be + and inside to be – in comparison e. Resting potential = difference in charges ...
1. Cell body
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapt er14/animation__the_nerve_impulse.html ...
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapt er14/animation__the_nerve_impulse.html ...
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I notes
... - depolarization is the movement of ions across the membrane so that the potential is decreased (to 0 mV maybe) - gated Na+ channels open in response to several types of stimuli on the membrane of the cell body and dendrites in neurons, such as stimulus from other neurons, pressure, some chemicals, ...
... - depolarization is the movement of ions across the membrane so that the potential is decreased (to 0 mV maybe) - gated Na+ channels open in response to several types of stimuli on the membrane of the cell body and dendrites in neurons, such as stimulus from other neurons, pressure, some chemicals, ...
Q24 Describe the mechanism of action of the
... Opioid receptors are serpentine structures which are linked to inhibitory G-‐proteins They are present both pre and post synaptically. o Presynaptically, activation causes closure of voltage gated calcium channel ...
... Opioid receptors are serpentine structures which are linked to inhibitory G-‐proteins They are present both pre and post synaptically. o Presynaptically, activation causes closure of voltage gated calcium channel ...
Nerve Cell Signaling - Mr. Moore`s Web Page
... • 4.4 Explain how the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, sensory neurons, motor neurons) mediates communication among different parts of the body and mediates the body’s interactions with the environment. ...
... • 4.4 Explain how the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, sensory neurons, motor neurons) mediates communication among different parts of the body and mediates the body’s interactions with the environment. ...
Psychology`s biological roots: neurons and neural communication
... It insulates like the plastic tubing of an electric cord ...
... It insulates like the plastic tubing of an electric cord ...
[j26]Chapter 7#
... 6. Myelin sheaths around axons within the CNS are formed by a. Schwann cells. b. microglia. c. astrocytes. d. oligodendrocytes. 7. The most abundant supporting (glial) cell in the CNS, which forms end-feet around capillaries associated with the blood-brain barrier, is the a. astrocyte. b. oligodendr ...
... 6. Myelin sheaths around axons within the CNS are formed by a. Schwann cells. b. microglia. c. astrocytes. d. oligodendrocytes. 7. The most abundant supporting (glial) cell in the CNS, which forms end-feet around capillaries associated with the blood-brain barrier, is the a. astrocyte. b. oligodendr ...
[j26]Chapter 7#
... 6. Myelin sheaths around axons within the CNS are formed by a. Schwann cells. b. microglia. c. astrocytes. d. oligodendrocytes. 7. The most abundant supporting (glial) cell in the CNS, which forms end-feet around capillaries associated with the blood-brain barrier, is the a. astrocyte. b. oligodendr ...
... 6. Myelin sheaths around axons within the CNS are formed by a. Schwann cells. b. microglia. c. astrocytes. d. oligodendrocytes. 7. The most abundant supporting (glial) cell in the CNS, which forms end-feet around capillaries associated with the blood-brain barrier, is the a. astrocyte. b. oligodendr ...
Document
... events •Same events occur no matter how strong or weak the stimulus •Intensity of stimulus determines frequency of action potentials ...
... events •Same events occur no matter how strong or weak the stimulus •Intensity of stimulus determines frequency of action potentials ...
here - STAO
... effect. Cocaine and amphetamines are similar in structure to norepinephrine, and therefore have similar effects. Caffeine is also a stimulant, but its actions are a little different from the previous two examples. Instead of exciting neurons, it inhibits inhibitory neurons. This causes the same end ...
... effect. Cocaine and amphetamines are similar in structure to norepinephrine, and therefore have similar effects. Caffeine is also a stimulant, but its actions are a little different from the previous two examples. Instead of exciting neurons, it inhibits inhibitory neurons. This causes the same end ...
supporting cells - Daniela Sartori
... • NT receptor is not part of the ion channel – Is a 1 subunit membrane polypeptide – Activates ion channel indirectly through G-proteins ...
... • NT receptor is not part of the ion channel – Is a 1 subunit membrane polypeptide – Activates ion channel indirectly through G-proteins ...
Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... potential at the next location. Cannot go backwards because initial action potential site is depolarized yielding one-way conduction of impulse. ...
... potential at the next location. Cannot go backwards because initial action potential site is depolarized yielding one-way conduction of impulse. ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.




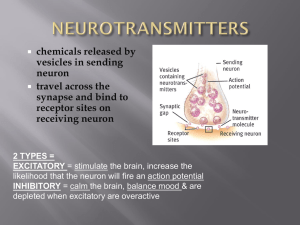












![[j26]Chapter 7#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009487154_1-bf88061009d68b903e2c1573596f45de-300x300.png)
![[j26]Chapter 7#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015520931_1-d3d263c2c8c221955c9bc7f03ee94039-300x300.png)



