Concepts and functions - Pécsi Tudományegyetem
... The cell types that make up nervous tissue are neurons and neuroglia. Neurons come in many shapes and sizes. There are billions of them in a human brain. Basically they have a cell body that contains the nucleus surrounded by cytoplasmic elements for protein synthesis and energy production. There ar ...
... The cell types that make up nervous tissue are neurons and neuroglia. Neurons come in many shapes and sizes. There are billions of them in a human brain. Basically they have a cell body that contains the nucleus surrounded by cytoplasmic elements for protein synthesis and energy production. There ar ...
Endocrine and nervous system - Glasgow Independent Schools
... Consists of: brain, spinal cord, nerves and sense organs ...
... Consists of: brain, spinal cord, nerves and sense organs ...
The Nervous System
... impulse) see diagram on next page All PNS nerves have a thin membrane called the neurillemma = promotes regeneration of damaged axons. Some nerve cells within the brain and spinal cord do NOT have myelin or neurillemma (celled grey matter), therefore ...
... impulse) see diagram on next page All PNS nerves have a thin membrane called the neurillemma = promotes regeneration of damaged axons. Some nerve cells within the brain and spinal cord do NOT have myelin or neurillemma (celled grey matter), therefore ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. ...
... More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. ...
Biosychology_Intro Reading
... organs, limbs and skin. These nerves extend from the central nervous system to the outermost areas of the body. The nerves that make up the peripheral nervous system are actually the axons or bundles of axons from neuron cells. In some cases, these nerves are very small but some nerve bundles are so ...
... organs, limbs and skin. These nerves extend from the central nervous system to the outermost areas of the body. The nerves that make up the peripheral nervous system are actually the axons or bundles of axons from neuron cells. In some cases, these nerves are very small but some nerve bundles are so ...
workbook - anglické gymnázium brno
... The nervous system gives directions to all the other systems in your body. It also gets information from your senses, and keeps track of how well the different parts of your body are working together. The nervous system is made up of two parts: the central nervous system (CNS), and the peripheral ne ...
... The nervous system gives directions to all the other systems in your body. It also gets information from your senses, and keeps track of how well the different parts of your body are working together. The nervous system is made up of two parts: the central nervous system (CNS), and the peripheral ne ...
Lecture 1 Intro, Nervous System
... • Medical (biological) model – Psychopathologies are biologically driven. – They can be treated with drugs. ...
... • Medical (biological) model – Psychopathologies are biologically driven. – They can be treated with drugs. ...
nervous_system_-_cns_and_pns_part_2_-_2015
... regulate the organs of the body without conscious control; involuntary • Control exists in the medulla • They work on smooth muscle (digestive system), cardiac muscle (heart) and glands (exocrine & endocrine) • Responsible for maintaining homeostasis during times of rest and during emergencies ...
... regulate the organs of the body without conscious control; involuntary • Control exists in the medulla • They work on smooth muscle (digestive system), cardiac muscle (heart) and glands (exocrine & endocrine) • Responsible for maintaining homeostasis during times of rest and during emergencies ...
Slide ()
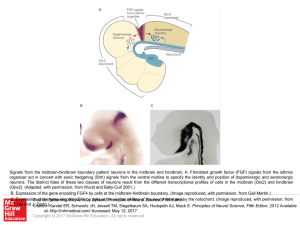
... Signals from the midbrain-hindbrain boundary pattern neurons in the midbrain and hindbrain. A. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signals from the isthmic organizer act in concert with sonic hedgehog (Shh) signals from the ventral midline to specify the identity and position of dopaminergic and serotone ...
... Signals from the midbrain-hindbrain boundary pattern neurons in the midbrain and hindbrain. A. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signals from the isthmic organizer act in concert with sonic hedgehog (Shh) signals from the ventral midline to specify the identity and position of dopaminergic and serotone ...
m5zn_363798b57fd4c88
... Function of the spinal cord The main functions of the spinal cord are: 1. The spinal cord communicates through nerve fibers, its nervous pathways, with various parts of the brain and through spinal nerves with organs. The spinal cord contains two kinds of nervous pathway: ascending (sensory) and d ...
... Function of the spinal cord The main functions of the spinal cord are: 1. The spinal cord communicates through nerve fibers, its nervous pathways, with various parts of the brain and through spinal nerves with organs. The spinal cord contains two kinds of nervous pathway: ascending (sensory) and d ...
Document
... • Molecules and organelles are moved along axons by motor molecules in two directions: • Anterograde—toward axonal terminal • Examples: mitochondria, membrane components, enzymes • Retrograde—toward the cell body • Examples: organelles to be degraded, signal molecules, viruses, and bacterial toxins ...
... • Molecules and organelles are moved along axons by motor molecules in two directions: • Anterograde—toward axonal terminal • Examples: mitochondria, membrane components, enzymes • Retrograde—toward the cell body • Examples: organelles to be degraded, signal molecules, viruses, and bacterial toxins ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
... • Molecules and organelles are moved along axons by motor molecules in two directions: • Anterograde—toward axonal terminal • Examples: mitochondria, membrane components, enzymes • Retrograde—toward the cell body • Examples: organelles to be degraded, signal molecules, viruses, and bacterial toxins ...
... • Molecules and organelles are moved along axons by motor molecules in two directions: • Anterograde—toward axonal terminal • Examples: mitochondria, membrane components, enzymes • Retrograde—toward the cell body • Examples: organelles to be degraded, signal molecules, viruses, and bacterial toxins ...
Chapter 3
... the effects of a neurotransmitter; may prevent reuptake 9. antagonist – chemical that blocks the effect of a neurotransmitter; block a receptor or enhance reuptake II. The Nervous System Diagram Fig. 2.8 p. 55 A. Spinal Cord – flexible rope of nerves that runs inside the backbone B. Central Nervous ...
... the effects of a neurotransmitter; may prevent reuptake 9. antagonist – chemical that blocks the effect of a neurotransmitter; block a receptor or enhance reuptake II. The Nervous System Diagram Fig. 2.8 p. 55 A. Spinal Cord – flexible rope of nerves that runs inside the backbone B. Central Nervous ...
Human Nervous system
... nerve impulses between parts of the body. The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions and transmit signals between different parts of human body. In Human nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The ...
... nerve impulses between parts of the body. The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions and transmit signals between different parts of human body. In Human nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The ...
Nervous System
... • Gamma amino butyric acid(GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter that is often referred to as “nature’s VALIUMlike substance”. When GABA is out of range (high or low excretion values), it is likely that an excitatory neurotransmitter is firing too often in the brain. GABA will be sent out ...
... • Gamma amino butyric acid(GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter that is often referred to as “nature’s VALIUMlike substance”. When GABA is out of range (high or low excretion values), it is likely that an excitatory neurotransmitter is firing too often in the brain. GABA will be sent out ...
Nervous System
... • Gamma amino butyric acid(GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter that is often referred to as “nature’s VALIUMlike substance”. When GABA is out of range (high or low excretion values), it is likely that an excitatory neurotransmitter is firing too often in the brain. GABA will be sent out ...
... • Gamma amino butyric acid(GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter that is often referred to as “nature’s VALIUMlike substance”. When GABA is out of range (high or low excretion values), it is likely that an excitatory neurotransmitter is firing too often in the brain. GABA will be sent out ...
The role of the nervous system in detecting and
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
Autonomic Nervous System - Cedar Bluffs Public Schools
... 2. Stimulation of brain during surgery ...
... 2. Stimulation of brain during surgery ...
PR_161115_Inaktive_Gehirnzellen_E
... given task, only a very small percentage of neurons take part, while their neighbours remain dormant, waiting for their ‘cue’, as it were. Memory functions in the brain work according to a principle that neuroscientists call ‘sparse coding’, i.e. a comparatively small number of neurons encode comple ...
... given task, only a very small percentage of neurons take part, while their neighbours remain dormant, waiting for their ‘cue’, as it were. Memory functions in the brain work according to a principle that neuroscientists call ‘sparse coding’, i.e. a comparatively small number of neurons encode comple ...
Chapter 4 - (www.forensicconsultation.org).
... • feed them when they are hungry • play with them when they are awake • “spoil” them as much as you can! (studies show that baby must learn that they have an effect on their environment, and therefore control over their own experience. Important for cognitive and social development • babies need to ...
... • feed them when they are hungry • play with them when they are awake • “spoil” them as much as you can! (studies show that baby must learn that they have an effect on their environment, and therefore control over their own experience. Important for cognitive and social development • babies need to ...
LAB 10 NEURON and SPINAL CORD
... except the brain and spinal cord. It consists of nerves and ganglia. It deliveries sensory information to the CNS and carries motor commands to peripheral tissues and system. ...
... except the brain and spinal cord. It consists of nerves and ganglia. It deliveries sensory information to the CNS and carries motor commands to peripheral tissues and system. ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.