biophysiology show 1
... • The signal that travels the length of the neuron is actually a change in the polarity of the outside of the axon. • The resting charge on the cell is -70 millivolts. • This charge is created by a membrane around the cell that keeps positively charged sodium ions (Na+) on the outside of the cell an ...
... • The signal that travels the length of the neuron is actually a change in the polarity of the outside of the axon. • The resting charge on the cell is -70 millivolts. • This charge is created by a membrane around the cell that keeps positively charged sodium ions (Na+) on the outside of the cell an ...
Neurotransmitter proteins
... Nervous System • Network of connected cells, tissue, and organs • Controls thoughts, movement, life processes • Quick responses – Ex: Sunny day pupils shrinking ...
... Nervous System • Network of connected cells, tissue, and organs • Controls thoughts, movement, life processes • Quick responses – Ex: Sunny day pupils shrinking ...
The Nervous System - Underground Notes
... There are many spinal nerves. Spinal nerves are identified by numbers and letters. C = A nerve connected to one of the cervical (neck) vertebrae T = A nerve connected to one of the thoracic (upper body) vertebrae L = A nerve connected to one of the lumbar ( middle body) vertebrae S = A nerve connect ...
... There are many spinal nerves. Spinal nerves are identified by numbers and letters. C = A nerve connected to one of the cervical (neck) vertebrae T = A nerve connected to one of the thoracic (upper body) vertebrae L = A nerve connected to one of the lumbar ( middle body) vertebrae S = A nerve connect ...
SENSATION - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... Bi-polar cells – neurons that connect the rods & cones to the ganglion cells Ganglion cells – connect to the bipolar cells. The bundled axons form the optic nerve. Blind spot – the point where the optic nerve leaves the eye & there are no rods or cones. ...
... Bi-polar cells – neurons that connect the rods & cones to the ganglion cells Ganglion cells – connect to the bipolar cells. The bundled axons form the optic nerve. Blind spot – the point where the optic nerve leaves the eye & there are no rods or cones. ...
Development & Neuroplasticity - U
... • Neural crest cells transplanted to a new part of the neural crest migrate to the destination that is appropriate for cells in the new location; thus the migration routes must be encoded in the medium through which they travel rather than in the cells themselves; many different types of chemical si ...
... • Neural crest cells transplanted to a new part of the neural crest migrate to the destination that is appropriate for cells in the new location; thus the migration routes must be encoded in the medium through which they travel rather than in the cells themselves; many different types of chemical si ...
Science 6th primary. 1st term unit 4 lesson 1 Why does this
... It is responsible for regulating the involuntary processes of the body as: 1 – regulating heartbeats. 2 – regulating the movement of the respiratory system parts during breathing. 3 –regulating the movements and functions of the digestive system. ...
... It is responsible for regulating the involuntary processes of the body as: 1 – regulating heartbeats. 2 – regulating the movement of the respiratory system parts during breathing. 3 –regulating the movements and functions of the digestive system. ...
Introduction to the Central Nervous System
... 2 Blood Supply in the CNS While the brain comprises only about 2% of body weight, it receives 15% of the blood supply. This is because neural activity is energetically expensive and requires a high metabolic rate to keep up with the demand. When the body is at rest, the brain consumes 20% of the bod ...
... 2 Blood Supply in the CNS While the brain comprises only about 2% of body weight, it receives 15% of the blood supply. This is because neural activity is energetically expensive and requires a high metabolic rate to keep up with the demand. When the body is at rest, the brain consumes 20% of the bod ...
The Structures of the Brain
... brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) between them. ...
... brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) between them. ...
Note: This hypothesis is mainly concerned with peripheral neurons
... In vitro assays have shown that NTs enhance both axonal and dendritic growth In vivo, the situation is more difficult to study Why? In standard knockouts, it is difficult to separate the survival effects of NTs from their effects on the morphology of neurons. This problem has begun to be addressed ...
... In vitro assays have shown that NTs enhance both axonal and dendritic growth In vivo, the situation is more difficult to study Why? In standard knockouts, it is difficult to separate the survival effects of NTs from their effects on the morphology of neurons. This problem has begun to be addressed ...
presentation
... The cell body of one neuron is located in the spinal cord and brain and the second extends to a visceral effector. The Preganglionic fiber is the axon within the cell body that is located in the brain and spinal cord in which it travels through the CNS and synapse with the neurons within an autonomi ...
... The cell body of one neuron is located in the spinal cord and brain and the second extends to a visceral effector. The Preganglionic fiber is the axon within the cell body that is located in the brain and spinal cord in which it travels through the CNS and synapse with the neurons within an autonomi ...
Chapter 10 Slides
... capacity for accurate axonal growth is lost in maturity Regeneration is virtually nonexistent in the CNS of adult mammals and unlikely, but possible, in the PNS ...
... capacity for accurate axonal growth is lost in maturity Regeneration is virtually nonexistent in the CNS of adult mammals and unlikely, but possible, in the PNS ...
music and the brain - College of Natural Sciences
... aspects of human brain function, from language and complex sequence processing to how the auditory and motor systems are joined together in beat perception and synchronization. All humans come into the world with a capability for music. Humans are the only species able to perform a beat consistent w ...
... aspects of human brain function, from language and complex sequence processing to how the auditory and motor systems are joined together in beat perception and synchronization. All humans come into the world with a capability for music. Humans are the only species able to perform a beat consistent w ...
Brain Bark
... abstract information like music, colors or shapes and to synthesize experiences by giving a quick, general sense of what is happening ...
... abstract information like music, colors or shapes and to synthesize experiences by giving a quick, general sense of what is happening ...
Silencing brain cells with
... chronic pain, epilepsy, brain injury, and Parkinson’s disease. The tools work on the principle that such disorders might be best treated by silencing, rather than stimulating, brain activity. These “super silencers” exert exquisite control over the timing of the shutdown of overactive neural circuit ...
... chronic pain, epilepsy, brain injury, and Parkinson’s disease. The tools work on the principle that such disorders might be best treated by silencing, rather than stimulating, brain activity. These “super silencers” exert exquisite control over the timing of the shutdown of overactive neural circuit ...
Slide ()
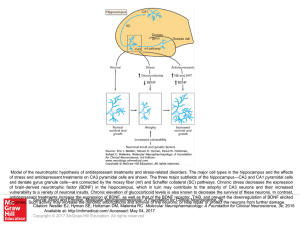
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
Where are the cell bodies of the primary afferent fibers that mediate
... Primary sensory neurons What are the key constituents in each of the: MLF, medial lemniscus, basis pedunculi, and central tegmental tract? MLF: second-order vestibular fibers; axons of brain stem neurons controlling eye movements Medial lemniscus-you should know this by now Basis pedunculi: descendi ...
... Primary sensory neurons What are the key constituents in each of the: MLF, medial lemniscus, basis pedunculi, and central tegmental tract? MLF: second-order vestibular fibers; axons of brain stem neurons controlling eye movements Medial lemniscus-you should know this by now Basis pedunculi: descendi ...
Central Nervous System PPT
... Pons out motor signals. left all and right domes of the heart rate, temperature, cerebrum. and sleep. waterworks, ...
... Pons out motor signals. left all and right domes of the heart rate, temperature, cerebrum. and sleep. waterworks, ...
You*ve had a concussion! How to return a player to the
... Neurons are basically like on/off switches of a light switch. Neurons are either resting or shooting an electrical impulse down a wire called an axon. Each of the neurons spit out chemicals that trigger other neurons. ...
... Neurons are basically like on/off switches of a light switch. Neurons are either resting or shooting an electrical impulse down a wire called an axon. Each of the neurons spit out chemicals that trigger other neurons. ...
Biopsychology and Perception
... • Wernicke's area , involved in receptive speech, is in the left temporal lobe ...
... • Wernicke's area , involved in receptive speech, is in the left temporal lobe ...
99 4A midterm studyq`s
... 4. Biologists use the Nernst and Goldman Equations to describe a neuron's ionic composition. Compare and contrast these two equations. 5. Compare and contrast the transmission of signals within one neuron and between two neurons, including the roles of ion channels, neurotransmitters, neuromodulator ...
... 4. Biologists use the Nernst and Goldman Equations to describe a neuron's ionic composition. Compare and contrast these two equations. 5. Compare and contrast the transmission of signals within one neuron and between two neurons, including the roles of ion channels, neurotransmitters, neuromodulator ...
Chapter 14
... anterior nucleus concerned with emotions, memory and acquisition of knowledge (cognition) ...
... anterior nucleus concerned with emotions, memory and acquisition of knowledge (cognition) ...
Student Guide Chapter 11
... The Synapse 13. Define synapse. Distinguish between electrical and chemical synapses by structure and by the way they transmit information. 14. Distinguish between excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. 15. Describe how synaptic events are integrated and modified. Neurotransmitters and T ...
... The Synapse 13. Define synapse. Distinguish between electrical and chemical synapses by structure and by the way they transmit information. 14. Distinguish between excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. 15. Describe how synaptic events are integrated and modified. Neurotransmitters and T ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.