What Our Brains Can Teach Us
... Union address, saying, “Now is the time to reach a level of research and development not seen since the height of the space race.” He mentioned mapping the human brain, but it’s more likely that scientists will start with smaller brains and central nervous systems — like those of worms, fruit flies, ...
... Union address, saying, “Now is the time to reach a level of research and development not seen since the height of the space race.” He mentioned mapping the human brain, but it’s more likely that scientists will start with smaller brains and central nervous systems — like those of worms, fruit flies, ...
Drugs and the Nervous System
... Drugs and the Nervous System Drug: Any substance, other than food, that changes the structure or function of the body ALL drugs (prescription, over the counter and illegal) have potential to do harm if abused or used improperly. Drugs differ in ways they affect the body. (kill bacteria, treat diseas ...
... Drugs and the Nervous System Drug: Any substance, other than food, that changes the structure or function of the body ALL drugs (prescription, over the counter and illegal) have potential to do harm if abused or used improperly. Drugs differ in ways they affect the body. (kill bacteria, treat diseas ...
The Nervous System
... Networks of neurons Neuron Structure and Synapses. The neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. Nerve impulses are conducted along a neuron. Dentrite cell body axon hillock axon Some axons are insulated by a myelin sheath. ...
... Networks of neurons Neuron Structure and Synapses. The neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. Nerve impulses are conducted along a neuron. Dentrite cell body axon hillock axon Some axons are insulated by a myelin sheath. ...
Answers - Mosaiced.org
... 30. if axon is damaged, end of severed axon seals and swells – amt of swelling can be used to time injury 31. axon hillock – most easily depolarised 32. Nodes of Ranvier 33. microtubules 34. synaptic vesicles, mitochondria, transmitters ...
... 30. if axon is damaged, end of severed axon seals and swells – amt of swelling can be used to time injury 31. axon hillock – most easily depolarised 32. Nodes of Ranvier 33. microtubules 34. synaptic vesicles, mitochondria, transmitters ...
Central nervous system
... • Consists of all nerves that lie outside the CNS – Somatic nervous system » Sensory and motor functions that control skeletal muscle – Autonomic nervous system » Controls smooth muscle, cardiac, muscle, and gland » Divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions ...
... • Consists of all nerves that lie outside the CNS – Somatic nervous system » Sensory and motor functions that control skeletal muscle – Autonomic nervous system » Controls smooth muscle, cardiac, muscle, and gland » Divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions ...
Drugs
... An acute viral infection, that can cause a small illness but eventually destroy ventral horns of the spinal cord (spinal polio) It is highly contagious and sometimes fatal disease that affects the nerves, and can cause paralysis. Can be caught by swallowing something with the virus on it. As the inf ...
... An acute viral infection, that can cause a small illness but eventually destroy ventral horns of the spinal cord (spinal polio) It is highly contagious and sometimes fatal disease that affects the nerves, and can cause paralysis. Can be caught by swallowing something with the virus on it. As the inf ...
53 XIX BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O`Brien)
... A. The anatomy of a neuron 1. Neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites, and one or more axons. Fig 45.3a 2. Neurons transmit information via electrical impulses. Fig 45.1a a. Sensory receptors transmit information about the internal or external environment to sensory neurons. b. Sensory neurons con ...
... A. The anatomy of a neuron 1. Neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites, and one or more axons. Fig 45.3a 2. Neurons transmit information via electrical impulses. Fig 45.1a a. Sensory receptors transmit information about the internal or external environment to sensory neurons. b. Sensory neurons con ...
computer
... In cognitive research, neural networks are not physical arrangements of actual networks of neurons !!! ...
... In cognitive research, neural networks are not physical arrangements of actual networks of neurons !!! ...
Slide 1
... • Relays information between the cerebellum or spinal cord and the cerebrum • Integrates sensory input Pons • A bridge between higher and lower brain centers Medulla oblongata • Contains autonomic centers for heart rate and digestive activities • Relays sensory information to thalamus ...
... • Relays information between the cerebellum or spinal cord and the cerebrum • Integrates sensory input Pons • A bridge between higher and lower brain centers Medulla oblongata • Contains autonomic centers for heart rate and digestive activities • Relays sensory information to thalamus ...
C8003 Psychobiology sample paper 2016-17
... 22. Patient H. M., the most studied case in neuropsychology, had which area of his brain removed to control his severe epilepsy? a) b) c) d) ...
... 22. Patient H. M., the most studied case in neuropsychology, had which area of his brain removed to control his severe epilepsy? a) b) c) d) ...
The Nervous System
... – Motor (efferent):Carries impulses from CNS to effector organs, muscles & glands & effect a motor response • Somatic (voluntary): allows conscious or voluntary control of skeletal muscles; reflexes are initiated involuntarily by same fibers • Autonomic (involuntary): regulates involuntary events of ...
... – Motor (efferent):Carries impulses from CNS to effector organs, muscles & glands & effect a motor response • Somatic (voluntary): allows conscious or voluntary control of skeletal muscles; reflexes are initiated involuntarily by same fibers • Autonomic (involuntary): regulates involuntary events of ...
Myers` Psychology for AP
... Right-Left Differences in the Intact Brain 8. Describe the distinct functions of the brain’s two hemispheres, and discuss research findings on brain organization and handedness. LO #7 9. Describe research that leads cognitive neuroscientists to infer how the brains dual-processing affects our percep ...
... Right-Left Differences in the Intact Brain 8. Describe the distinct functions of the brain’s two hemispheres, and discuss research findings on brain organization and handedness. LO #7 9. Describe research that leads cognitive neuroscientists to infer how the brains dual-processing affects our percep ...
Parts of the Neuron 45
... also convey messages to your glands, causing them to release hormones, chemical substances that help regulate bodily processes. Interneurons (also called associative neurons) are the most common type of neuron in the nervous system. They connect neurons to neurons. In the spinal cord, they connect s ...
... also convey messages to your glands, causing them to release hormones, chemical substances that help regulate bodily processes. Interneurons (also called associative neurons) are the most common type of neuron in the nervous system. They connect neurons to neurons. In the spinal cord, they connect s ...
Bio101Lab13
... – Be able to identify and name the structures listed in your Lab Study Guide using the human brain models or photographs of the human brains (from designated slides in Lab 13) – Be able to identify and state the number and name of four of the twelve cranial nerves: I, II, III, and V on the human bra ...
... – Be able to identify and name the structures listed in your Lab Study Guide using the human brain models or photographs of the human brains (from designated slides in Lab 13) – Be able to identify and state the number and name of four of the twelve cranial nerves: I, II, III, and V on the human bra ...
11)
... 4. ____________ support nervous tissue, whereas ____________ conduct the electrical impulses. a. leucocytes, erythrocytes b. axons, dendrites c. neuroglia, neurons d. proteins, lipids 5. Collagen fibers are proteins that are particularly abundant in a. epithelium b. muscle c. nervous tissue d. carti ...
... 4. ____________ support nervous tissue, whereas ____________ conduct the electrical impulses. a. leucocytes, erythrocytes b. axons, dendrites c. neuroglia, neurons d. proteins, lipids 5. Collagen fibers are proteins that are particularly abundant in a. epithelium b. muscle c. nervous tissue d. carti ...
The Nervous System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... body then divides into two branches; one connecting to a peripheral body part and functioning as a dendrite, and the other entering the brain or spinal cord and functioning as an axon; some cell bodies gather in specialized masses of nervous tissue called ganglia(located outside the brain or spinal ...
... body then divides into two branches; one connecting to a peripheral body part and functioning as a dendrite, and the other entering the brain or spinal cord and functioning as an axon; some cell bodies gather in specialized masses of nervous tissue called ganglia(located outside the brain or spinal ...
8a nerve cells 10a
... NEUROLEMMA is the name of the plasma membrane (outermost covering) of a neuron. DENDRITES function to receive the signal and carry the nerve conduction toward the cell body. SOMA (cell body) is where the nucleus, ribosomes, and most organelles are located AXON HILLOCK is the area on the soma where t ...
... NEUROLEMMA is the name of the plasma membrane (outermost covering) of a neuron. DENDRITES function to receive the signal and carry the nerve conduction toward the cell body. SOMA (cell body) is where the nucleus, ribosomes, and most organelles are located AXON HILLOCK is the area on the soma where t ...
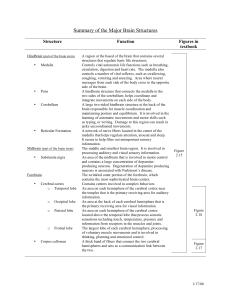
Summary of the Major Brain Structures
... A region at the based of the brain that contains several structures that regulate basic life structures. Controls vital autonomic life functions such as breathing, circulation, digestion and heart rate. The medulla also controls a number of vital reflexes, such as swallowing, coughing, vomiting and ...
... A region at the based of the brain that contains several structures that regulate basic life structures. Controls vital autonomic life functions such as breathing, circulation, digestion and heart rate. The medulla also controls a number of vital reflexes, such as swallowing, coughing, vomiting and ...
Right Brain and Left Brain Hemisphere
... Directions: Label the following items below and color in the 4 different lobes. Use pages 60, 62 and 63 ...
... Directions: Label the following items below and color in the 4 different lobes. Use pages 60, 62 and 63 ...
Netter`s Atlas of Neuroscience - 9780323265119 | US Elsevier
... mainly through axonal terminations on the cell body and dendrites. These synapses are isolated and protected by astrocytic processes. The dendrites usually provide the greatest surface area of the neuron. Some protrusions from dendritic branches (dendritic spines) are sites of specific axo-dendritic ...
... mainly through axonal terminations on the cell body and dendrites. These synapses are isolated and protected by astrocytic processes. The dendrites usually provide the greatest surface area of the neuron. Some protrusions from dendritic branches (dendritic spines) are sites of specific axo-dendritic ...
Mirror Neurons
... Purchasing institutions may not grant rights to any third party, nor make the material available to external organisations, without prior written permission from Uniview Worldwide Ltd. Uniview Worldwide Ltd maintains control of all copyright permissions and retains the right to request access to ass ...
... Purchasing institutions may not grant rights to any third party, nor make the material available to external organisations, without prior written permission from Uniview Worldwide Ltd. Uniview Worldwide Ltd maintains control of all copyright permissions and retains the right to request access to ass ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.