Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Synaptic Cleft: Information Transfer Nerve impulses (AP) reach the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron ...
... Synaptic Cleft: Information Transfer Nerve impulses (AP) reach the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron ...
BOX 2.2 CAJAL: ICONOCLAST TO ICON Santiago Ramón y Cajal
... Cajal saw immediately that it offered great hope in solving the most vexing problem of nineteenthcentury neuroscience: How do adult nerve cells interact with one another? This realization galvanized and directed the rest of his scientific life, which was extremely productive in terms of originality, ...
... Cajal saw immediately that it offered great hope in solving the most vexing problem of nineteenthcentury neuroscience: How do adult nerve cells interact with one another? This realization galvanized and directed the rest of his scientific life, which was extremely productive in terms of originality, ...
General Neurophysiology
... Behavior as a chain of reflexes? LOCUST Two pairs of wings Each pair beat in synchrony but the rear wings lead the front wings in the beat cycle by about ...
... Behavior as a chain of reflexes? LOCUST Two pairs of wings Each pair beat in synchrony but the rear wings lead the front wings in the beat cycle by about ...
nervous system B
... • The experiences are unique to each individual (i.e. there is no universal association between a certain letter or a certain color), are not made up or learned, and usually remain the same throughout life. ...
... • The experiences are unique to each individual (i.e. there is no universal association between a certain letter or a certain color), are not made up or learned, and usually remain the same throughout life. ...
Development
... ganglionic eminence can be seen through the interventricular foramen. B, C: transverse sections through the developing brain. ...
... ganglionic eminence can be seen through the interventricular foramen. B, C: transverse sections through the developing brain. ...
Neurofeedback
... • Virtual Reality – Enhance neurofeedback in a couple ways • The total immersion and totality of the feedback allows the patient to focus completely on his physiology without distraction • More engaging and motivating for the client ...
... • Virtual Reality – Enhance neurofeedback in a couple ways • The total immersion and totality of the feedback allows the patient to focus completely on his physiology without distraction • More engaging and motivating for the client ...
Chapter 9 Part II Review
... a.sensory/afferent neurons b.Association/interneurons c.Motor/efferent neurons ...
... a.sensory/afferent neurons b.Association/interneurons c.Motor/efferent neurons ...
Neurons - Honors Biology 10 - 2222-03
... 1. Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs to the spinal cord and brain. 2. Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and the spinal cord to muscles and glands. 3. Interneurons process information from sensory neurons and then send commands to motor neurons. ...
... 1. Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs to the spinal cord and brain. 2. Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and the spinal cord to muscles and glands. 3. Interneurons process information from sensory neurons and then send commands to motor neurons. ...
Neurophysiology
... - pain, heat, cold, and touch - Nerve impulses are passed by 3 neurones to sensory area in opposite hemisphere of cerebrum where sensation and its location are perceived - Crossing to other side, decussation, occurs either at level of entry into spinal cord (spinothalamic) or in the medulla (posteri ...
... - pain, heat, cold, and touch - Nerve impulses are passed by 3 neurones to sensory area in opposite hemisphere of cerebrum where sensation and its location are perceived - Crossing to other side, decussation, occurs either at level of entry into spinal cord (spinothalamic) or in the medulla (posteri ...
Slide ()
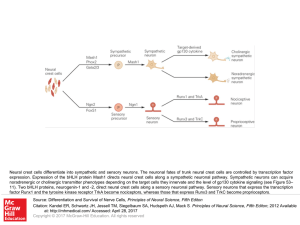
... Neural crest cells differentiate into sympathetic and sensory neurons. The neuronal fates of trunk neural crest cells are controlled by transcription factor expression. Expression of the bHLH protein Mash1 directs neural crest cells along a sympathetic neuronal pathway. Sympathetic neurons can acqui ...
... Neural crest cells differentiate into sympathetic and sensory neurons. The neuronal fates of trunk neural crest cells are controlled by transcription factor expression. Expression of the bHLH protein Mash1 directs neural crest cells along a sympathetic neuronal pathway. Sympathetic neurons can acqui ...
Figure 7.16
... • Nerves and ganglia outside the central nervous system • Nerve = bundle of neuron fibers • Neuron fibers are bundled by connective tissue ...
... • Nerves and ganglia outside the central nervous system • Nerve = bundle of neuron fibers • Neuron fibers are bundled by connective tissue ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-24
... o Adjusts output of other somatic motor centers in brain and spinal cord How does the CNS get its adult shape? Embryonic Development of the Nervous System Understanding the embryology helps to understand both anatomy and function of the brain The nervous system begins forming around embryonic ...
... o Adjusts output of other somatic motor centers in brain and spinal cord How does the CNS get its adult shape? Embryonic Development of the Nervous System Understanding the embryology helps to understand both anatomy and function of the brain The nervous system begins forming around embryonic ...
PPT10Chapter10TheNervousSystem
... blood vessels and lies delicately over the brain and spinal cord. Blood vessels supply the brain with much of it’s blood. ...
... blood vessels and lies delicately over the brain and spinal cord. Blood vessels supply the brain with much of it’s blood. ...
The Brain & Cerebral Hemispheres
... The ________ of the brain Patients with ______ problems gave 1st clues about how the brain controls language 1981 Dr Paul Broca described a patient who could only say the word “tan”. When the patient died Broca examined the brain and found damage to the ____________________ This part of the brain is ...
... The ________ of the brain Patients with ______ problems gave 1st clues about how the brain controls language 1981 Dr Paul Broca described a patient who could only say the word “tan”. When the patient died Broca examined the brain and found damage to the ____________________ This part of the brain is ...
Eye Structure - WordPress.com
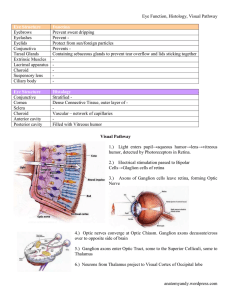
... Prevents Containing sebaceous glands to prevent tear overflow and lids sticking together ...
... Prevents Containing sebaceous glands to prevent tear overflow and lids sticking together ...
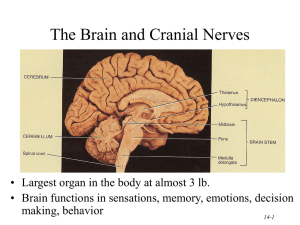
14-1
... infundibulum suspends the pituitary gland • Major regulator of homeostasis – receives somatic and visceral input, taste, smell & hearing information; monitors osmotic pressure, temperature of blood ...
... infundibulum suspends the pituitary gland • Major regulator of homeostasis – receives somatic and visceral input, taste, smell & hearing information; monitors osmotic pressure, temperature of blood ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... performing a function in virtue of its components parts, component operations, and their organization. • The orchestrated functioning of the mechanism is responsible for one or more phenomena.” (Bechtel & Abrahamsen; Bechtel) ...
... performing a function in virtue of its components parts, component operations, and their organization. • The orchestrated functioning of the mechanism is responsible for one or more phenomena.” (Bechtel & Abrahamsen; Bechtel) ...
Parts of the Brain - University of Peradeniya
... Few facts from your A/Levels or high school biology • In a Fresh brain or Spinal cord., – White is due to myelinated (protein +l ipid); nerve fibers or Axons – Gay is due to cells; neurons & glia But in imaging techniques gray and white may look different ...
... Few facts from your A/Levels or high school biology • In a Fresh brain or Spinal cord., – White is due to myelinated (protein +l ipid); nerve fibers or Axons – Gay is due to cells; neurons & glia But in imaging techniques gray and white may look different ...
Nervous System - Discovery Education
... cord and through the peripheral nerve to your arm. This is a voluntary action that is controlled by conscious thought. This is referred to as the somatic nervous system. There are other actions that are not voluntary or under conscious control. This part of the peripheral nervous system is called t ...
... cord and through the peripheral nerve to your arm. This is a voluntary action that is controlled by conscious thought. This is referred to as the somatic nervous system. There are other actions that are not voluntary or under conscious control. This part of the peripheral nervous system is called t ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... 1. Relay station for all synaptic input 2. Crude awareness of sensation 3. Some degree of consciousness 4. Role in motor control 1. Regulation of many homeostatic functions, such as temperature control, thirst, urine output, and food intake 2. Important link between nervous and endocrine systems 3. ...
... 1. Relay station for all synaptic input 2. Crude awareness of sensation 3. Some degree of consciousness 4. Role in motor control 1. Regulation of many homeostatic functions, such as temperature control, thirst, urine output, and food intake 2. Important link between nervous and endocrine systems 3. ...
The Discovery of the Neuron By Mo Costandi from the History of
... meeting of the German Anatomical Society. It was at this meeting that Cajal met other investigators, some of whom were so impressed by his work that they abandoned their beliefs in the reticular theory. During his acceptance speech for the Nobel Prize in Physiology, which he was awarded with Golgi i ...
... meeting of the German Anatomical Society. It was at this meeting that Cajal met other investigators, some of whom were so impressed by his work that they abandoned their beliefs in the reticular theory. During his acceptance speech for the Nobel Prize in Physiology, which he was awarded with Golgi i ...
the limbic system
... On page 970, Genoux and colleagues report that an enzyme known as protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) actively suppresses in mice, during and after a learning One ofmemories PP1's targets is aboth gene-transcription factor called exercise. … CREB, which becomes inactive when dephosphorylated by PP1. CREB is ...
... On page 970, Genoux and colleagues report that an enzyme known as protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) actively suppresses in mice, during and after a learning One ofmemories PP1's targets is aboth gene-transcription factor called exercise. … CREB, which becomes inactive when dephosphorylated by PP1. CREB is ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Synaptic Cleft: Information Transfer Nerve impulses (AP) reach the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron ...
... Synaptic Cleft: Information Transfer Nerve impulses (AP) reach the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron ...
Central nervous system practical block
... demyelinated plaque and perivascular lymphocytic cuffs. C, The same lesion stained for axons shows relative preservation ...
... demyelinated plaque and perivascular lymphocytic cuffs. C, The same lesion stained for axons shows relative preservation ...
Glial cell - TheTruthAboutStuff.com
... gation, search Jump to: navi This article does not cite any references or sources . h m, et involved! ) Please help i mprove this article by adding citations to reliable sources .( a L nveriliahle material may be challenged and removed. This article has been tagged since August 2006. ...
... gation, search Jump to: navi This article does not cite any references or sources . h m, et involved! ) Please help i mprove this article by adding citations to reliable sources .( a L nveriliahle material may be challenged and removed. This article has been tagged since August 2006. ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.