Five basic concepts illustrate the usefulness of neuroscience to
... Five basic concepts illustrate the usefulness of neuroscience to counseling 1) Neuroplasticity: Simply put, the brain can change — it is not fixed. Instead, it responds to external environmental events and/or actions initiated by the individual. The old idea that the brain does not change is simply ...
... Five basic concepts illustrate the usefulness of neuroscience to counseling 1) Neuroplasticity: Simply put, the brain can change — it is not fixed. Instead, it responds to external environmental events and/or actions initiated by the individual. The old idea that the brain does not change is simply ...
A1987F573800001
... H-thymidine, I found that in the rhesus monkey, granule cells have their last mitotic division during the late gestational and early neonatal period. How do postmitotic cells find their way through neural tissue that, at this age, is already densely packed with synapses? ...
... H-thymidine, I found that in the rhesus monkey, granule cells have their last mitotic division during the late gestational and early neonatal period. How do postmitotic cells find their way through neural tissue that, at this age, is already densely packed with synapses? ...
27: Protection and Support of the Central Nervous System
... Consists of two layers made of dense fibrous connective tissue (DFCT). The outer layer lines the skull, and the inner layer folds down to form the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli. Spaces between these layers contain venous blood (blood returning to the heart) and are known as the ‘venous sinuse ...
... Consists of two layers made of dense fibrous connective tissue (DFCT). The outer layer lines the skull, and the inner layer folds down to form the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli. Spaces between these layers contain venous blood (blood returning to the heart) and are known as the ‘venous sinuse ...
neuroplasticity 2016
... by producing more receptors – These new receptors will respond to neurotransmitters that are released by adjacent axons ...
... by producing more receptors – These new receptors will respond to neurotransmitters that are released by adjacent axons ...
Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz
... Adrenal glands: inner part helps trigger fight-or-flight response Testis: male sex hormone Ovary: female sex hormone Parathyroid: help regulate level of calcium in blood Pituitary gland: secrets many different hormones some which affect other glands Pancreas: regulate level of sugar in b ...
... Adrenal glands: inner part helps trigger fight-or-flight response Testis: male sex hormone Ovary: female sex hormone Parathyroid: help regulate level of calcium in blood Pituitary gland: secrets many different hormones some which affect other glands Pancreas: regulate level of sugar in b ...
Ageing and the nervous system
... • Adverse reactions and side effects are more frequent The main significance of these problems is that drug doses should be modified, in order to cause as less as possible problems to the already weak organism. ...
... • Adverse reactions and side effects are more frequent The main significance of these problems is that drug doses should be modified, in order to cause as less as possible problems to the already weak organism. ...
Transcripts/01_05 1
... a. Going over basic properties of cells in the brain. II. Building Blocks [S2] a. Almost 100 years ago, people didn’t know the basic theory behind the building blocks of the nervous system. b. The most popular theory was the reticular theory, which had the nervous system much like the vasculature (b ...
... a. Going over basic properties of cells in the brain. II. Building Blocks [S2] a. Almost 100 years ago, people didn’t know the basic theory behind the building blocks of the nervous system. b. The most popular theory was the reticular theory, which had the nervous system much like the vasculature (b ...
Nervous tissue
... • result of Cl- flowing into the cell or K+ leaving the cell • glycine and GABA are inhibitory neurotransmitters ...
... • result of Cl- flowing into the cell or K+ leaving the cell • glycine and GABA are inhibitory neurotransmitters ...
Sponges - Weebly
... Sponges are important because: • Protect coral reefs from wave action • Homes/habitats to many organisms • Used for commercial products ...
... Sponges are important because: • Protect coral reefs from wave action • Homes/habitats to many organisms • Used for commercial products ...
Biological_Bases
... The nervous system is “plastic” (change/modeled) especially at early ages of development. ...
... The nervous system is “plastic” (change/modeled) especially at early ages of development. ...
Developing an integrated digital content strategy to drive
... Understanding what controls the time windows of sensitivity will require us to combine functional imaging with an understanding of the individuality of each brain cell, and the key epigenetic variations that underlie this. This will guide how we best use the “appropriate” kind of intervention to sh ...
... Understanding what controls the time windows of sensitivity will require us to combine functional imaging with an understanding of the individuality of each brain cell, and the key epigenetic variations that underlie this. This will guide how we best use the “appropriate” kind of intervention to sh ...
Slide 1
... – Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations. – Somatosensory cortex - area of neurons running down ...
... – Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations. – Somatosensory cortex - area of neurons running down ...
The Nervous System
... The Nervous system has two major divisions 1. The Central Nervous System (CNS) – consist of the Brain and the Spinal Cord. – The average adult human brain weighs 1.3 to 1.4 kg .The brain contains about 100 billion nerve cells,called Neurons and trillons of "support cells" called glia. – The spinal ...
... The Nervous system has two major divisions 1. The Central Nervous System (CNS) – consist of the Brain and the Spinal Cord. – The average adult human brain weighs 1.3 to 1.4 kg .The brain contains about 100 billion nerve cells,called Neurons and trillons of "support cells" called glia. – The spinal ...
Marina Florack
... to participants (ex. Computer generated list of every 5th person) o Naturalistic Observation: observe subjects in their natural habitats w/o interacting w/ them Con: control is sacrificed o Experimenter Effects: Observer effect: changes in behavior due to awareness of a person or animal being ob ...
... to participants (ex. Computer generated list of every 5th person) o Naturalistic Observation: observe subjects in their natural habitats w/o interacting w/ them Con: control is sacrificed o Experimenter Effects: Observer effect: changes in behavior due to awareness of a person or animal being ob ...
Chapter Three - New Providence School District
... A third method in this line of investigation is to study children who have been separated from their biological parents at a very early age and raised by adoptive parents. The idea behind these studies is that if the adoptive children more closely resemble their biological parents with respect to a ...
... A third method in this line of investigation is to study children who have been separated from their biological parents at a very early age and raised by adoptive parents. The idea behind these studies is that if the adoptive children more closely resemble their biological parents with respect to a ...
Studying the Living Human Brain
... Animal studies and clinical observations are useful, but often, such as when we need to diagnose or treat illness, we want to know what is happening inside the brain of a living human. For this we have: ...
... Animal studies and clinical observations are useful, but often, such as when we need to diagnose or treat illness, we want to know what is happening inside the brain of a living human. For this we have: ...
Symptoms: visual disturbances, ______, loss of
... ii. Axosomatic- between the axon of one neuron and the _______ of another iii. Less common 1. Axoaxonic (axon to axon) 2. Dendrodendritic (dendrite to dendrite) 3. Dendrosomatic (dendrite to soma) e. Electrical ___________ i. Less common than chemical synapses ii. Neurons are electrically coupled (j ...
... ii. Axosomatic- between the axon of one neuron and the _______ of another iii. Less common 1. Axoaxonic (axon to axon) 2. Dendrodendritic (dendrite to dendrite) 3. Dendrosomatic (dendrite to soma) e. Electrical ___________ i. Less common than chemical synapses ii. Neurons are electrically coupled (j ...
UsabilityPs3
... Yakking drivers are four times more likely to crash their cars. Using a hands-free headset instead of handheld phone made no difference at all. The brain can be intensely aware of what is coming through either the eyes or the ears but not both at the same time. (Certain brain regions were activate ...
... Yakking drivers are four times more likely to crash their cars. Using a hands-free headset instead of handheld phone made no difference at all. The brain can be intensely aware of what is coming through either the eyes or the ears but not both at the same time. (Certain brain regions were activate ...
UsabilityPs3
... Yakking drivers are four times more likely to crash their cars. Using a hands-free headset instead of handheld phone made no difference at all. The brain can be intensely aware of what is coming through either the eyes or the ears but not both at the same time. (Certain brain regions were activate ...
... Yakking drivers are four times more likely to crash their cars. Using a hands-free headset instead of handheld phone made no difference at all. The brain can be intensely aware of what is coming through either the eyes or the ears but not both at the same time. (Certain brain regions were activate ...
Nerve tissue File
... The supporting cells (neuroglia or glial cells): Provide a supportive scaffolding for neurons Segregate and insulate neurons Guide young neurons to the proper connections Promote health and growth ...
... The supporting cells (neuroglia or glial cells): Provide a supportive scaffolding for neurons Segregate and insulate neurons Guide young neurons to the proper connections Promote health and growth ...
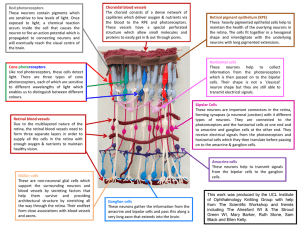
Click here to view a labelled image of the Knitted Retina
... to amacrine and ganglion cells at the other end. They receive electrical signals from the photoreceptors and horizontal cells which they then translate before passing on to the amacrine & ganglion cells. ...
... to amacrine and ganglion cells at the other end. They receive electrical signals from the photoreceptors and horizontal cells which they then translate before passing on to the amacrine & ganglion cells. ...
CNS=Central Nervous System
... 9) What is the difference between white matter and grey matter? Grey matter is a collection of neuronal cell bodies, including dendrites. It is the region of the cerebrum where synapses are made. White matter refers to the collection of axons of those neurons. It is where nerve fibers are located. ...
... 9) What is the difference between white matter and grey matter? Grey matter is a collection of neuronal cell bodies, including dendrites. It is the region of the cerebrum where synapses are made. White matter refers to the collection of axons of those neurons. It is where nerve fibers are located. ...
Unit 6 Powerpoint
... Specialized structures of the nervous system which provide information about the environment in which we live to help maintain homeostasis ...
... Specialized structures of the nervous system which provide information about the environment in which we live to help maintain homeostasis ...
Unit 7 PowerPoint (PDF file)
... Specialized structures of the nervous system which provide information about the environment in which we live to help maintain homeostasis ...
... Specialized structures of the nervous system which provide information about the environment in which we live to help maintain homeostasis ...
PAC Newsletter - March 2015
... The “wiring” of the brain has been compared to the wiring of a telephone .Billions and billions of neurons are reaching out to billions and billions of other neurons to make connections. These synaptic connections are enhanced by repeated use through our experiences in our environment creating pathw ...
... The “wiring” of the brain has been compared to the wiring of a telephone .Billions and billions of neurons are reaching out to billions and billions of other neurons to make connections. These synaptic connections are enhanced by repeated use through our experiences in our environment creating pathw ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.