Chapter 10 - Nervous System I
... Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect components of the nervous system. B. Organs of the nervous system can be divided into the central nervous system (CNS), made up of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), made up of peripheral nerves that conne ...
... Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect components of the nervous system. B. Organs of the nervous system can be divided into the central nervous system (CNS), made up of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), made up of peripheral nerves that conne ...
Slide 1 - Teachers TryScience
... nerve glue cells Astrocytes: • type of glial cell • 50% of nerve tissue • protect neurons from harmful substances in blood ...
... nerve glue cells Astrocytes: • type of glial cell • 50% of nerve tissue • protect neurons from harmful substances in blood ...
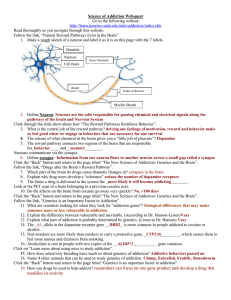
Science of Addiction WebquestKEY
... Click through the slide show about how “The Reward Pathways Reinforce Behavior”. 3. What is the central job of the reward pathway? driving our feelings of motivation, reward and behavior make us feel good when we engage in behaviors that are necessary for our survival 4. The release of what chemical ...
... Click through the slide show about how “The Reward Pathways Reinforce Behavior”. 3. What is the central job of the reward pathway? driving our feelings of motivation, reward and behavior make us feel good when we engage in behaviors that are necessary for our survival 4. The release of what chemical ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... following in your description: hyperpolarization, depolarization, threshold, and refractory period. 7. Describe how the nodes of Ranvier speed up transmission of a nerve signal. 8. In the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin sheaths gradually harden and deteriorate. Discuss how this affects nervous sy ...
... following in your description: hyperpolarization, depolarization, threshold, and refractory period. 7. Describe how the nodes of Ranvier speed up transmission of a nerve signal. 8. In the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin sheaths gradually harden and deteriorate. Discuss how this affects nervous sy ...
File
... 3. The capillaries in the brain and other NS structures are different and do not allow blood to flow easily to nerve tissues…..in other parts of the body the capillaries allow blood to flow easily to cells. ...
... 3. The capillaries in the brain and other NS structures are different and do not allow blood to flow easily to nerve tissues…..in other parts of the body the capillaries allow blood to flow easily to cells. ...
I. Organization and Functions of the Nervous System
... Concept: Neurons come in many forms, but all contain dendrites for reception and an axon for the conduction of nerve impulses. The various types of neurons may be classified on the basis of structure or function. Different types of neuroglia support the neurons, both structurally and functionally. ...
... Concept: Neurons come in many forms, but all contain dendrites for reception and an axon for the conduction of nerve impulses. The various types of neurons may be classified on the basis of structure or function. Different types of neuroglia support the neurons, both structurally and functionally. ...
Biological Bases of Behavior: Neural Processing and the Endocrine
... • Neuron a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. • Building blocks • Sensory Neuron neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord for processing. • Motor Neuron neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spi ...
... • Neuron a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. • Building blocks • Sensory Neuron neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord for processing. • Motor Neuron neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spi ...
Neural Development
... • Visual information changed in these patients– Objects flashed for the right eye were correctly identified (Left hemisphere is language) – Objects flashed for the left eye were not identified. – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZMLzP1VCANo ...
... • Visual information changed in these patients– Objects flashed for the right eye were correctly identified (Left hemisphere is language) – Objects flashed for the left eye were not identified. – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZMLzP1VCANo ...
Division of Brain Sciences Department of Medicine PhD studentship
... Payment of Home/EU Fees and a stipend of £17,500 per annum for 3 years The pathological hallmark Parkinson’s disease is the gradual loss of the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the midbrain. The root causes for degeneration of this inherently vulnerable neuronal populati ...
... Payment of Home/EU Fees and a stipend of £17,500 per annum for 3 years The pathological hallmark Parkinson’s disease is the gradual loss of the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the midbrain. The root causes for degeneration of this inherently vulnerable neuronal populati ...
Chapter 7 The Nervous System
... 6. Some neurons sprout new axons and establish new synapses a. New synapses = net increase in connections b. Learning requires development of new synapses ...
... 6. Some neurons sprout new axons and establish new synapses a. New synapses = net increase in connections b. Learning requires development of new synapses ...
Autonomic NS
... Imagine you are in an acutely stressful situation such as when you encounter a bear during a hike in the woods. What branch of the efferent peripheral nervous system contains the neurons that will increase activity to control visceral organ system responses to this situation? (Circle your answer) ...
... Imagine you are in an acutely stressful situation such as when you encounter a bear during a hike in the woods. What branch of the efferent peripheral nervous system contains the neurons that will increase activity to control visceral organ system responses to this situation? (Circle your answer) ...
Chater 2 - Study Guide
... EEG is to CT scan as: amplified recording of brain waves is to x-ray photography. x-ray photography is to amplified recording of brain waves. radioactive emission is to amplified recording of brain waves. amplified recording of brain waves is to radioactive emission. ...
... EEG is to CT scan as: amplified recording of brain waves is to x-ray photography. x-ray photography is to amplified recording of brain waves. radioactive emission is to amplified recording of brain waves. amplified recording of brain waves is to radioactive emission. ...
Neuron Notes Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the
... Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the nervous system 3types: 1. sensory neurons- carry impulses from sense organs to brain; 2. motor neurons- carry impulses from brain to muscles/glands. 3. Interneuron: carry impulses between sensory and motor neurons (connects them) Parts of the Neuron: ...
... Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the nervous system 3types: 1. sensory neurons- carry impulses from sense organs to brain; 2. motor neurons- carry impulses from brain to muscles/glands. 3. Interneuron: carry impulses between sensory and motor neurons (connects them) Parts of the Neuron: ...
Reward” and “Punishment” Function of the Limbic System
... Aside from direct control of brain activity by transmission of nerve signals from the lower brain areas to the cortical regions of the brain, still another physiologic mechanism is very often used to control brain activity by secreting excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitter agents into the substa ...
... Aside from direct control of brain activity by transmission of nerve signals from the lower brain areas to the cortical regions of the brain, still another physiologic mechanism is very often used to control brain activity by secreting excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitter agents into the substa ...
File
... - Simplest spinal reflex - Monosynaptic reflex - e.g knee jerk 1. Receptor muscle sense the action (e.g hammer on knee) 2. Message sent along afferent nerve axon to spinal cord 3. Afferent synapses with efferent of same muscles 4. Impulse in transmitted along efferent pathway 5. Motor unit contracts ...
... - Simplest spinal reflex - Monosynaptic reflex - e.g knee jerk 1. Receptor muscle sense the action (e.g hammer on knee) 2. Message sent along afferent nerve axon to spinal cord 3. Afferent synapses with efferent of same muscles 4. Impulse in transmitted along efferent pathway 5. Motor unit contracts ...
The_road_to_brain-scale_simulation
... This is the story of the endeavor of the Brain and Neural Systems Team (BNT) to make the computational power of K available to the field of computational neuroscience. An extended version of this report can be found at [1]. The human brain comprises about 1011 neurons, each connected to 10000 others ...
... This is the story of the endeavor of the Brain and Neural Systems Team (BNT) to make the computational power of K available to the field of computational neuroscience. An extended version of this report can be found at [1]. The human brain comprises about 1011 neurons, each connected to 10000 others ...
Document
... This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, and even specific concepts. ...
... This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, and even specific concepts. ...
2
... This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, and even specific concepts. ...
... This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, and even specific concepts. ...
Nervous System Fundamentals
... a. The severed end of an ________ and its myelin sheath degenerate b. ______________ remove the debris c. A ______________ _______ is formed by the Schwann cell neurilemma d. The tube guides the growing ______ back to its original destination e. Skeletal muscle cells _____________ when their nerve f ...
... a. The severed end of an ________ and its myelin sheath degenerate b. ______________ remove the debris c. A ______________ _______ is formed by the Schwann cell neurilemma d. The tube guides the growing ______ back to its original destination e. Skeletal muscle cells _____________ when their nerve f ...
Nervous Tissue NOTES
... this happens at one location on the axon, it affects the next section, and the next section… This sends the electrical impulse (action potential) along the entire axon As the signal travels along the axon, Na+ rushes into the cell as K+ rushes out of the cell to try to repolarize the membran ...
... this happens at one location on the axon, it affects the next section, and the next section… This sends the electrical impulse (action potential) along the entire axon As the signal travels along the axon, Na+ rushes into the cell as K+ rushes out of the cell to try to repolarize the membran ...
Chapter 3 – early studies of the central nervous system
... brain of animals were crude and often lethal. Electrical stimulation was first accomplished by Gustav Fritsch (1839-1927) & Edward Hitzig (1838-1907) to produce motor movements. Stimulation ...
... brain of animals were crude and often lethal. Electrical stimulation was first accomplished by Gustav Fritsch (1839-1927) & Edward Hitzig (1838-1907) to produce motor movements. Stimulation ...
1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study
... A) PET scan. B) CT scan. C) EEG. D) MRI. 12. The technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer images of structures within the brain is called: A) the EEG. B) a CT scan. C) a PET scan. D) MRI. 13. Following a head injury, a person has ongoing difficulties staying awake. Mos ...
... A) PET scan. B) CT scan. C) EEG. D) MRI. 12. The technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer images of structures within the brain is called: A) the EEG. B) a CT scan. C) a PET scan. D) MRI. 13. Following a head injury, a person has ongoing difficulties staying awake. Mos ...
PDF
... targets plays a role in restricting its activity to ASEL or ASER, and thus in controlling neuronal subtype specification. The cis-regulatory mechanisms involved are surprisingly diverse, and future work should shed light on the upstream events that lead to their differential ...
... targets plays a role in restricting its activity to ASEL or ASER, and thus in controlling neuronal subtype specification. The cis-regulatory mechanisms involved are surprisingly diverse, and future work should shed light on the upstream events that lead to their differential ...
PDF
... targets plays a role in restricting its activity to ASEL or ASER, and thus in controlling neuronal subtype specification. The cis-regulatory mechanisms involved are surprisingly diverse, and future work should shed light on the upstream events that lead to their differential ...
... targets plays a role in restricting its activity to ASEL or ASER, and thus in controlling neuronal subtype specification. The cis-regulatory mechanisms involved are surprisingly diverse, and future work should shed light on the upstream events that lead to their differential ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.