Introduction to the Brain
... The brain is made of billions of brain cells. Some cells, known as neurons are responsible for carrying messages to and from the brain. Other cells, known as ...
... The brain is made of billions of brain cells. Some cells, known as neurons are responsible for carrying messages to and from the brain. Other cells, known as ...
Introduction to the Brain
... The brain is made of billions of brain cells. Some cells, known as neurons are responsible for carrying messages to and from the brain. Other cells, known as glia provide the support structure for the neurons. Neurons require oxygen to function, and begin to die within 3 to 5 minutes without it. The ...
... The brain is made of billions of brain cells. Some cells, known as neurons are responsible for carrying messages to and from the brain. Other cells, known as glia provide the support structure for the neurons. Neurons require oxygen to function, and begin to die within 3 to 5 minutes without it. The ...
Activity of Spiking Neurons Stimulated by External Signals of
... Spiking neuron systems gained increasing interest in recent years because they represent spatio-temporal relations within simulated systems, unlike the spatial simple neuron models found in artificial neural systems. They are also closer to biophysical models of neurons, synapses, and related elemen ...
... Spiking neuron systems gained increasing interest in recent years because they represent spatio-temporal relations within simulated systems, unlike the spatial simple neuron models found in artificial neural systems. They are also closer to biophysical models of neurons, synapses, and related elemen ...
Structure and functions of the Human Nervous system
... Act like a cable connecting the brain with other parts of the body Extends from the brain down the length of the back Protected by bones forming the spinal column Spinal cord made up of columns of white matter = bundles fo axons covered with myelin Where the axon leaves the spinal cord the ...
... Act like a cable connecting the brain with other parts of the body Extends from the brain down the length of the back Protected by bones forming the spinal column Spinal cord made up of columns of white matter = bundles fo axons covered with myelin Where the axon leaves the spinal cord the ...
Nervous System
... (morphine, heroin, cocaine, amphetamines, LSD, mescaline, …) have their effects by functioning as, blocking, or altering chemical synaptic activity. ...
... (morphine, heroin, cocaine, amphetamines, LSD, mescaline, …) have their effects by functioning as, blocking, or altering chemical synaptic activity. ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology - University of British Columbia
... These axons become embedded in the Schwann cell, which provides structural support and nutrients. ...
... These axons become embedded in the Schwann cell, which provides structural support and nutrients. ...
What happens in a neuron
... broad spectrum of signs and symptoms. Disease onset usually occurs in young adults, and it is more common in women. MS affects the ability of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord to communicate with each other effectively. Nerve cells communicate by sending electrical signals called action poten ...
... broad spectrum of signs and symptoms. Disease onset usually occurs in young adults, and it is more common in women. MS affects the ability of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord to communicate with each other effectively. Nerve cells communicate by sending electrical signals called action poten ...
Keshara Senanayake Towle Notes Chapter 50 "Nervous System
... >action potential starts at the point where the cell body of the neuron joins the axon >voltage gated channels exist along the entire length of the axons >as the 1st segment of the axon becomes (+) charged the rise in the voltage opens channel in the adjacent segment of the axon membrane >as before ...
... >action potential starts at the point where the cell body of the neuron joins the axon >voltage gated channels exist along the entire length of the axons >as the 1st segment of the axon becomes (+) charged the rise in the voltage opens channel in the adjacent segment of the axon membrane >as before ...
The Nervous System
... branching, which increases their surface area to receive signals from other neurons. The number of dendrites on a neuron varies. They are called afferent processes because they transmit impulses to the neuron cell body. There is only one axon that projects from each cell body. It is usually elongate ...
... branching, which increases their surface area to receive signals from other neurons. The number of dendrites on a neuron varies. They are called afferent processes because they transmit impulses to the neuron cell body. There is only one axon that projects from each cell body. It is usually elongate ...
The Nervous System - Hartland High School
... b. Integration – processing and interpreting sensory input and makes decisions about what needs to be done at each moment. c. Motor Output – effecting a response by activating muscles or glands. 3. What other body system helps the nervous system along in its quest to maintain homeostasis? Works clos ...
... b. Integration – processing and interpreting sensory input and makes decisions about what needs to be done at each moment. c. Motor Output – effecting a response by activating muscles or glands. 3. What other body system helps the nervous system along in its quest to maintain homeostasis? Works clos ...
human ana tomy 13
... entire mass is the skin, the largest organ of the body. The science of the structure of this complicated “machine” is called anatomy. 2. One of the major systems is the musculoskeletal system. The body is supported and given shape by this structure, it consists of more than 200 bones and the muscles ...
... entire mass is the skin, the largest organ of the body. The science of the structure of this complicated “machine” is called anatomy. 2. One of the major systems is the musculoskeletal system. The body is supported and given shape by this structure, it consists of more than 200 bones and the muscles ...
I. Functions and Divisions of the Nervous System A. The nervous
... 2. The neuron cell body, also called the perikaryon or soma, is the major biosynthetic center containing the usual organelles except for centrioles. 3. Neurons have armlike processes that extend from the cell body. a. Dendrites are cell processes that are the receptive regions of the cell and provid ...
... 2. The neuron cell body, also called the perikaryon or soma, is the major biosynthetic center containing the usual organelles except for centrioles. 3. Neurons have armlike processes that extend from the cell body. a. Dendrites are cell processes that are the receptive regions of the cell and provid ...
histology lab 3
... Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Facts • main component of the nervous system. • Contains 2 major cells types: 1. Neurons – are highly specialized nerve cells that generate and conduct nerve impulses. 2. Neuroglia – are supporting cells that are nonconducting that insulate and protect the neurons. ...
... Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Facts • main component of the nervous system. • Contains 2 major cells types: 1. Neurons – are highly specialized nerve cells that generate and conduct nerve impulses. 2. Neuroglia – are supporting cells that are nonconducting that insulate and protect the neurons. ...
The Nervous System - Hastings High School
... 1. The neuron is normally at rest. At this point in time, the difference in charge between the outside and the inside of the cell is -70 mV. This difference exists because there are more positive ions outside the cell and fewer positively charged ions inside the cell. 2. Part of the neuron received ...
... 1. The neuron is normally at rest. At this point in time, the difference in charge between the outside and the inside of the cell is -70 mV. This difference exists because there are more positive ions outside the cell and fewer positively charged ions inside the cell. 2. Part of the neuron received ...
Nervous System
... • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract and remove the paw ...
... • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract and remove the paw ...
Nervous System Pathology
... Anterior root = axons of LMNs Posterior root = spinal ganglia and cytoplasmic extensions ...
... Anterior root = axons of LMNs Posterior root = spinal ganglia and cytoplasmic extensions ...
Chapter 3: The nerve cell Multiple Choice Questions (1
... 7. Making predictions about which interpretation of an ambiguous stimulus is likely to be correct involves a kind of processing. a. lateral b. input-driven c. top-down d. bottom-up 8. Which of the following is the best metaphor for neuronal choice points? a. sliding on a slide b. swinging on a swin ...
... 7. Making predictions about which interpretation of an ambiguous stimulus is likely to be correct involves a kind of processing. a. lateral b. input-driven c. top-down d. bottom-up 8. Which of the following is the best metaphor for neuronal choice points? a. sliding on a slide b. swinging on a swin ...
The Nervous System
... •This gland is a big player in puberty, ultimately producing sperm in males and eggs in females • This little gland also plays a role with lots of other hormones, like ones that control the amount of sugars and water in your body. And it ...
... •This gland is a big player in puberty, ultimately producing sperm in males and eggs in females • This little gland also plays a role with lots of other hormones, like ones that control the amount of sugars and water in your body. And it ...
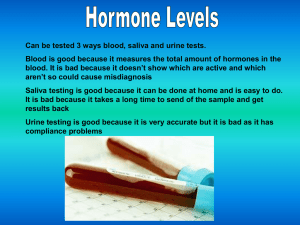
Hormone Levels and EEG (Ashanti)
... EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to sub-millisecond. It is also good because other methods for exploring functions in the brain rely on blood flow or ...
... EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to sub-millisecond. It is also good because other methods for exploring functions in the brain rely on blood flow or ...
MF011_fhs_lnt_008a_Jan11
... The brainstem coordinates and conducts information between brain centers The brainstem has three parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata The midbrain contains centers for receipt and integration of sensory information The pons regulates breathing centers in the medulla The medulla o ...
... The brainstem coordinates and conducts information between brain centers The brainstem has three parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata The midbrain contains centers for receipt and integration of sensory information The pons regulates breathing centers in the medulla The medulla o ...
animal nervous system - mf011
... The brainstem coordinates and conducts information between brain centers The brainstem has three parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata The midbrain contains centers for receipt and integration of sensory information The pons regulates breathing centers in the medulla The medulla o ...
... The brainstem coordinates and conducts information between brain centers The brainstem has three parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata The midbrain contains centers for receipt and integration of sensory information The pons regulates breathing centers in the medulla The medulla o ...
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... 10. Explain how action potentials are generated and propagated along neurons. 11. Define absolute and relative refractory periods. 12. Define salutatory conduction and contrast it to conduction along unmyelinated fibers. 13. Define synapse. Distinguish between electrical and chemical synapses struct ...
... 10. Explain how action potentials are generated and propagated along neurons. 11. Define absolute and relative refractory periods. 12. Define salutatory conduction and contrast it to conduction along unmyelinated fibers. 13. Define synapse. Distinguish between electrical and chemical synapses struct ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.