EES Review for Final Exam
... Ch. 18 – Water in the Atmosphere Salinity – about 3.5% (35 parts per thousand) Processes that affect salinity – icebergs, runoff, sea ice, evaporation Thermocline – ocean temperature variation Pycnocline – ocean density variation; salinity and pressure affect ocean density Ocean layering: surface zo ...
... Ch. 18 – Water in the Atmosphere Salinity – about 3.5% (35 parts per thousand) Processes that affect salinity – icebergs, runoff, sea ice, evaporation Thermocline – ocean temperature variation Pycnocline – ocean density variation; salinity and pressure affect ocean density Ocean layering: surface zo ...
ultrasonic sound waves with frequencies above 20,000 Hz
... compound, such as ethene or ethyne, that contains at least one double or triple bond between carbon atoms. any solution that can dissolve more solute at a given temperature. mountains formed when blocks of Earth’s crust are pushed up by forces inside Earth. vertical circulation in the ocean that bri ...
... compound, such as ethene or ethyne, that contains at least one double or triple bond between carbon atoms. any solution that can dissolve more solute at a given temperature. mountains formed when blocks of Earth’s crust are pushed up by forces inside Earth. vertical circulation in the ocean that bri ...
Ocean Web Quest Task Sheet PLEASE REMEMBER TO WRITE IN
... FOR FILL-IN THE BLANK QUESTIONS. http://www.mos.org/oceans/motion/wind.html 1. The size of a wave depends on It depends on how far, how fast, or how long the wind blows. 2. Waves travel through water, they do not take the water with them. http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/ocean/Waves.shtml 3 ...
... FOR FILL-IN THE BLANK QUESTIONS. http://www.mos.org/oceans/motion/wind.html 1. The size of a wave depends on It depends on how far, how fast, or how long the wind blows. 2. Waves travel through water, they do not take the water with them. http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/ocean/Waves.shtml 3 ...
practice exam. - UTEP Geology Homepage
... d. a major volcanic eruption of gas and dust, which contaminated the atmosphere and ...
... d. a major volcanic eruption of gas and dust, which contaminated the atmosphere and ...
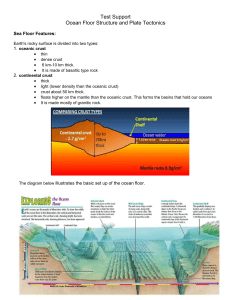
Unit 5: Ocean Floor Structure and Plate Tectonics
... Both the continental shelf and slope are considered structurally part of the continents, even though they are below the sea surface. Continental Rise – The gentler slope at the bottom of the slope It is made of sand and sediments that comes from the land and the continental self. Kind of lik ...
... Both the continental shelf and slope are considered structurally part of the continents, even though they are below the sea surface. Continental Rise – The gentler slope at the bottom of the slope It is made of sand and sediments that comes from the land and the continental self. Kind of lik ...
Global warming & its effects
... Draw a profile diagram include: continental shelf continental slope abyssal plain mid-ocean ridge ...
... Draw a profile diagram include: continental shelf continental slope abyssal plain mid-ocean ridge ...
First day of Spring Semester
... • Oceans absorb long, invisible infrared wavelengths. • The amount of infrared determines ocean temperature. • Ocean water freezes at -2 Celsius. ...
... • Oceans absorb long, invisible infrared wavelengths. • The amount of infrared determines ocean temperature. • Ocean water freezes at -2 Celsius. ...
Study Notes for Chapter 19: The Ocean Basins Directions: Use the
... Directions: Use the following notes to complete your study notes and then to prepare for the test. Please do not take this copy from the classroom. Thank you. Chapter 19 Section 1: The Water Planet 1. Earth’s oceans cover about ¾ th’s of Earth’s surface. 2. Of all the water on Earth, 97% is found in ...
... Directions: Use the following notes to complete your study notes and then to prepare for the test. Please do not take this copy from the classroom. Thank you. Chapter 19 Section 1: The Water Planet 1. Earth’s oceans cover about ¾ th’s of Earth’s surface. 2. Of all the water on Earth, 97% is found in ...
Chapter 7-2 Ocean Currents and Climate
... – Currents along the eastern coasts originate at the equator, where the amount of energy absorbed from the Sun is the greatest; currents along western coasts originate at high latitudes where water receives less solar energy. ...
... – Currents along the eastern coasts originate at the equator, where the amount of energy absorbed from the Sun is the greatest; currents along western coasts originate at high latitudes where water receives less solar energy. ...
Chapter 9/10 Oceans
... Much of this lost to solar wind. Accounts for perhaps 10% of the Earth’s atmosphere and ocean material. ...
... Much of this lost to solar wind. Accounts for perhaps 10% of the Earth’s atmosphere and ocean material. ...
1 Introduction to Marine Ecology jh part 2 2009
... •Heat transfer away form equator by atmosphere ...
... •Heat transfer away form equator by atmosphere ...
P7 notes as of 12/2
... Greenland doing what he loved to do-researching the weather Exactly 50 when he died…born in 1880 AW’s evidence that SUGGESTS plate mvmt (HAD) 1) land features: continents fit together like puzzle pieces (N/ SA & Africa) ...
... Greenland doing what he loved to do-researching the weather Exactly 50 when he died…born in 1880 AW’s evidence that SUGGESTS plate mvmt (HAD) 1) land features: continents fit together like puzzle pieces (N/ SA & Africa) ...
Landforms and Oceans Class Notes
... 6. Weathering causes the _________________ of the Earth to dissolve, decompose, and break into smaller pieces. 7. _____________________ is an important cause of weathering. Plants cause weathering when ___________ break apart a rock. Anything that causes rock to wear down or break apart is a cause o ...
... 6. Weathering causes the _________________ of the Earth to dissolve, decompose, and break into smaller pieces. 7. _____________________ is an important cause of weathering. Plants cause weathering when ___________ break apart a rock. Anything that causes rock to wear down or break apart is a cause o ...
StudyGuide-for-Oceans-2015-key
... 30. A large stream of moving water that flows through an ocean is known as a _Current_.In the 31. Surface currents are caused by _____Wind____. 32. Northern Hemisphere currents curve to the right because of the Coriolis Effect_ 33. A large powerful warm surface current in the Atlantic Ocean that aff ...
... 30. A large stream of moving water that flows through an ocean is known as a _Current_.In the 31. Surface currents are caused by _____Wind____. 32. Northern Hemisphere currents curve to the right because of the Coriolis Effect_ 33. A large powerful warm surface current in the Atlantic Ocean that aff ...
Hydrology Unit 4 Review What process in the water cycle is MOST
... 3. What would MOST LIKELY occur if the rate of evaporation over the ocean were to decrease for an extended length of time? The amount of precipitation on land would DECREASE 4. What 2 physical changes are essential processes in the water cycle? Evaporation and condensation 5. Define condensation. Wh ...
... 3. What would MOST LIKELY occur if the rate of evaporation over the ocean were to decrease for an extended length of time? The amount of precipitation on land would DECREASE 4. What 2 physical changes are essential processes in the water cycle? Evaporation and condensation 5. Define condensation. Wh ...
Ch. 22 The Water Planet
... take CO2 out of water and replace with oxygen basis of food chain in ocean Diatoms are examples with silica shells; deposited on seafloor when ...
... take CO2 out of water and replace with oxygen basis of food chain in ocean Diatoms are examples with silica shells; deposited on seafloor when ...
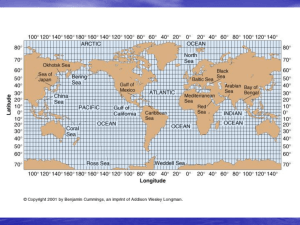
OCEANIC GEOGRAPHY and the EARTH
... b. Theory #2: comets with ice constantly bombard Earth and fill up basins with water; this theory is probably wrong because most comets have a different isotope of hydrogen than most of earth’s water 3. ocean surface area (largest to smallest): Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic a. Antarctic Ocean [S ...
... b. Theory #2: comets with ice constantly bombard Earth and fill up basins with water; this theory is probably wrong because most comets have a different isotope of hydrogen than most of earth’s water 3. ocean surface area (largest to smallest): Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic a. Antarctic Ocean [S ...
Water Masses and Density Currents
... together they govern the density ( mass per unit volume) of seawater. Density differences drive the vertical and horizontal circulation of about 90% of the ocean. Surface seawater that is made denser by cooling, increased salinity, or mixing, sinks to depths where its density is the same as the surr ...
... together they govern the density ( mass per unit volume) of seawater. Density differences drive the vertical and horizontal circulation of about 90% of the ocean. Surface seawater that is made denser by cooling, increased salinity, or mixing, sinks to depths where its density is the same as the surr ...
2016-2017 Ocean resource exploration climate
... cold water to the ocean surface. Surface winds blow parallel to the land because of the Coriolis effect. Cold, deep water continually replaces the surface water that is pushed away from the coast. This cold water causes cool summers and fog in San Francisco. ...
... cold water to the ocean surface. Surface winds blow parallel to the land because of the Coriolis effect. Cold, deep water continually replaces the surface water that is pushed away from the coast. This cold water causes cool summers and fog in San Francisco. ...
Gr.8-Ch.2-Review-Sheet-2014
... 19. _____ is a force of erosion in the development of continental drainage systems. 20. Water on earth came from_____ and _____. 21. Water collected in the lowest parts of the Earth’s surface known as the _____. 22. A tumble of water when a wave collapses onshore is called _____. 23. Giant waves tha ...
... 19. _____ is a force of erosion in the development of continental drainage systems. 20. Water on earth came from_____ and _____. 21. Water collected in the lowest parts of the Earth’s surface known as the _____. 22. A tumble of water when a wave collapses onshore is called _____. 23. Giant waves tha ...
Salinity of Ocean water Salty ocean waters constitute 97% of all the
... the earth is fresh. Most of the fresh water exists as ice sheet with only about 0.04% found in lakes, rivers and reservoirs. Interestingly, the volume of waters on the earth (around 1.3 billion cubic kilometers) remains constant and so also the salinity and composition of oceanic waters over time. W ...
... the earth is fresh. Most of the fresh water exists as ice sheet with only about 0.04% found in lakes, rivers and reservoirs. Interestingly, the volume of waters on the earth (around 1.3 billion cubic kilometers) remains constant and so also the salinity and composition of oceanic waters over time. W ...
Oceans Sonar Bathymetry Powerpoint
... a. abyssal plain - flat, featureless region similar to a desert; common in Atlantic and Indian Oceans, rare in the Pacific b. abyssal hill - occur where sediment is not thick enough to cover the underlying rock completely. Usually extinct volcanoes or small formations of rock once extruded in molten ...
... a. abyssal plain - flat, featureless region similar to a desert; common in Atlantic and Indian Oceans, rare in the Pacific b. abyssal hill - occur where sediment is not thick enough to cover the underlying rock completely. Usually extinct volcanoes or small formations of rock once extruded in molten ...
Chapter 19 Study Notes: The Ocean Basins
... transmission is to send out a series of _______ waves. – sonar – sound. ...
... transmission is to send out a series of _______ waves. – sonar – sound. ...
Chapter 14 – The Movement of Ocean Water
... 3. Continental Deflection – When currents flow into ...
... 3. Continental Deflection – When currents flow into ...
Ocean

An ocean (from Ancient Greek Ὠκεανός, transc. Okeanós, the sea of classical antiquity) is a body of saline water that composes much of a planet's hydrosphere. On Earth, an ocean is one of the major conventional divisions of the World Ocean, which covers almost 71% of its surface. These are, in descending order by area, the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans. The word sea is often used interchangeably with ""ocean"" in American English but, strictly speaking, a sea is a body of saline water (generally a division of the world ocean) partly or fully enclosed by land.Saline water covers approximately 72% of the planet's surface (~3.6×108 km2) and is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas, with the ocean covering approximately 71% of Earth's surface. The ocean contains 97% of Earth's water, and oceanographers have stated that only 5% of the World Ocean has been explored. The total volume is approximately 1.35 billion cubic kilometers (320 million cu mi) with an average depth of nearly 3,700 meters (12,100 ft).As it is the principal component of Earth's hydrosphere, the world ocean is integral to all known life, forms part of the carbon cycle, and influences climate and weather patterns. It is the habitat of 230,000 known species, although much of the oceans depths remain unexplored, and over two million marine species are estimated to exist. The origin of Earth's oceans remains unknown; oceans are thought to have formed in the Hadean period and may have been the impetus for the emergence of life.Extraterrestrial oceans may be composed of water or other elements and compounds. The only confirmed large stable bodies of extraterrestrial surface liquids are the lakes of Titan, although there is evidence for the existence of oceans elsewhere in the Solar System. Early in their geologic histories, Mars and Venus are theorized to have had large water oceans. The Mars ocean hypothesis suggests that nearly a third of the surface of Mars was once covered by water, and a runaway greenhouse effect may have boiled away the global ocean of Venus. Compounds such as salts and ammonia dissolved in water lower its freezing point, so that water might exist in large quantities in extraterrestrial environments as brine or convecting ice. Unconfirmed oceans are speculated beneath the surface of many dwarf planets and natural satellites; notably, the ocean of Europa is estimated to have over twice the water volume of Earth. The Solar System's giant planets are also thought to have liquid atmospheric layers of yet to be confirmed compositions. Oceans may also exist on exoplanets and exomoons, including surface oceans of liquid water within a circumstellar habitable zone. Ocean planets are a hypothetical type of planet with a surface completely covered with liquid.