proposal2000a.doc
... trimming period. Thus, these overall decreases after deprivation were suggested as a downregulating mechanism that compensates for the reduced sensory input (Fuchs and Salazar, ’98). The contributions of GABAB receptors to the barrel circuitry have been recently studied (Micheva and Beaulieu, ’97). ...
... trimming period. Thus, these overall decreases after deprivation were suggested as a downregulating mechanism that compensates for the reduced sensory input (Fuchs and Salazar, ’98). The contributions of GABAB receptors to the barrel circuitry have been recently studied (Micheva and Beaulieu, ’97). ...
e.4.1 state that some presynaptic neurons excite post synaptic
... post-synaptic neuron and _____________ APs. GABA is important in regulating nervous processes – a “_____________” or depressive effect (reducing activity). It prevents neurons from __________, and can be used as a drug to help people with anxiety or stress-related disorders. ________ mimics th ...
... post-synaptic neuron and _____________ APs. GABA is important in regulating nervous processes – a “_____________” or depressive effect (reducing activity). It prevents neurons from __________, and can be used as a drug to help people with anxiety or stress-related disorders. ________ mimics th ...
Our brain is made of so many neurons, which communicate each
... Our brain is made of so many neurons, which communicate each other through synapses (synaptic transmission). The efficacy of the synaptic transmission flexibly changes in response to various environmental stimuli (synaptic plasticity), and the synaptic plasticity has often been argued to play an imp ...
... Our brain is made of so many neurons, which communicate each other through synapses (synaptic transmission). The efficacy of the synaptic transmission flexibly changes in response to various environmental stimuli (synaptic plasticity), and the synaptic plasticity has often been argued to play an imp ...
Seizure, neurotransmitter release, and gene expression are closely
... acid and aspartic acid take part in the induction, maintenance, and propagation of seizures and mediate some of the neuropathological effects of neuronal hyperactivity (Sloviter and Dempster, 1985; Peña and Tapia, 2000). Glutamate (GLU) and aspartate (ASP) are epileptogenic and excitotoxic to nerve ...
... acid and aspartic acid take part in the induction, maintenance, and propagation of seizures and mediate some of the neuropathological effects of neuronal hyperactivity (Sloviter and Dempster, 1985; Peña and Tapia, 2000). Glutamate (GLU) and aspartate (ASP) are epileptogenic and excitotoxic to nerve ...
SDL 2- CNS Malformations Neural Tube Defects Failure of a portion
... Neurons and glial cells that form the cerebral cortex migrate to cortex guided by adhesion molecules, cortical development entails the generatio of stem cells and their differentiation to neurons and glia, migration to cortex and organization to functional layers. 1. Neurons fail to migrate from the ...
... Neurons and glial cells that form the cerebral cortex migrate to cortex guided by adhesion molecules, cortical development entails the generatio of stem cells and their differentiation to neurons and glia, migration to cortex and organization to functional layers. 1. Neurons fail to migrate from the ...
conductance versus current-based integrate-and - Neuro
... linearly with increasing drive. However, if this balance does not exist, for example by only increasing the presynaptic excitatory rate, the corresponding increase in conductance leads to a sub-linear depolarization with the drive. (ii) Increase of the voltage variance: It was recently suggested th ...
... linearly with increasing drive. However, if this balance does not exist, for example by only increasing the presynaptic excitatory rate, the corresponding increase in conductance leads to a sub-linear depolarization with the drive. (ii) Increase of the voltage variance: It was recently suggested th ...
the nervous system
... synaptic vesicles: synaptic cleft: post synaptic neuron: post synaptic receptors. ...
... synaptic vesicles: synaptic cleft: post synaptic neuron: post synaptic receptors. ...
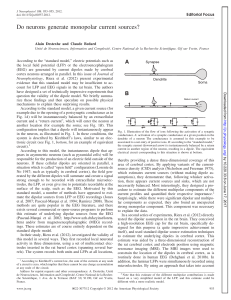
Do neurons generate monopolar current sources?
... According to the “standard model,” electric potentials such as the local field potential (LFP) or the electroencephalogram (EEG) are generated by current dipoles made by cerebral cortex neurons arranged in parallel. In this issue of Journal of Neurophysiology, Riera et al. (2012) present experimenta ...
... According to the “standard model,” electric potentials such as the local field potential (LFP) or the electroencephalogram (EEG) are generated by current dipoles made by cerebral cortex neurons arranged in parallel. In this issue of Journal of Neurophysiology, Riera et al. (2012) present experimenta ...
Multimodal imaging and the neural basis of EEG and fMRI
... creates an electrical potential (about -70 millivolt) between the inside and the outside of the cell. Neurotransmitter leads to the opening of ions channels through which some ions, such as sodium (Na+), chloride (Cl-), potassium (K+) and calcium (Ca2+) will diffuse. ...
... creates an electrical potential (about -70 millivolt) between the inside and the outside of the cell. Neurotransmitter leads to the opening of ions channels through which some ions, such as sodium (Na+), chloride (Cl-), potassium (K+) and calcium (Ca2+) will diffuse. ...
Learning-related changes in coordinated fast oscillations
... the BLA, perirhinal and entorhinal cortices. Given earlier findings suggesting that neuronal oscillations coordinate the activity of cerebral networks, we first tested whether there are correlated fluctuations in the power of BLA and rhinal field activity at any frequency. Field potentials were simu ...
... the BLA, perirhinal and entorhinal cortices. Given earlier findings suggesting that neuronal oscillations coordinate the activity of cerebral networks, we first tested whether there are correlated fluctuations in the power of BLA and rhinal field activity at any frequency. Field potentials were simu ...
210_disorders
... • Paroxysmal depolarizing shift (PDS) Large abrupt depolarization of affected neurons Triggers a train of action potentials Followed by a period of hyperpolarization Excitatory activity overwhelms the GABA-inhibitory system and high frequency action potentials begin to occur ...
... • Paroxysmal depolarizing shift (PDS) Large abrupt depolarization of affected neurons Triggers a train of action potentials Followed by a period of hyperpolarization Excitatory activity overwhelms the GABA-inhibitory system and high frequency action potentials begin to occur ...
Slides for Lecture 14
... • Paroxysmal depolarizing shift (PDS) Large abrupt depolarization of affected neurons Triggers a train of action potentials Followed by a period of hyperpolarization Excitatory activity overwhelms the GABA-inhibitory system and high frequency action potentials begin to occur ...
... • Paroxysmal depolarizing shift (PDS) Large abrupt depolarization of affected neurons Triggers a train of action potentials Followed by a period of hyperpolarization Excitatory activity overwhelms the GABA-inhibitory system and high frequency action potentials begin to occur ...
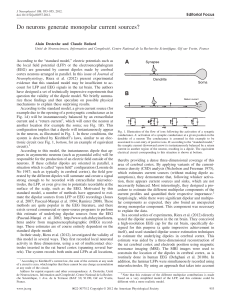
Do neurons generate monopolar current sources?
... According to the “standard model,” electric potentials such as the local field potential (LFP) or the electroencephalogram (EEG) are generated by current dipoles made by cerebral cortex neurons arranged in parallel. In this issue of Journal of Neurophysiology, Riera et al. (2012) present experimenta ...
... According to the “standard model,” electric potentials such as the local field potential (LFP) or the electroencephalogram (EEG) are generated by current dipoles made by cerebral cortex neurons arranged in parallel. In this issue of Journal of Neurophysiology, Riera et al. (2012) present experimenta ...
System Architecture of ERS/ERD
... • Brain computer interface devices (BCI) detect and translate neural activity into command sequences for computers and prostheses. ...
... • Brain computer interface devices (BCI) detect and translate neural activity into command sequences for computers and prostheses. ...
Toward STDP-based population action in large networks of spiking
... coupling contraints. Several implementations of the STDP update mechanism have been proposed in the literature. Our implementation is all-to-all [18] and additive: the weight update depends on every previous synaptic event (the influence of the less recent events fading with time) and doesn’t take i ...
... coupling contraints. Several implementations of the STDP update mechanism have been proposed in the literature. Our implementation is all-to-all [18] and additive: the weight update depends on every previous synaptic event (the influence of the less recent events fading with time) and doesn’t take i ...
The Neuron - Austin Community College
... the cell body. At the trigger zone, it is below threshold and therefore does not initiate an action potential. ...
... the cell body. At the trigger zone, it is below threshold and therefore does not initiate an action potential. ...
sion to superior salivatory neurons in rats
... GABAA, and glycine receptors. Especially, GABAA and glycine receptor-mediated responses show a marked change. That is, the activation of GABAA and glycine receptors causes hyperpolarization in mature neurons, but depolarization in immature neurons [2, 3]. Thus, such an electrophysiological character ...
... GABAA, and glycine receptors. Especially, GABAA and glycine receptor-mediated responses show a marked change. That is, the activation of GABAA and glycine receptors causes hyperpolarization in mature neurons, but depolarization in immature neurons [2, 3]. Thus, such an electrophysiological character ...
Ch 48 Notes - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... If a depolarization shifts the membrane potential sufficiently, it results in a massive change in membrane voltage called an action potential ...
... If a depolarization shifts the membrane potential sufficiently, it results in a massive change in membrane voltage called an action potential ...
Carl L.Faingold, Manish Raisinghani, Prosper N`Gouemo
... responses of the inferior colliculus (IC) to acoustic stimulation, and defects in specific forms of inhibition are key causative factors in audiogenic seizure initiation. Line (A) illustrates binaural inhibition common in ICc neurons. In the poststimulus time histogram (PSTH) example in line (A) (“N ...
... responses of the inferior colliculus (IC) to acoustic stimulation, and defects in specific forms of inhibition are key causative factors in audiogenic seizure initiation. Line (A) illustrates binaural inhibition common in ICc neurons. In the poststimulus time histogram (PSTH) example in line (A) (“N ...
Orexin-A excites rat lateral vestibular nucleus neurons and improves
... lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle weakness without impairment of consciousness. However, most studies so far on th ...
... lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle weakness without impairment of consciousness. However, most studies so far on th ...
CNS neurotransmitters
... A seminal discovery during the 1960s and 1970s was the presence of endogenous substances in mammalian brain that appeared to possess the pharmacological qualities of morphine and other opioid analgesics. It had been known for quite awhile that most “drug receptors” were in fact receptors for endog ...
... A seminal discovery during the 1960s and 1970s was the presence of endogenous substances in mammalian brain that appeared to possess the pharmacological qualities of morphine and other opioid analgesics. It had been known for quite awhile that most “drug receptors” were in fact receptors for endog ...
E4 - Neurotransmitters and Synapses - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... potential at its axon hillock, it will produce an action potential pre-synaptic neurons can vary in the frequency, but not intensity of their input, since action potentials are "all-or-none“ rule ...
... potential at its axon hillock, it will produce an action potential pre-synaptic neurons can vary in the frequency, but not intensity of their input, since action potentials are "all-or-none“ rule ...
Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and
... In addition to the field potentials of the cortical surface and the membrane potentials of the pyramidal tract cells, field potentials were also recorded in the fifth lamina. Under these conditions, it can be shown that every PDS is associated with a negative monophasic field potential in the depth ...
... In addition to the field potentials of the cortical surface and the membrane potentials of the pyramidal tract cells, field potentials were also recorded in the fifth lamina. Under these conditions, it can be shown that every PDS is associated with a negative monophasic field potential in the depth ...
Basic Mechanisms Underlying Seizures and Epilepsy
... Kindling model: repeated subconvulsive stimuli resulting in electrical afterdischarges • Eventually lead to stimulation-induced clinical seizures • In some cases, lead to spontaneous seizures (epilepsy) • Applicability to human epilepsy uncertain ...
... Kindling model: repeated subconvulsive stimuli resulting in electrical afterdischarges • Eventually lead to stimulation-induced clinical seizures • In some cases, lead to spontaneous seizures (epilepsy) • Applicability to human epilepsy uncertain ...
Spike-and-wave

Spike-and-wave is the term that describes a particular pattern of the electroencephalogram (EEG) typically observed during epileptic seizures. A spike-and-wave discharge is a regular, symmetrical, generalized EEG pattern seen particularly during absence epilepsy, also known as ‘petit mal’ epilepsy. The basic mechanisms underlying these patterns are complex and involve part of the cerebral cortex, the thalamocortical network, and intrinsic neuronal mechanisms. The first spike-and-wave pattern was recorded in the early twentieth century by Hans Berger. Many aspects of the pattern are still being researched and discovered, and still many aspects are uncertain. The spike-and-wave pattern is most commonly researched in absence epilepsy, but is common in several epilepsies such as Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) and Ohtahara syndrome. Anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) are commonly prescribed to treat epileptic seizures, and new ones are being discovered with less adverse effects. Today, most of the research is focused on the origin of the generalized bilateral spike-and-wave discharge. One proposal suggests that a thalamocortical (TC) loop is involved in the initiation spike-and-wave oscillations. Although there are several theories, the use of animal models has provided new insight on spike-and-wave discharge in humans.