Engines of the brain
... embedded loops: one (b) largely topographic, and incorporating negative feedback (− ) ; the other (c) largely non-topographic, and driven by positive feedback (see text). Thalamocortical “core” circuits. In the core loop, simulated superficial cells that initially respond to a particular input patte ...
... embedded loops: one (b) largely topographic, and incorporating negative feedback (− ) ; the other (c) largely non-topographic, and driven by positive feedback (see text). Thalamocortical “core” circuits. In the core loop, simulated superficial cells that initially respond to a particular input patte ...
Development and function of human cerebral cortex neural networks
... Received 27 February 2015; Accepted 6 July 2015 ...
... Received 27 February 2015; Accepted 6 July 2015 ...
Lange Physiology > Section II
... neurotransmitter receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, and usually a postsynaptic thickening called the postsynaptic density (Figures 4–2 and 4–3). The postsynaptic density is an ordered complex of specific receptors, binding proteins, and enzymes induced by postsynaptic effects. Inside the presyn ...
... neurotransmitter receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, and usually a postsynaptic thickening called the postsynaptic density (Figures 4–2 and 4–3). The postsynaptic density is an ordered complex of specific receptors, binding proteins, and enzymes induced by postsynaptic effects. Inside the presyn ...
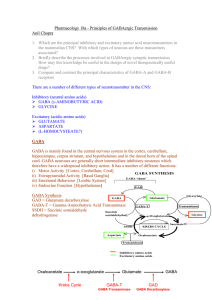
Pharmacology 18a – Priciples of GABAergic Transmission
... GABA is stored in vesicles in nerve terminals (like any other neurotransmitter) and is released by exocytosis upon influx of calcium ions. GABA Receptors There are 2 types of GABA receptor: GABAA Generally POSTsynaptic When activated by GABA cause influx of Cl- ions This causes the cell to hyp ...
... GABA is stored in vesicles in nerve terminals (like any other neurotransmitter) and is released by exocytosis upon influx of calcium ions. GABA Receptors There are 2 types of GABA receptor: GABAA Generally POSTsynaptic When activated by GABA cause influx of Cl- ions This causes the cell to hyp ...
PDF Format
... 2) Are the patterns of thalamic spindles different in intactcortex and decorticated hemispheres under the same anesthetic agent? This question arose in view of data indicating that strong corticofugal volleys, associated with the sharp depolarizations of corticothalamic neurons during the slow oscil ...
... 2) Are the patterns of thalamic spindles different in intactcortex and decorticated hemispheres under the same anesthetic agent? This question arose in view of data indicating that strong corticofugal volleys, associated with the sharp depolarizations of corticothalamic neurons during the slow oscil ...
Sliding
... Closing the eye for a brief period causes a shift in the responses towards the non-deprived eye. These shifts in ocular dominance can be easely interpreted as resulting from LTP/D like mechanisms ...
... Closing the eye for a brief period causes a shift in the responses towards the non-deprived eye. These shifts in ocular dominance can be easely interpreted as resulting from LTP/D like mechanisms ...
Membrane potential synchrony of simultaneously recorded striatal
... precisely timed, synchronous component of the membrane potential signals activation of cell assemblies and enables ®ring to occur. The asynchronous component, with low redundancy, determines the ®ne temporal pattern of spikes. The membrane potential of striatal spiny projection neurons recorded in a ...
... precisely timed, synchronous component of the membrane potential signals activation of cell assemblies and enables ®ring to occur. The asynchronous component, with low redundancy, determines the ®ne temporal pattern of spikes. The membrane potential of striatal spiny projection neurons recorded in a ...
What We Can and What We Can`t Do with fMRI
... both the precise definition of the conditions that would justify assigning a functional role to an “active” area, and interpretation of the fMRI maps. Changes in E-I balance—whether they lead to net excitation, inhibition, or simple sensitivityadjustment—inevitably and strongly affect regional metab ...
... both the precise definition of the conditions that would justify assigning a functional role to an “active” area, and interpretation of the fMRI maps. Changes in E-I balance—whether they lead to net excitation, inhibition, or simple sensitivityadjustment—inevitably and strongly affect regional metab ...
nervous system part 6 EEG, walkfulness and sleep
... the pons and like a wave it activates the lateral geniculate nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds befo ...
... the pons and like a wave it activates the lateral geniculate nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds befo ...
EEG - pressthebar
... the pons and like a wave it activates the lateral geniculate nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds befo ...
... the pons and like a wave it activates the lateral geniculate nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds befo ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... the pons and like a wave it activates the lateral geniculate nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds befo ...
... the pons and like a wave it activates the lateral geniculate nucleus (first relay of visual information) and then the occipital lobe, specifically in the visual cortex (which receives and puts together the visual information that comes from the lat. geniculate nucleus). PGO waves appear seconds befo ...
Lecture 7 Rhythms of the Brain
... • Function seems to be memory housekeeping: flush useless clutter and consolidate new memories and information with existing ...
... • Function seems to be memory housekeeping: flush useless clutter and consolidate new memories and information with existing ...
PPT - 서울대 Biointelligence lab
... Cortical oscillations be useful for understanding how large populations of cortical neurons may be coordinated so that they can directly code information or support complex neuronal operations State dependence found in EEG study: rhythms at other frequency ranges are to some extent state dependent, ...
... Cortical oscillations be useful for understanding how large populations of cortical neurons may be coordinated so that they can directly code information or support complex neuronal operations State dependence found in EEG study: rhythms at other frequency ranges are to some extent state dependent, ...
Integrator or coincidence detector? The role of the cortical neuron
... clarity of the simulation shown in pane/s A and B, the number of PSPs has been kept small and their size large. The of action potentials. Coincidence value of both parameters is not crucial for the qualitative difference observed. detection, by contrast, implies that most PSPs do not actually contri ...
... clarity of the simulation shown in pane/s A and B, the number of PSPs has been kept small and their size large. The of action potentials. Coincidence value of both parameters is not crucial for the qualitative difference observed. detection, by contrast, implies that most PSPs do not actually contri ...
Synchronization of Fast (30-40 Hz)
... and intracellular activities from neocortical areas, simultaneously with field potential recordings from thalamic foci that belong, grossly, to the same sensory or motor system. In those experiments, however, the different cortical and thalamic foci were not identified formally as reciprocally linke ...
... and intracellular activities from neocortical areas, simultaneously with field potential recordings from thalamic foci that belong, grossly, to the same sensory or motor system. In those experiments, however, the different cortical and thalamic foci were not identified formally as reciprocally linke ...
Phases
... membrane potential affects the permeability, which then further affects the membrane potential. This sets up the possibility for positive feedback, which is a key part of the rising phase of the action potential. ...
... membrane potential affects the permeability, which then further affects the membrane potential. This sets up the possibility for positive feedback, which is a key part of the rising phase of the action potential. ...
EEG Alpha Oscillations The inhibition
... ERS when a learned motor task must be withhold • Experiment by Hummel 1. Subjects trained for a finger movement task 2. In ACT condition the subject should look at the cue and perform the ...
... ERS when a learned motor task must be withhold • Experiment by Hummel 1. Subjects trained for a finger movement task 2. In ACT condition the subject should look at the cue and perform the ...
The Information Processing Mechanism of the Brain
... > The pattern that is recalled is not an exact replica of the original pattern. Some cross-over effects between patterns stored in the network occur, but if the stored patterns are approximately orthogonal (constituting a unique set of activities), the recalled pattern can be distinguished as the or ...
... > The pattern that is recalled is not an exact replica of the original pattern. Some cross-over effects between patterns stored in the network occur, but if the stored patterns are approximately orthogonal (constituting a unique set of activities), the recalled pattern can be distinguished as the or ...
Memory from the dynamics of intrinsic membrane currents
... Sustained neuronal activity in response to a brief stimulus has been proposed to underlie some short-term memory tasks (see other papers in this colloquium). For many years, the assumption was made that such sustained activity resulted from reverberating activity through excitatory feedback loops. H ...
... Sustained neuronal activity in response to a brief stimulus has been proposed to underlie some short-term memory tasks (see other papers in this colloquium). For many years, the assumption was made that such sustained activity resulted from reverberating activity through excitatory feedback loops. H ...
Gain-of-function mutation in Nav 1.7 in familial
... Sodium channels contribute to dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neuron hyperexcitability associated with acquired pain (Waxman et al., 1999; Black et al., 2002), but their role in hereditary pain syndromes is less well understood. Primary erythromelalgia (also called primary erythermalgia) is an autosomal ...
... Sodium channels contribute to dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neuron hyperexcitability associated with acquired pain (Waxman et al., 1999; Black et al., 2002), but their role in hereditary pain syndromes is less well understood. Primary erythromelalgia (also called primary erythermalgia) is an autosomal ...
medical student anti.. - University of Illinois at Chicago
... In 1931, Sen and Bose described the tranquilizing and antihypertensive effects of R. Serpentina root extracts. (Rauwolfia Serpentina: a new Indian drug for insanity and high BP. Indian Medical World 1931:11:194-201). In 1952, reserpine was isolated from Rauwolfia extracts. Arvid Carlsson (Swed ...
... In 1931, Sen and Bose described the tranquilizing and antihypertensive effects of R. Serpentina root extracts. (Rauwolfia Serpentina: a new Indian drug for insanity and high BP. Indian Medical World 1931:11:194-201). In 1952, reserpine was isolated from Rauwolfia extracts. Arvid Carlsson (Swed ...
Signaling in large-scale neural networks
... stimulus was applied. It is in this model that we have seen motoneurons and interneurons enter the high conductance state due to a parallel increase in excitatory and inhibitory synaptic activity during scratching (Alaburda et al. 2005; Berg et al. 2007). This was a surprising finding for two reason ...
... stimulus was applied. It is in this model that we have seen motoneurons and interneurons enter the high conductance state due to a parallel increase in excitatory and inhibitory synaptic activity during scratching (Alaburda et al. 2005; Berg et al. 2007). This was a surprising finding for two reason ...
Auto-structure of presynaptic activity defines postsynaptic firing
... AMPA and GABA mediated receptors. The membrane time constant was set to τm = 20 ms. The synaptic conductance strength ggaba and gampa were chosen to be identical across all synapses of the same type. We model the postsynaptic neuron to be in a state close to balanced excitation and inhibition. To th ...
... AMPA and GABA mediated receptors. The membrane time constant was set to τm = 20 ms. The synaptic conductance strength ggaba and gampa were chosen to be identical across all synapses of the same type. We model the postsynaptic neuron to be in a state close to balanced excitation and inhibition. To th ...
Large-scale recording of neuronal ensembles
... spikes outside of place field with low level of activity (top) and in the middle of field with maximum as they relate to behavior, without reference activity (bottom), respectively. (b) In vivo intracellular recording from the proximal apical dendrite of a to the types of neurons that give rise to t ...
... spikes outside of place field with low level of activity (top) and in the middle of field with maximum as they relate to behavior, without reference activity (bottom), respectively. (b) In vivo intracellular recording from the proximal apical dendrite of a to the types of neurons that give rise to t ...
Spike-and-wave

Spike-and-wave is the term that describes a particular pattern of the electroencephalogram (EEG) typically observed during epileptic seizures. A spike-and-wave discharge is a regular, symmetrical, generalized EEG pattern seen particularly during absence epilepsy, also known as ‘petit mal’ epilepsy. The basic mechanisms underlying these patterns are complex and involve part of the cerebral cortex, the thalamocortical network, and intrinsic neuronal mechanisms. The first spike-and-wave pattern was recorded in the early twentieth century by Hans Berger. Many aspects of the pattern are still being researched and discovered, and still many aspects are uncertain. The spike-and-wave pattern is most commonly researched in absence epilepsy, but is common in several epilepsies such as Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) and Ohtahara syndrome. Anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) are commonly prescribed to treat epileptic seizures, and new ones are being discovered with less adverse effects. Today, most of the research is focused on the origin of the generalized bilateral spike-and-wave discharge. One proposal suggests that a thalamocortical (TC) loop is involved in the initiation spike-and-wave oscillations. Although there are several theories, the use of animal models has provided new insight on spike-and-wave discharge in humans.