Intrinsic Connections of Macaque of Cells Outside Lamina 4c` Striate
... spreading efferents in laminae 2/3A and 1. It is possible to produce a prominent patch of retrogradely labeled neurons in lamina 5A by making an injection into 3B/4A (Figs. 28 and 6) or into lamina 4B (Fig. 9A). If lamina 2/3A is injected, one observes (Fig. 6) a column of labeled neurons that lies ...
... spreading efferents in laminae 2/3A and 1. It is possible to produce a prominent patch of retrogradely labeled neurons in lamina 5A by making an injection into 3B/4A (Figs. 28 and 6) or into lamina 4B (Fig. 9A). If lamina 2/3A is injected, one observes (Fig. 6) a column of labeled neurons that lies ...
Control and Coordination
... Have you ever had goose bumps form on your arms when you were cold? These bumps form because muscle cells in your skin respond to the cold temperature. As the muscle cells contract, or shorten, bumps form, and the hairs on your arms rise up. The hairs trap air, which helps to insulate the skin. This ...
... Have you ever had goose bumps form on your arms when you were cold? These bumps form because muscle cells in your skin respond to the cold temperature. As the muscle cells contract, or shorten, bumps form, and the hairs on your arms rise up. The hairs trap air, which helps to insulate the skin. This ...
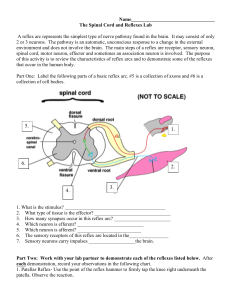
Name__________________________________ The Spinal Cord
... Name__________________________________ The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve ...
... Name__________________________________ The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve ...
Pergamon - Anatomical Neuropharmacology Unit
... perikarya had characteristics of interneurons, most were identified as medium-sized spiny neurons. Immunoreactivity for D~ receptor but not D 2 receptor was associated with the axons of the striatonigral pathway and axons and terminals in the substantia nigra pars reticulata and the entopeduncular n ...
... perikarya had characteristics of interneurons, most were identified as medium-sized spiny neurons. Immunoreactivity for D~ receptor but not D 2 receptor was associated with the axons of the striatonigral pathway and axons and terminals in the substantia nigra pars reticulata and the entopeduncular n ...
in systems and translational endocrinology
... Neurons expressing the GnRH secretagogue kisspeptin, which has been shown to play a critical role in the onset of puberty, also may control the timing of the proestrus GnRH surge. Mice lacking either Kiss1 or its receptor, GPR54, generally do not have an LH surge, and the circadian expression of Kis ...
... Neurons expressing the GnRH secretagogue kisspeptin, which has been shown to play a critical role in the onset of puberty, also may control the timing of the proestrus GnRH surge. Mice lacking either Kiss1 or its receptor, GPR54, generally do not have an LH surge, and the circadian expression of Kis ...
Neural Syntax: Cell Assemblies, Synapsembles, and
... (C) Reader-defined cell assemblies. Neurons that fire within the time integrating window of a reader mechanism (e.g., the ability of a reader neuron to integrate its inputs within the time frame of its membrane time constant) define an assembly (irrespective of whether assembly members are connected ...
... (C) Reader-defined cell assemblies. Neurons that fire within the time integrating window of a reader mechanism (e.g., the ability of a reader neuron to integrate its inputs within the time frame of its membrane time constant) define an assembly (irrespective of whether assembly members are connected ...
Passive Properties of Swimmeret Motor Neurons
... motor neurons that innervate the swimmerets—limbs that occur in pairs on several abdominal segments—perform both tasks (Heitler 1978, 1983; Sherff and Mulloney 1996). When crustaceans swim forward by beating their swimmerets, each limb moves rhythmically through cycles of power strokes and return st ...
... motor neurons that innervate the swimmerets—limbs that occur in pairs on several abdominal segments—perform both tasks (Heitler 1978, 1983; Sherff and Mulloney 1996). When crustaceans swim forward by beating their swimmerets, each limb moves rhythmically through cycles of power strokes and return st ...
View PDF - MRC BNDU - University of Oxford
... have been described, cholinergic, GABAergic and glutamatergic, and yet electrophysiological evidence suggests heterogeneity within these subtypes. To gain further insight into the molecular composition of these three populations in the rat, we investigated the pattern of expression of calcium bindin ...
... have been described, cholinergic, GABAergic and glutamatergic, and yet electrophysiological evidence suggests heterogeneity within these subtypes. To gain further insight into the molecular composition of these three populations in the rat, we investigated the pattern of expression of calcium bindin ...
tracts - Anatomický ústav 1. LF UK
... They enter into the spinal canal through the foramen intervertebralia . Another source in the cranial part are direct branches of the intracranial vertebral aa. entering the spinal canal through the foramen magnum . Spinal arteries send branches to the walls of the spinal canal (postcentral and prel ...
... They enter into the spinal canal through the foramen intervertebralia . Another source in the cranial part are direct branches of the intracranial vertebral aa. entering the spinal canal through the foramen magnum . Spinal arteries send branches to the walls of the spinal canal (postcentral and prel ...
Interactions between Adjacent Ganglia Bring About the Bilaterally
... immunoreactivities transiently or not at all. Experimental studies have shown that both right and left homologuesare capable of manifesting the mature AS phenotype and suggestthat there is a determinative interaction betweenthese 2 neurons that is responsiblefor their asymmetricdifferentiation (Mart ...
... immunoreactivities transiently or not at all. Experimental studies have shown that both right and left homologuesare capable of manifesting the mature AS phenotype and suggestthat there is a determinative interaction betweenthese 2 neurons that is responsiblefor their asymmetricdifferentiation (Mart ...
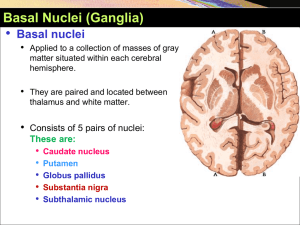
Basal Ganglia YAYDAR 2012-2013
... Basically the activity of basal nuclei begins by information received from sensory cortex, thalamus, substantia nigra, and red nucleus, according to thoughts of mind. • These information is integrated within corpus striatum and channeled within globus pallidus and outflow back to motor areas of cere ...
... Basically the activity of basal nuclei begins by information received from sensory cortex, thalamus, substantia nigra, and red nucleus, according to thoughts of mind. • These information is integrated within corpus striatum and channeled within globus pallidus and outflow back to motor areas of cere ...
Neuro Objectives 22 - U
... Inferior cerebellar peduncle (Afferent input to the cerebellum): dorsolateral in the medulla Middle cerebellar peduncle (Pontine nuclei → contralateral cortex): connects caudal pons to the cerebellum Superior cerebellar peduncle (Efferent output of the cerebellum): dentate nucleus in the cerebellum ...
... Inferior cerebellar peduncle (Afferent input to the cerebellum): dorsolateral in the medulla Middle cerebellar peduncle (Pontine nuclei → contralateral cortex): connects caudal pons to the cerebellum Superior cerebellar peduncle (Efferent output of the cerebellum): dentate nucleus in the cerebellum ...
Functional Specialization Within the Cat Red Nucleus
... by RNm stimulation. Although the shoulder muscles, sd and ss, were more likely to be facilitated by RNp stimulation (49 vs. 21%), the overall pattern of muscle activation between RNm and RNp was not significantly different (2 ⫽ 2.9, 6 df, P ⬎ 0.50). Therefore stimulation within RN did not support a ...
... by RNm stimulation. Although the shoulder muscles, sd and ss, were more likely to be facilitated by RNp stimulation (49 vs. 21%), the overall pattern of muscle activation between RNm and RNp was not significantly different (2 ⫽ 2.9, 6 df, P ⬎ 0.50). Therefore stimulation within RN did not support a ...
Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier and Neuronal Cell Death in
... activity and m2-muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (m2-AChR). Animals subjected to stress and chemicals exhibited both disruption of the BBB and neuronal cell death in the cingulate cortex, the dentate gyrus, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus. Other regions of the brain, although they demonstrated ...
... activity and m2-muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (m2-AChR). Animals subjected to stress and chemicals exhibited both disruption of the BBB and neuronal cell death in the cingulate cortex, the dentate gyrus, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus. Other regions of the brain, although they demonstrated ...
Anatomical origins of the classical receptive field and modulatory
... response.Fit, direct thalamic input can determine the size of the initial activating RF at high contrast. Second lateral connections can enlarge the RF at low contrast by pooling information from larger regions of cortex that are otherwise ineft%ctive when high contrast thalamic inpnt is driving the ...
... response.Fit, direct thalamic input can determine the size of the initial activating RF at high contrast. Second lateral connections can enlarge the RF at low contrast by pooling information from larger regions of cortex that are otherwise ineft%ctive when high contrast thalamic inpnt is driving the ...
Duration Sensitivity to Other Response Properties of the Rat
... ranges of sound durations to which neurons are tuned correspond closely to the range of durations found in behaviorally important sounds. This matching of neural sensitivity to the duration of vocalizations has been described in frogs, where neurons’ duration tuning matches the durations of communic ...
... ranges of sound durations to which neurons are tuned correspond closely to the range of durations found in behaviorally important sounds. This matching of neural sensitivity to the duration of vocalizations has been described in frogs, where neurons’ duration tuning matches the durations of communic ...
Decoding Complete Reach and Grasp Actions from Local Primary
... populations control highly flexible coordinated limb movements not only has important implications for understanding volitional movement control but also for the design of neuroprosthetic devices that attempt to reproduce reach and grasp actions from neural activity. The goal of this study was to de ...
... populations control highly flexible coordinated limb movements not only has important implications for understanding volitional movement control but also for the design of neuroprosthetic devices that attempt to reproduce reach and grasp actions from neural activity. The goal of this study was to de ...
Ventral Medial Nucleus Neurons Send Thalamocortical Afferents
... 2004; Kuramoto et al. 2011) and relays basal ganglia information to the cerebral cortex including motor areas. Thus, the VM is at least partly associated with the motor function as well as with other cortical functions. In addition to the VM, the ventral anterior and ventral lateral nuclear complex ...
... 2004; Kuramoto et al. 2011) and relays basal ganglia information to the cerebral cortex including motor areas. Thus, the VM is at least partly associated with the motor function as well as with other cortical functions. In addition to the VM, the ventral anterior and ventral lateral nuclear complex ...
Cell Type-Specific, Presynaptic LTP of Inhibitory Synapses on Fast
... by averaging 15–30 consecutive responses: onset latency (from the peak of presynaptic action potentials to the onset of uIPSC); peak amplitude (from the baseline to the peak of uIPSC); base-to-peak rising time (from the onset of uIPSC to its peak); and rising slope (slope of a fitting line from 10 t ...
... by averaging 15–30 consecutive responses: onset latency (from the peak of presynaptic action potentials to the onset of uIPSC); peak amplitude (from the baseline to the peak of uIPSC); base-to-peak rising time (from the onset of uIPSC to its peak); and rising slope (slope of a fitting line from 10 t ...
Central circuitries for body temperature regulation and fever
... thermoregulatory command neurons that are located in the POA. Skin thermoreceptors are situated strategically to detect changes in environmental temperature. Also, skin temperature should be affected by body core temperature, especially when recruitment of heat from internal body to the skin is faci ...
... thermoregulatory command neurons that are located in the POA. Skin thermoreceptors are situated strategically to detect changes in environmental temperature. Also, skin temperature should be affected by body core temperature, especially when recruitment of heat from internal body to the skin is faci ...
PDF
... corridor for the tangential migration of interneurons and it contains Cajal-Retzius neurons. Preplate (PP). A transient cell-dense structure, which was formerly termed the early MZ or primordial plexiform layer, that contains some of the earliest-born cortical neurons. It is split by incoming CP neu ...
... corridor for the tangential migration of interneurons and it contains Cajal-Retzius neurons. Preplate (PP). A transient cell-dense structure, which was formerly termed the early MZ or primordial plexiform layer, that contains some of the earliest-born cortical neurons. It is split by incoming CP neu ...
Investigating circadian rhythmicity in pain sensitivity using
... the dorsal horn. The dorsal horn serves as a processing center for incoming pain signals, while the midbrain and cortex, as a whole referred to as descending or topdown inhibition [22], serve as a modulator of the pain circuit in the dorsal horn. As a result, there is a tradition of modeling pain pr ...
... the dorsal horn. The dorsal horn serves as a processing center for incoming pain signals, while the midbrain and cortex, as a whole referred to as descending or topdown inhibition [22], serve as a modulator of the pain circuit in the dorsal horn. As a result, there is a tradition of modeling pain pr ...
Central circuitries for body temperature regulation and fever
... thermoregulatory command neurons that are located in the POA. Skin thermoreceptors are situated strategically to detect changes in environmental temperature. Also, skin temperature should be affected by body core temperature, especially when recruitment of heat from internal body to the skin is faci ...
... thermoregulatory command neurons that are located in the POA. Skin thermoreceptors are situated strategically to detect changes in environmental temperature. Also, skin temperature should be affected by body core temperature, especially when recruitment of heat from internal body to the skin is faci ...
Nervous System
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump, using ATP, restores the original configuration ...
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump, using ATP, restores the original configuration ...