Slide ()
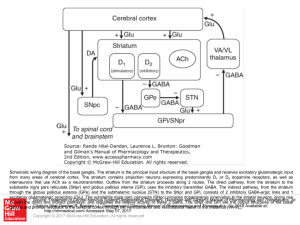
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Skeletal, Muscular, & Nervous System
... contains the nucleus, the control center of the cell Neuron cells have limited ability to repair damage or replace destroyed cells ...
... contains the nucleus, the control center of the cell Neuron cells have limited ability to repair damage or replace destroyed cells ...
Nervous System
... 1. Conduction of nerve impulses – The spinal cord is a two-way communication system between the brain and parts of the body. ...
... 1. Conduction of nerve impulses – The spinal cord is a two-way communication system between the brain and parts of the body. ...
REVIEW THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... 40. The Human Nervous System is divided into TWO Major Divisions, list them: ____________________________________&__________________________________ 41. _________________________ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 42. The depolarization and repolarization of a neuron’s membran ...
... 40. The Human Nervous System is divided into TWO Major Divisions, list them: ____________________________________&__________________________________ 41. _________________________ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 42. The depolarization and repolarization of a neuron’s membran ...
Terms being described
... 15. It’s the ability of a potential change to spread along the axon that is analogous to the conduction of electricity by a wire. 17. It’s another name for the nerve impulse. 19. They are the parts of the neuron that function in receiving stimulation. 21. They are a type of ion channel that open in ...
... 15. It’s the ability of a potential change to spread along the axon that is analogous to the conduction of electricity by a wire. 17. It’s another name for the nerve impulse. 19. They are the parts of the neuron that function in receiving stimulation. 21. They are a type of ion channel that open in ...
Itch neurons play a role in managing pain
... often accompanied by mild pain such as burning and stinging sensations. But when it comes to sending signals toward your brain through your spinal cord, itch and mild pain can go through the same set of spinal cord neurons, researchers report February 22 in Neuron. This finding explains why pain oft ...
... often accompanied by mild pain such as burning and stinging sensations. But when it comes to sending signals toward your brain through your spinal cord, itch and mild pain can go through the same set of spinal cord neurons, researchers report February 22 in Neuron. This finding explains why pain oft ...
Nervous System: Reflexes and Peripheral Nervous System
... those integrating many different types of information ...
... those integrating many different types of information ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... FIGURE 24.6 The two classes of nociceptors that conduct action potentials in the C and Ad ranges are peripheral components for two types of pain. First pain carried by Ad axons reaches consciousness rapidly and is discriminative. Both the location and the subjective intensity of the stimulus can be ...
... FIGURE 24.6 The two classes of nociceptors that conduct action potentials in the C and Ad ranges are peripheral components for two types of pain. First pain carried by Ad axons reaches consciousness rapidly and is discriminative. Both the location and the subjective intensity of the stimulus can be ...
Introduction of the Nervous System
... We must not confuse these with "reactions", which are different from reflexes in that they are voluntary responses to a stimulus from the environment. ...
... We must not confuse these with "reactions", which are different from reflexes in that they are voluntary responses to a stimulus from the environment. ...
Metabolic acidosis inhibits hypothalamic warm
... Downloaded from http://jap.physiology.org/ by 10.220.32.247 on June 17, 2017 ...
... Downloaded from http://jap.physiology.org/ by 10.220.32.247 on June 17, 2017 ...
FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATION OF THE HUMAN BODY
... processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body. Endocrine glands release more than 20 major hormones directly into the bloodstream where they can be transported to cells in other parts of the body. F. The “Waste Removal” System- Some other systems like the r ...
... processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body. Endocrine glands release more than 20 major hormones directly into the bloodstream where they can be transported to cells in other parts of the body. F. The “Waste Removal” System- Some other systems like the r ...
The Central Nervous System
... A membrane potential exists across the cell membrane because: (1) the cytosol and the extracellular fluid differ in their ionic composition, and (2) the cell membrane is selectively permeable to these ions. The membrane potential can quickly change, as the ionic permeability of the cell membrane cha ...
... A membrane potential exists across the cell membrane because: (1) the cytosol and the extracellular fluid differ in their ionic composition, and (2) the cell membrane is selectively permeable to these ions. The membrane potential can quickly change, as the ionic permeability of the cell membrane cha ...
A&P Ch 8 PowerPoint(Nervous System)
... A membrane potential exists across the cell membrane because: (1) the cytosol and the extracellular fluid differ in their ionic composition, and (2) the cell membrane is selectively permeable to these ions. The membrane potential can quickly change, as the ionic permeability of the cell membrane cha ...
... A membrane potential exists across the cell membrane because: (1) the cytosol and the extracellular fluid differ in their ionic composition, and (2) the cell membrane is selectively permeable to these ions. The membrane potential can quickly change, as the ionic permeability of the cell membrane cha ...
Nervous system summary
... Some drugs, like marijuana and heroin, have chemical structures that mimic that of a neurotransmitter that naturally occurs in our bodies. In fact, these drugs can “fool” our receptors, lock onto them, and activate the nerve cells. However, they don't work the same way as a natural neurotransmitter, ...
... Some drugs, like marijuana and heroin, have chemical structures that mimic that of a neurotransmitter that naturally occurs in our bodies. In fact, these drugs can “fool” our receptors, lock onto them, and activate the nerve cells. However, they don't work the same way as a natural neurotransmitter, ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
... A neuron can produce only one kind of neurotransmitter at its synapse. The post-synaptic neuron will have receptors for this neurotransmitter that will either cause an increase or decrease in membrane potential. Acetylcholine (ACh) Released by neurons that control muscles (motor neurons), neurons th ...
... A neuron can produce only one kind of neurotransmitter at its synapse. The post-synaptic neuron will have receptors for this neurotransmitter that will either cause an increase or decrease in membrane potential. Acetylcholine (ACh) Released by neurons that control muscles (motor neurons), neurons th ...
mspn1a
... muscle spindle (See Muscle Spindle Question). Cells in this area are organized into motor pools with somatotopic organization in regard to the muscles they innervate (See Question 2). b. Dorsal Horn The dorsal horn has a somatosensory function. It receives input from the dorsal root ganglia and othe ...
... muscle spindle (See Muscle Spindle Question). Cells in this area are organized into motor pools with somatotopic organization in regard to the muscles they innervate (See Question 2). b. Dorsal Horn The dorsal horn has a somatosensory function. It receives input from the dorsal root ganglia and othe ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... Sympathetic fibers increase heart and respiratory rates, and inhibit digestion and elimination ...
... Sympathetic fibers increase heart and respiratory rates, and inhibit digestion and elimination ...
Paralys
... neurotrophins are likely to be unpredictable. Too little neurotrophin is ineffective, but with increasing dosage come negative side effects; for example, a consequence of too much NGF is significant pain. For this reason, the therapeutic dosages are often much less than those proven to be effective ...
... neurotrophins are likely to be unpredictable. Too little neurotrophin is ineffective, but with increasing dosage come negative side effects; for example, a consequence of too much NGF is significant pain. For this reason, the therapeutic dosages are often much less than those proven to be effective ...
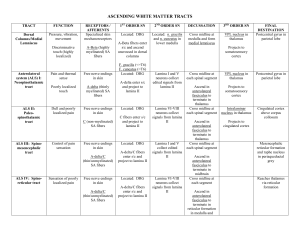
ASCENDING WHITE MATTER TRACTS
... CB via inferior CB peduncle Spinal border cells of lamina V-VII ...
... CB via inferior CB peduncle Spinal border cells of lamina V-VII ...
PSB 4002 - Developmental Psychobiology Laboratory
... • Over about 277 days of gestation, this one fertilized cell will become trillions of cells, all organized into the various glands, tissues, organs, etc. that constitute our brain/body system. ...
... • Over about 277 days of gestation, this one fertilized cell will become trillions of cells, all organized into the various glands, tissues, organs, etc. that constitute our brain/body system. ...
Garza-Juliann-Project(1)
... Peripheral Nervous System Nervous tissue is made up of 2 principal ...
... Peripheral Nervous System Nervous tissue is made up of 2 principal ...
Central nervous system practical block
... A schwannoma. typically has dense areas called Antoni A (black arrow) and looser areas called Antoni B (blue arrows). The cells are elongated (spindle shaped) and the nuclei have a tendency to line up as seen here in the Antoni A area. ...
... A schwannoma. typically has dense areas called Antoni A (black arrow) and looser areas called Antoni B (blue arrows). The cells are elongated (spindle shaped) and the nuclei have a tendency to line up as seen here in the Antoni A area. ...
AP-Anatomy
... THE REFLEX ARC AS A FEEDBACK SYSTEM CONTROLLED CONDITION A stimulus or stress disrupts membrane homeostasis by altering some controlled condition ...
... THE REFLEX ARC AS A FEEDBACK SYSTEM CONTROLLED CONDITION A stimulus or stress disrupts membrane homeostasis by altering some controlled condition ...
document
... A biological neuron may have as many as 10,000 different inputs, and may send its output (the presence or absence of a short-duration spike) to many other neurons. Neurons are wired up in a 3dimensional pattern. Real brains, however, are orders of magnitude more complex than any artificial neur ...
... A biological neuron may have as many as 10,000 different inputs, and may send its output (the presence or absence of a short-duration spike) to many other neurons. Neurons are wired up in a 3dimensional pattern. Real brains, however, are orders of magnitude more complex than any artificial neur ...