
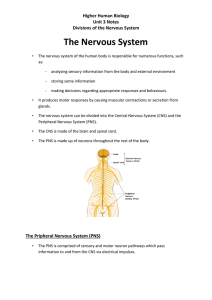
Review
... Motor unit Fine vs. course muscle control Role of acetylcholine, synaptic cleft, interstitial fluid Depolarization vs. repolarization Role of calcium during muscle contraction Role of acetylcholinesterase Energy sources for muscle contraction o Role of creatine phosphate o Purpose of glycolysis o Ae ...
... Motor unit Fine vs. course muscle control Role of acetylcholine, synaptic cleft, interstitial fluid Depolarization vs. repolarization Role of calcium during muscle contraction Role of acetylcholinesterase Energy sources for muscle contraction o Role of creatine phosphate o Purpose of glycolysis o Ae ...
Resting potential
... 2. Lets researchers see what areas of brain are most active during certain tasks – Can do while brain is at rest, sleeping, etc. ...
... 2. Lets researchers see what areas of brain are most active during certain tasks – Can do while brain is at rest, sleeping, etc. ...
Nervous System - Calgary Christian School
... The blood-brain barrier protects the neurons and glial cells in the brain from substances that could harm them. Unlike blood vessels in other parts of the body that are relatively leaky to a variety of molecules, the blood-brain barrier keeps many substances, including toxins, away from the neurons ...
... The blood-brain barrier protects the neurons and glial cells in the brain from substances that could harm them. Unlike blood vessels in other parts of the body that are relatively leaky to a variety of molecules, the blood-brain barrier keeps many substances, including toxins, away from the neurons ...
Regents Biology
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
File
... 1- The brain is responsible for integrating most sensory information and coordinating body functions. Complex functions such as thinking, emotions, movement, speech, consciousness and body temperature are controlled by different parts of the brain. 2- The spinal cord acts as a channel for signals ...
... 1- The brain is responsible for integrating most sensory information and coordinating body functions. Complex functions such as thinking, emotions, movement, speech, consciousness and body temperature are controlled by different parts of the brain. 2- The spinal cord acts as a channel for signals ...
Lecture 14 - ANS
... • An important aspect of ANS function because: – If a nerve is inactive under normal conditions, it can only increase its activity – However, if nerve maintains a constant background level of activity, then it can either increase or decrease its activity ...
... • An important aspect of ANS function because: – If a nerve is inactive under normal conditions, it can only increase its activity – However, if nerve maintains a constant background level of activity, then it can either increase or decrease its activity ...
Hypothalamus
... 4.List the efferent connections of the hypothalamus 5.List the functions of hypothalamus ...
... 4.List the efferent connections of the hypothalamus 5.List the functions of hypothalamus ...
Neuromuscular spindle The central nervous system continuously
... neuromuscular spindle becomes slack. If the spindle remains slack, no further information about changes in muscle length can be transmitted to the spinal cord. This situation is corrected by a feedback control mechanism by which the sensory region of the spindle activates gamma motor neurons, which ...
... neuromuscular spindle becomes slack. If the spindle remains slack, no further information about changes in muscle length can be transmitted to the spinal cord. This situation is corrected by a feedback control mechanism by which the sensory region of the spindle activates gamma motor neurons, which ...
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Reflexes
... Stimulation of beta- or alph2-receptors leads to activation of Gs or Gi, which then act as transducers to activate (Gs) or inhibit (Gi) adenylyl cyclase. This results in increased or decreased production of cAMP from ATP alph1-Receptors work through Gp, which activates phospholipase C to promote con ...
... Stimulation of beta- or alph2-receptors leads to activation of Gs or Gi, which then act as transducers to activate (Gs) or inhibit (Gi) adenylyl cyclase. This results in increased or decreased production of cAMP from ATP alph1-Receptors work through Gp, which activates phospholipase C to promote con ...
The Nervous System - Cathkin High School
... The nerves of the ANS arise in the medulla region of the brain and emerge from the spinal cord at numerous points to reach the organs that they stimulate. ...
... The nerves of the ANS arise in the medulla region of the brain and emerge from the spinal cord at numerous points to reach the organs that they stimulate. ...
Lecture 14 - ANS
... postganglionic fibers of the sympathetic division (instead of NE) • Important because ACh causes dilation of these blood vessels, whereas NE causes constriction of the blood vessels in the abdominopelvic cavity • Thus widespead sympathetic activation leads to a redistribution of blood away from skin ...
... postganglionic fibers of the sympathetic division (instead of NE) • Important because ACh causes dilation of these blood vessels, whereas NE causes constriction of the blood vessels in the abdominopelvic cavity • Thus widespead sympathetic activation leads to a redistribution of blood away from skin ...
Motor
... neurons innervating axial musculature are located medially, whereas those innervating the distal musculature are located more laterally. ...
... neurons innervating axial musculature are located medially, whereas those innervating the distal musculature are located more laterally. ...
[j26]Chapter 8#
... addition, these more primitive areas of the brain provide essential electrical links to the many hormones released by the complex endocrine system. Triggered by nerve impulses, endocrine glands secrete many hormones into the blood that ultimately control many of the body's homeostatic processes, esp ...
... addition, these more primitive areas of the brain provide essential electrical links to the many hormones released by the complex endocrine system. Triggered by nerve impulses, endocrine glands secrete many hormones into the blood that ultimately control many of the body's homeostatic processes, esp ...
neural and chemical regulation of respiration
... They respond when PO2 decreases to less than 60mmHg DECREASE IN ARTERIAL PO2 If arterial PO2 is b/w 100 and 60mmhg, the breathing rate is relatively constant. However, if arterial po2 is less than 60mmhg, the breathing rate increases in a very steep and linear fashion. In this range of po2 pc are ve ...
... They respond when PO2 decreases to less than 60mmHg DECREASE IN ARTERIAL PO2 If arterial PO2 is b/w 100 and 60mmhg, the breathing rate is relatively constant. However, if arterial po2 is less than 60mmhg, the breathing rate increases in a very steep and linear fashion. In this range of po2 pc are ve ...
BRAIN
... – Interneurons (association neurons) — shuttle signals through CNS pathways; Responsible for integrating afferent information and formulating an efferent response to include higher cognitive functions ...
... – Interneurons (association neurons) — shuttle signals through CNS pathways; Responsible for integrating afferent information and formulating an efferent response to include higher cognitive functions ...
3-Biological Bases-table - Miami Beach Senior High School
... The endocrine system is another type of communication system that uses a set of glands which produce hormones (like neurotransmitters) that circulate through the bloodstream, enabling communication. Hypothalamus- part of the brain that links the brain to the endocrine system through control of the p ...
... The endocrine system is another type of communication system that uses a set of glands which produce hormones (like neurotransmitters) that circulate through the bloodstream, enabling communication. Hypothalamus- part of the brain that links the brain to the endocrine system through control of the p ...
Neuroscience and Behavior Term Explanation
... Antagonist is like a key that fits a lock but does not turn the lock, hence not opening the door- the key is now stuck in the lock, preventing any other key from entering The endocrine system uses the bloodstream making it much slower than the nervous system, which uses electricity ...
... Antagonist is like a key that fits a lock but does not turn the lock, hence not opening the door- the key is now stuck in the lock, preventing any other key from entering The endocrine system uses the bloodstream making it much slower than the nervous system, which uses electricity ...
Stimulus Response Time Lab
... The Nervous System: Stimulus Response Time Lab Activity Introduction: The human nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord (Central Nervous System, CNS) and the nerves which branch out from the CNS, the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). Sensory neurons of the PNS carry information to the ...
... The Nervous System: Stimulus Response Time Lab Activity Introduction: The human nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord (Central Nervous System, CNS) and the nerves which branch out from the CNS, the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). Sensory neurons of the PNS carry information to the ...
Brain
... Structure of the Cortex Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes that are separated by prominent fissures. These lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of ...
... Structure of the Cortex Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes that are separated by prominent fissures. These lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of ...
Document
... It controls important sensations involved in maintaining homeostasis, such as hunger and thirst. Temperature, water balance, and blood pressure are also controlled by the hypothalamus . In addition, it also regulates the release of many hormones. ...
... It controls important sensations involved in maintaining homeostasis, such as hunger and thirst. Temperature, water balance, and blood pressure are also controlled by the hypothalamus . In addition, it also regulates the release of many hormones. ...
[j26]Chapter 9#
... b. They emerge from the brain and sacral regions. c. They form white and grey rami communicantes fibers. d. They may have ganglia located along the spinal cord. ___ 12. Which of the following ganglia is not a collateral (prevertebral) ganglion? a. celiac b. superior mesenteric c. inferior mesenteric ...
... b. They emerge from the brain and sacral regions. c. They form white and grey rami communicantes fibers. d. They may have ganglia located along the spinal cord. ___ 12. Which of the following ganglia is not a collateral (prevertebral) ganglion? a. celiac b. superior mesenteric c. inferior mesenteric ...
Mammalian Physiology Sensory Nervous System
... Basic Functions of the Nervous System Sensory Input - provides the central nervous system with information about the internal and external environment Integration - CNS takes all the incoming information, processes it, then selects an appropriate action Motor Output – effects the physical responses ...
... Basic Functions of the Nervous System Sensory Input - provides the central nervous system with information about the internal and external environment Integration - CNS takes all the incoming information, processes it, then selects an appropriate action Motor Output – effects the physical responses ...











![[j26]Chapter 8#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009531099_1-530d7c194a24d89985e18840d7e0199e-300x300.png)









![[j26]Chapter 9#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009372212_1-45723eed01d76cad9811e1514890dc2a-300x300.png)
