Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
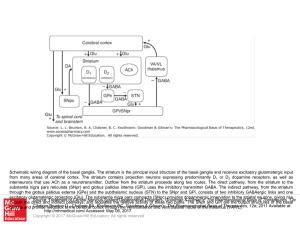
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Chapter 9 Lesson Two-Nervous System
... Cerebral palsy is caused by damage to the brain as it is growing. ...
... Cerebral palsy is caused by damage to the brain as it is growing. ...
Higher Mind - Source Naturals
... and balance the mind, enhancing mental focus. Along with taurine, these two relaxing neurotransmitters provide a balancing influence to the other, excitatory neurotransmitters. Taurine is found in brain tissue more than anywhere else in the body. It has antioxidant properties and serves as a nerve c ...
... and balance the mind, enhancing mental focus. Along with taurine, these two relaxing neurotransmitters provide a balancing influence to the other, excitatory neurotransmitters. Taurine is found in brain tissue more than anywhere else in the body. It has antioxidant properties and serves as a nerve c ...
Drosophila as a model to study mechanisms underlying alcohol
... synchronization. In the swimmeret system of crayfish (1), we found a perfect example, were not only the components of the pattern generating kernel were described (2), but were also the coordinating network is known and can be analyzed (3, 4). Recent studies in the crayfish swimmeret system show tha ...
... synchronization. In the swimmeret system of crayfish (1), we found a perfect example, were not only the components of the pattern generating kernel were described (2), but were also the coordinating network is known and can be analyzed (3, 4). Recent studies in the crayfish swimmeret system show tha ...
Neuroanatomy PP - Rincon History Department
... A neuron fires an impulse, when it receives signals from sense receptors…the impulse is called ...
... A neuron fires an impulse, when it receives signals from sense receptors…the impulse is called ...
Brain - El Camino College
... A. The brain may be divided into four major parts: 1. ____________ – largest, superior part of the brain 2. _______________ – thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, and pituitary gland 3. _______________ – midbrain, pons, & medulla oblongata 4. ________________ – most posterior, inferior part of brain ...
... A. The brain may be divided into four major parts: 1. ____________ – largest, superior part of the brain 2. _______________ – thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, and pituitary gland 3. _______________ – midbrain, pons, & medulla oblongata 4. ________________ – most posterior, inferior part of brain ...
Brain - Cloudfront.net
... Is called the “master gland.” The anterior pituitary lobe releases hormones that regulate other glands. The posterior lobe regulates water and salt balance. Brain->pituitary->other glands->hormones->brain ...
... Is called the “master gland.” The anterior pituitary lobe releases hormones that regulate other glands. The posterior lobe regulates water and salt balance. Brain->pituitary->other glands->hormones->brain ...
JARINGAN SYARAF TIRUAN
... The Nervous System The human nervous system can be broken down into three stages that may be represented in block diagram form as: ...
... The Nervous System The human nervous system can be broken down into three stages that may be represented in block diagram form as: ...
nervous system
... When a nerve gets pinched (e.g. herniated vertebral disc), it damages the nerve by interfering with its signal transmission, causing weakness, pain, or paralysis. Blood supply interfered with When a body part “falls asleep”, the region is lacking blood flow, impairing the nerve signals as well. Unli ...
... When a nerve gets pinched (e.g. herniated vertebral disc), it damages the nerve by interfering with its signal transmission, causing weakness, pain, or paralysis. Blood supply interfered with When a body part “falls asleep”, the region is lacking blood flow, impairing the nerve signals as well. Unli ...
Muscle
... -Enteric nervous system (controlling the gastrointestinal tract, the pancreas and the gallbladder) can operate completely independently but autonomic nervous system can also modulate its activity. It contains about 100 millions of neurons (as many as the spinal cord). The enteric system consists of ...
... -Enteric nervous system (controlling the gastrointestinal tract, the pancreas and the gallbladder) can operate completely independently but autonomic nervous system can also modulate its activity. It contains about 100 millions of neurons (as many as the spinal cord). The enteric system consists of ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... – Neurotransmitters (chemicals) cross the synapse: different ones send different impulses and need to find receptors – It can either excite (fire) or inhibit (prevent firing) ...
... – Neurotransmitters (chemicals) cross the synapse: different ones send different impulses and need to find receptors – It can either excite (fire) or inhibit (prevent firing) ...
Brain
... increases heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate, blood flow to skeletal muscles, glucose metabolism decreases the activities that are not essential at the moment (digestive system organs are subdued- decreased blood flow to that system ...
... increases heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate, blood flow to skeletal muscles, glucose metabolism decreases the activities that are not essential at the moment (digestive system organs are subdued- decreased blood flow to that system ...
autonomic nervous system i
... • involuntary emptying of the bladder, when it occurs, does so in seconds • marked changes in blood pressure (rise or fall) can take place in about 5 secs. A precipitous fall in blood pressure causes fainting. ...
... • involuntary emptying of the bladder, when it occurs, does so in seconds • marked changes in blood pressure (rise or fall) can take place in about 5 secs. A precipitous fall in blood pressure causes fainting. ...
09. Assessment of Neurologic System
... Major function to receive sensory input such as position sense, touch, shape and texture of objects ...
... Major function to receive sensory input such as position sense, touch, shape and texture of objects ...
Slide 1
... - crude touch and pressure -The fibers of 1st order neurons terminate by synapsing with cells in the posterior gray column (substantia gelatinosa) -The axons of 2nd order neurons cross obliquely to the opposite side in the anterior gray and white commissures , ascending in the contralateral white co ...
... - crude touch and pressure -The fibers of 1st order neurons terminate by synapsing with cells in the posterior gray column (substantia gelatinosa) -The axons of 2nd order neurons cross obliquely to the opposite side in the anterior gray and white commissures , ascending in the contralateral white co ...
ANIMAL RESPONSES TO ENVIRONMENT
... • Human response to these changes in the environment occurs to maintain stability/balance within the organism. • Organisms sense changes in the environment as a stimulus. • These impulses are send to the brain which interpret the information and sends a different message back to the part of the body ...
... • Human response to these changes in the environment occurs to maintain stability/balance within the organism. • Organisms sense changes in the environment as a stimulus. • These impulses are send to the brain which interpret the information and sends a different message back to the part of the body ...
Autonomic_notes
... Hypothalamus oversees autonomic centers in pons (respiratory control) and medulla (many autonomic functions including respiration, heart, blood vessels, swallow, cough, etc). Medulla controls autonomic outflow from spinal cord and vagus nerve. Hypothalamus is controlled by higher brain areas includi ...
... Hypothalamus oversees autonomic centers in pons (respiratory control) and medulla (many autonomic functions including respiration, heart, blood vessels, swallow, cough, etc). Medulla controls autonomic outflow from spinal cord and vagus nerve. Hypothalamus is controlled by higher brain areas includi ...
GBA deficiency promotes SNCA/α-synuclein accumulation through
... Figure S4. C2-ceramide treatment conditions for maximal PPP2A activity. Optimal C2 concentration and application time (5 μM for 8 h) were determined according to the peak increase in PPP2A activity. *P<0.05 vs. control group, #P<0.05 vs. other C2 treatment groups; n=6. ...
... Figure S4. C2-ceramide treatment conditions for maximal PPP2A activity. Optimal C2 concentration and application time (5 μM for 8 h) were determined according to the peak increase in PPP2A activity. *P<0.05 vs. control group, #P<0.05 vs. other C2 treatment groups; n=6. ...
Anti-fear hormone oxytocin transported directly to target sites in the
... extensions, where it is stored temporarily and released into the blood when required. The hormone then reaches the target organs, like the womb and mammary glands, via the blood. But how does the oxytocin reach the central areas of the brain that can control behaviour, for example the amygdala, the ...
... extensions, where it is stored temporarily and released into the blood when required. The hormone then reaches the target organs, like the womb and mammary glands, via the blood. But how does the oxytocin reach the central areas of the brain that can control behaviour, for example the amygdala, the ...
Skeletal, Muscular, & Nervous System
... contains the nucleus, the control center of the cell Neuron cells have limited ability to repair damage or replace destroyed cells ...
... contains the nucleus, the control center of the cell Neuron cells have limited ability to repair damage or replace destroyed cells ...