The Nervous System
... - responsible for conscious/voluntary activities of the body - divided into 2 sections called ______________________, controlling the opposite side of the body - the _________ hemisphere may control creativity and artistic ability - the left hemisphere may control analytical and mathematical ability ...
... - responsible for conscious/voluntary activities of the body - divided into 2 sections called ______________________, controlling the opposite side of the body - the _________ hemisphere may control creativity and artistic ability - the left hemisphere may control analytical and mathematical ability ...
12-1 Chapter 12 Lecture Outline See PowerPoint Image Slides for
... • Qualitative information (taste or hearing) depends upon which neurons fire – labeled line code = brain knows what type of sensory information travels on each fiber ...
... • Qualitative information (taste or hearing) depends upon which neurons fire – labeled line code = brain knows what type of sensory information travels on each fiber ...
Chapter 12
... • Qualitative information (taste or hearing) depends upon which neurons fire – labeled line code = brain knows what type of sensory information travels on each fiber ...
... • Qualitative information (taste or hearing) depends upon which neurons fire – labeled line code = brain knows what type of sensory information travels on each fiber ...
Ch 4 V Cortexb - Texas A&M University
... • A blind man who damaged the occipital lobe can still navigate and walk without bumping into objects. ch 4 ...
... • A blind man who damaged the occipital lobe can still navigate and walk without bumping into objects. ch 4 ...
Somatic senses
... Rapidly transferred to CNS by small myelinated fibeers Slow pain – more diffused pain Carried by small unmyelinated fibers ...
... Rapidly transferred to CNS by small myelinated fibeers Slow pain – more diffused pain Carried by small unmyelinated fibers ...
Organization of Vertebrate Body Organization of
... As animals have evolved, specialization of body structures has increased For cells to function efficiently and interact properly, internal body conditions must be relatively constant -The dynamic constancy of the internal environment is called homeostasis -It is essential for life ...
... As animals have evolved, specialization of body structures has increased For cells to function efficiently and interact properly, internal body conditions must be relatively constant -The dynamic constancy of the internal environment is called homeostasis -It is essential for life ...
Biology 11 - Human Anatomy Lecture
... 1. ______________ N.S. – involved in “fight or flight” responses 2. ________sympathetic N.S. – involved in “rest & digest” activities ...
... 1. ______________ N.S. – involved in “fight or flight” responses 2. ________sympathetic N.S. – involved in “rest & digest” activities ...
No Slide Title
... • Qualitative information (taste or hearing) depends upon which neurons fire – labeled line code = brain knows what type of sensory information travels on each fiber ...
... • Qualitative information (taste or hearing) depends upon which neurons fire – labeled line code = brain knows what type of sensory information travels on each fiber ...
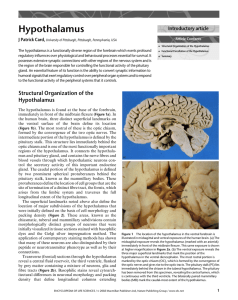
Hypothalamus
... However, the parvocellular neurons release their secretory products into fenestrated capillaries that drain into the long portal vessels that drain into the anterior lobe. The magnocellular neurons secrete either vasopressin or oxytocin, and are largely concentrated in the supraoptic (SON) and parav ...
... However, the parvocellular neurons release their secretory products into fenestrated capillaries that drain into the long portal vessels that drain into the anterior lobe. The magnocellular neurons secrete either vasopressin or oxytocin, and are largely concentrated in the supraoptic (SON) and parav ...
Visual Field - Warren`s Science Page
... Makes mistake because of nervous system construction Sensory inputs of ...
... Makes mistake because of nervous system construction Sensory inputs of ...
the autonomic nervous system
... Sympathetic stimulation often activates many different kinds of effector organs at the same time as a result of CNS stimulation or epinephrine and norepinephrine release from the adrenal medulla. ...
... Sympathetic stimulation often activates many different kinds of effector organs at the same time as a result of CNS stimulation or epinephrine and norepinephrine release from the adrenal medulla. ...
Islamic University Nursing College Final Exam,summer Anatomy
... III-Put / or X between the brackets (20 points) ( ) Pronation is opposite to rotation ( ) The posterior root of the spinal nerve contains sensory neurons only ( ) Most of the endocrine system is regulated by negative feedback mechanisms ( ) The cardiac muscle is striated and branched ( ) T3 & T4 hor ...
... III-Put / or X between the brackets (20 points) ( ) Pronation is opposite to rotation ( ) The posterior root of the spinal nerve contains sensory neurons only ( ) Most of the endocrine system is regulated by negative feedback mechanisms ( ) The cardiac muscle is striated and branched ( ) T3 & T4 hor ...
Jackson Rancheria Casino Shooting
... reflects its activity. Because of its complexity, the structures of the nervous system are described in terms of two principal divisions—the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS, consisting of the brain and spinal cord, interprets incoming sensory information ...
... reflects its activity. Because of its complexity, the structures of the nervous system are described in terms of two principal divisions—the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS, consisting of the brain and spinal cord, interprets incoming sensory information ...
Endocrine System: Overview
... Somatic Motor Pathways 9. What two main somatic motor pathways convey action potentials to skeletal muscles? ...
... Somatic Motor Pathways 9. What two main somatic motor pathways convey action potentials to skeletal muscles? ...
Document
... brain’s own pain killers. (These are considered neuromodulators rather than neurotransmitters when they are produced in other than the presynaptic neuron.) ...
... brain’s own pain killers. (These are considered neuromodulators rather than neurotransmitters when they are produced in other than the presynaptic neuron.) ...
The Anatomy of Language Sydney Lamb Rice University, Houston
... Provides long-distance connections between cortical columns Consists of axons of pyramidal neurons The cell bodies of those neurons are in the gray matter Each such axon is surrounded by a myelin sheath, which.. ...
... Provides long-distance connections between cortical columns Consists of axons of pyramidal neurons The cell bodies of those neurons are in the gray matter Each such axon is surrounded by a myelin sheath, which.. ...
8Neurotrophins PCD
... them often have no blatant developmental abnormalities – or at least, can survive. Note: autocrine, paracrine, afferants (anterograde transport). 3. BDNF, NT3, NT4, and their receptors are most widespread in the brain (NGF less so mostly periphery), particularly in the cortex and hippocampus. ...
... them often have no blatant developmental abnormalities – or at least, can survive. Note: autocrine, paracrine, afferants (anterograde transport). 3. BDNF, NT3, NT4, and their receptors are most widespread in the brain (NGF less so mostly periphery), particularly in the cortex and hippocampus. ...
Unit IV-D Outline
... away from the cell body and send them either to other neurons or to effectors, range in length from less than a centimeter to more than one meter f. Schwann cells – produce layers of a white, fatty substance called myelin which covers the axon, gaps between neighboring cells are called nodes of Ranv ...
... away from the cell body and send them either to other neurons or to effectors, range in length from less than a centimeter to more than one meter f. Schwann cells – produce layers of a white, fatty substance called myelin which covers the axon, gaps between neighboring cells are called nodes of Ranv ...
Basic Anatomy and Terminology of the Head and Brain Scalp and
... complex has numerous roles, with involvement in endocrine (hormone) function, hunger, thirst, satiation, temperature regulation, sweating, water balance, short-term memory, sexual function and emotion. Basal Ganglia, Thalamus, and Hypothalamus ...
... complex has numerous roles, with involvement in endocrine (hormone) function, hunger, thirst, satiation, temperature regulation, sweating, water balance, short-term memory, sexual function and emotion. Basal Ganglia, Thalamus, and Hypothalamus ...
Nolte Chapter 9 – Sensory Receptors and the Peripheral Nervous
... that increases the probability of its openings. These same channels have binding sites for various botanical molecules, leading to the warm and cool feelings of chili peppers and menthol. Nociceptors can detect stimuli that provide nxious levels of heat or cold or chemicals that are released by dama ...
... that increases the probability of its openings. These same channels have binding sites for various botanical molecules, leading to the warm and cool feelings of chili peppers and menthol. Nociceptors can detect stimuli that provide nxious levels of heat or cold or chemicals that are released by dama ...