Elicited Behavior Chapter 2 pp. 32-53 and the internet if you can`t
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
Biology Name____________________ Introduction to the Nervous
... Identify whether the characteristic or structure is true of or part of the central nervous system (CNS) or the peripheral nervous system (PNS). ______ Brain ______ Spinal Cord ______ Nerves ______ Integrates and coordinates sensory data and motor commands ______ Center of higher functions (intellige ...
... Identify whether the characteristic or structure is true of or part of the central nervous system (CNS) or the peripheral nervous system (PNS). ______ Brain ______ Spinal Cord ______ Nerves ______ Integrates and coordinates sensory data and motor commands ______ Center of higher functions (intellige ...
Action_ Resting_Potential
... Unlike an action potential, a PSP doesn’t conform to the all-or-none law. At any one time, a single neuron can receive a huge number of excitatory PSPs and inhibitory PSPs because its dendrites are influenced by axons from many other neurons. Whether or not an action potential is generated in the ne ...
... Unlike an action potential, a PSP doesn’t conform to the all-or-none law. At any one time, a single neuron can receive a huge number of excitatory PSPs and inhibitory PSPs because its dendrites are influenced by axons from many other neurons. Whether or not an action potential is generated in the ne ...
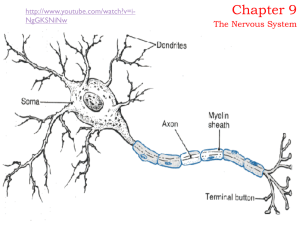
Chapter 9 Nerves
... Fill spaces, support neurons, hold nervous tissue togther, produce myelin, help regulate the concentrations of nutrients and ions, carry ...
... Fill spaces, support neurons, hold nervous tissue togther, produce myelin, help regulate the concentrations of nutrients and ions, carry ...
a positive electrical signal
... The binding of neurotransmitters to the receptors of dendrites triggers the opening of a few Na+ channels This causes a slightly positive charge When the charge reaches the threshold (-55mV), many voltagecontrolled Na+ channels open, causing a flood of positive charges ...
... The binding of neurotransmitters to the receptors of dendrites triggers the opening of a few Na+ channels This causes a slightly positive charge When the charge reaches the threshold (-55mV), many voltagecontrolled Na+ channels open, causing a flood of positive charges ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... Chapter 48 – Neurons, Synapses and Signaling – Homework 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contra ...
... Chapter 48 – Neurons, Synapses and Signaling – Homework 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contra ...
Nervous System Cells
... This process continues as a chain-reaction along the axon. The influx of sodium depolarizes the axon, and the ourflow of potassium repolarizes the axon. ...
... This process continues as a chain-reaction along the axon. The influx of sodium depolarizes the axon, and the ourflow of potassium repolarizes the axon. ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... What name is given to the electrical-type message that travels along a neuron? ...
... What name is given to the electrical-type message that travels along a neuron? ...
here
... 22. Draw a graph and label the following: polarization, stimulus, full depolarization, action potential, repolarization, refractory period. Use units on your y axis. ...
... 22. Draw a graph and label the following: polarization, stimulus, full depolarization, action potential, repolarization, refractory period. Use units on your y axis. ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CH 48 AND 49
... D. How the nerve impulse moves from one cell to another • The space between two nerve cells is called a synapse • Two nerves communicate with each other by synaptic signaling • How: – When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, it stimulates the release of neurotransmitters into the syna ...
... D. How the nerve impulse moves from one cell to another • The space between two nerve cells is called a synapse • Two nerves communicate with each other by synaptic signaling • How: – When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, it stimulates the release of neurotransmitters into the syna ...
Text 4-Nervous system: Organization and Physiology
... •Real neurons receive as many as 200,000 synapses each •Ion flows from all inputs summate or average at the initial segment •An action potential in the postsynaptic neuron occurs if the membrane potential at the initial segment reaches threshold ...
... •Real neurons receive as many as 200,000 synapses each •Ion flows from all inputs summate or average at the initial segment •An action potential in the postsynaptic neuron occurs if the membrane potential at the initial segment reaches threshold ...
Technical Definitions
... the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a “bigger” response; the neuron simply fires as opposed to not firing. If the stimulus does not exceed this potential, the neuron will not fire at all (Redman, 1990). Comparison and Contrast: Most n ...
... the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a “bigger” response; the neuron simply fires as opposed to not firing. If the stimulus does not exceed this potential, the neuron will not fire at all (Redman, 1990). Comparison and Contrast: Most n ...
Nerve activates contraction - Silver Falls School District
... Found in neural pathways in CNS Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
... Found in neural pathways in CNS Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
PowerPoint for 9/29
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
Slide 1
... Voltage-gated – responds to a change in the membrane potential. Stretch or pressure gated – mechanical forces. ...
... Voltage-gated – responds to a change in the membrane potential. Stretch or pressure gated – mechanical forces. ...
The NERVOUS System
... -regulates the activity of cardiac and smooth muscles. -regulates hormonal activity ...
... -regulates the activity of cardiac and smooth muscles. -regulates hormonal activity ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.