Objectives included for the test File
... VI- Nerves State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that can carry rapid electrical impulses. Draw and label a diagram of the structure of a motor neuron. State that nerve impulses are conducted from rec ...
... VI- Nerves State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that can carry rapid electrical impulses. Draw and label a diagram of the structure of a motor neuron. State that nerve impulses are conducted from rec ...
Neuron Structure
... • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC binds to receptors, person feels high!!! • No THC in chocolate, but there are chemicals in choc that act like THC • You would have to eat 25 lbs of choc to ...
... • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC binds to receptors, person feels high!!! • No THC in chocolate, but there are chemicals in choc that act like THC • You would have to eat 25 lbs of choc to ...
Nervous - Lamont High
... • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC binds to receptors, person feels high!!! • No THC in chocolate, but there are chemicals in choc that act like THC • You would have to eat 25 lbs of choc to ...
... • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC binds to receptors, person feels high!!! • No THC in chocolate, but there are chemicals in choc that act like THC • You would have to eat 25 lbs of choc to ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 3. Which division of the nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord? 4. Draw two touching neurons in which a nerve impulse moves from the one on the left to the one on the right. (Use Figure 48.4 as a reference) Label the following elements: cell body, dendrites, axon, synapse, presynaptic ce ...
... 3. Which division of the nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord? 4. Draw two touching neurons in which a nerve impulse moves from the one on the left to the one on the right. (Use Figure 48.4 as a reference) Label the following elements: cell body, dendrites, axon, synapse, presynaptic ce ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 3. Which division of the nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord? 4. Draw two touching neurons in which a nerve impulse moves from the one on the left to the one on the right. (Use Figure 48.4 as a reference) Label the following elements: cell body, dendrites, axon, synapse, presynaptic ce ...
... 3. Which division of the nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord? 4. Draw two touching neurons in which a nerve impulse moves from the one on the left to the one on the right. (Use Figure 48.4 as a reference) Label the following elements: cell body, dendrites, axon, synapse, presynaptic ce ...
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
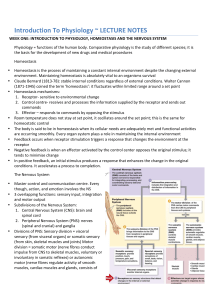
... 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes the information supplied by the receptor and sends out commands 3. Effector – responds to commands by opposing the stimulus Room temperature does not stay at set ...
... 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes the information supplied by the receptor and sends out commands 3. Effector – responds to commands by opposing the stimulus Room temperature does not stay at set ...
Q1 (from chapter 1)
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
File
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
Drugs Change the way Neurons communicate
... • Alcohol binds to GABA receptors on the dendrites of neurons which release GABA as their neurotransmitter. • Alcohol is an inhibitory signal (CNS depressant) so it reduces the activity of the presynaptic neuron (which releases GABA as its neurotransmitter). • The presynaptic neuron will release les ...
... • Alcohol binds to GABA receptors on the dendrites of neurons which release GABA as their neurotransmitter. • Alcohol is an inhibitory signal (CNS depressant) so it reduces the activity of the presynaptic neuron (which releases GABA as its neurotransmitter). • The presynaptic neuron will release les ...
PPTX - Bonham Chemistry
... Hormone: A chemical messenger released by an endocrine gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse ...
... Hormone: A chemical messenger released by an endocrine gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse ...
Neurotransmitter proteins
... proteins sent from one cell to another • Steps: – Impulse reaches neuron’s terminal (end) – Vesicle releases neurotransmitters, which attach to receptors on neighbor – New impulse created ...
... proteins sent from one cell to another • Steps: – Impulse reaches neuron’s terminal (end) – Vesicle releases neurotransmitters, which attach to receptors on neighbor – New impulse created ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
Chapter 7 Nervous System Every conscious action is governed by
... Motor – take impulses from the CNS to an effector (i.e. gland or muscle fiber) Nerve impulses move from the dendrite through the cell body and then down the axon From the axon terminus, the signal is transferred to the next neuron Nerve impulses Neurons function because without any impulse, ...
... Motor – take impulses from the CNS to an effector (i.e. gland or muscle fiber) Nerve impulses move from the dendrite through the cell body and then down the axon From the axon terminus, the signal is transferred to the next neuron Nerve impulses Neurons function because without any impulse, ...
Chapter 5: SENSATION - Charles Best Library
... Transmitted via the bones of the middle ear (the hammer, anvil, and stirrup) to the fluid-filled cochlea in the inner ear, these vibrations create movement in tiny hair cells on the basilar membrane, triggering neural messages to be sent (via the thalamus) to the auditory cortex in the brain. ...
... Transmitted via the bones of the middle ear (the hammer, anvil, and stirrup) to the fluid-filled cochlea in the inner ear, these vibrations create movement in tiny hair cells on the basilar membrane, triggering neural messages to be sent (via the thalamus) to the auditory cortex in the brain. ...
Learning Objectives
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
Nervous System Notes
... amplitude, action potentials are all-or-none 2. Duration – graded potentials are much longer (several milliseconds to several minutes) than action potentials (1/2 to 2 milliseconds) 3. Channels – graded use chemically, mechanically and light gated ion channels, action potentials use voltage gated ch ...
... amplitude, action potentials are all-or-none 2. Duration – graded potentials are much longer (several milliseconds to several minutes) than action potentials (1/2 to 2 milliseconds) 3. Channels – graded use chemically, mechanically and light gated ion channels, action potentials use voltage gated ch ...
Neuron, Impulse Generation, and Reflex Arc
... neurotransmitters stored in vesicles in the axon bulb. They are released when triggered by an action potential arriving at the axon bulb of the pre-synaptic neuron. The action potential causes an influx of Ca2+ into the axon bulb and Ca causes the vesicles to fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane (exo ...
... neurotransmitters stored in vesicles in the axon bulb. They are released when triggered by an action potential arriving at the axon bulb of the pre-synaptic neuron. The action potential causes an influx of Ca2+ into the axon bulb and Ca causes the vesicles to fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane (exo ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.