Lecture 2 (Neurons)
... Neuron – A specialized cell of the body that can communicate information quickly by using ionic currents and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Nerve - Many neurons that are bundled together and covered by a connective tissue sheath. Nervous System – The entire network of interconnecting neu ...
... Neuron – A specialized cell of the body that can communicate information quickly by using ionic currents and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Nerve - Many neurons that are bundled together and covered by a connective tissue sheath. Nervous System – The entire network of interconnecting neu ...
Nervous System III
... • Receptors in internal organs • Conveys info such as fullness, gas, pain originating from internal organs ...
... • Receptors in internal organs • Conveys info such as fullness, gas, pain originating from internal organs ...
File
... Overview of the Nervous System • STRUCTURES: brain, spinal cord, & peripheral nerves • FUNCTION: Recognizes and coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments ...
... Overview of the Nervous System • STRUCTURES: brain, spinal cord, & peripheral nerves • FUNCTION: Recognizes and coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments ...
Cellular and Molecul..
... • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...
... • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...
Bridget Lecture 2 Notes The Neurons o Functional classes (CNS
... ▪ Force of diffusion flows high to low into the cell ▪ Electrostatic pressure based on cell repulsion pushes the ion back out o Intracellular o Anion o High concentration K+ ...
... ▪ Force of diffusion flows high to low into the cell ▪ Electrostatic pressure based on cell repulsion pushes the ion back out o Intracellular o Anion o High concentration K+ ...
The somatic sensory system
... Somatosensory information ascends the spinal column along several pathways, which synapse at the midbrain &/or thalamus before reaching the cortex Sensory processes have different sub-modalities of somatosensory information Later stages of processing combine information across the submodalities, & w ...
... Somatosensory information ascends the spinal column along several pathways, which synapse at the midbrain &/or thalamus before reaching the cortex Sensory processes have different sub-modalities of somatosensory information Later stages of processing combine information across the submodalities, & w ...
48 - Groupfusion.net
... ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels. In the synapse illustrated here, both Na+ and K+ can diffuse through the channels 6) The neurotransmitter is released from the receptors, and the channels close. Synaptic transmission ends when the neurotransmitter diffuses out of the ...
... ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels. In the synapse illustrated here, both Na+ and K+ can diffuse through the channels 6) The neurotransmitter is released from the receptors, and the channels close. Synaptic transmission ends when the neurotransmitter diffuses out of the ...
Structure of a Neuron
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
Nerves Ganglia Spinal nerves Cranial nerves Afferent neurons
... Division of the ANS that regulates resting and nutrition-related functions such as digestion, defecation, and urination ...
... Division of the ANS that regulates resting and nutrition-related functions such as digestion, defecation, and urination ...
Print › Nervous System | Quizlet
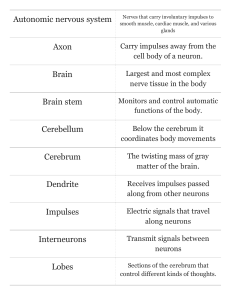
... Nerves that carry involuntary impulses to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and various ...
... Nerves that carry involuntary impulses to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and various ...
nervous tissue organization neurons neuroglia action potentials
... synaptic plasticity = the ability of a synapse to change synaptic potentiation = ability to make transmission easier immediate = able to hold for a few seconds short term = remember for a few sec to hours, then forgotten working = stored in brain & can be recalled by new input, facilitated synapses ...
... synaptic plasticity = the ability of a synapse to change synaptic potentiation = ability to make transmission easier immediate = able to hold for a few seconds short term = remember for a few sec to hours, then forgotten working = stored in brain & can be recalled by new input, facilitated synapses ...
Power Point
... end of the axon/synaptic knob – The action potential cannot cross the synaptic cleft • Causes neurotransmitters to be released from vesicles in the synaptic knob ...
... end of the axon/synaptic knob – The action potential cannot cross the synaptic cleft • Causes neurotransmitters to be released from vesicles in the synaptic knob ...
Nervous Systems
... • Carrying information to and from the brain • Integration of simple responses ...
... • Carrying information to and from the brain • Integration of simple responses ...
Dynamic Equilibrium Review 1. Describe the structure and function
... How does this important to a neuron? The outside of the cell is more positive, relative to the inside. This assists in ion exchange (Na+ in, K+ out) that is the process of neuron firing. 3. How is both passive and active transport part of the function of a neuron? Sodium will rush in once the ion ch ...
... How does this important to a neuron? The outside of the cell is more positive, relative to the inside. This assists in ion exchange (Na+ in, K+ out) that is the process of neuron firing. 3. How is both passive and active transport part of the function of a neuron? Sodium will rush in once the ion ch ...
neurons
... Neurotransmitters in the synapse are reabsorbed into the sending neurons through the process of ...
... Neurotransmitters in the synapse are reabsorbed into the sending neurons through the process of ...
Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term…
... This is mostly review for those of you that took 2606 The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells ...
... This is mostly review for those of you that took 2606 The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells ...
Carrie Heath
... 12. What are the advantages for using the squid giant neuron for experiments rather than using mammalian neurons? 13. What structures make up the blood brain barrier and what is its function? 14. What are the three input vessels and the three output vessels to the Circle of Willis? Why is this consi ...
... 12. What are the advantages for using the squid giant neuron for experiments rather than using mammalian neurons? 13. What structures make up the blood brain barrier and what is its function? 14. What are the three input vessels and the three output vessels to the Circle of Willis? Why is this consi ...
Introduction to Anatomy
... basic properties of their cell membranes: 1. There is an electrical voltage, called the resting membrane potential, across the cell membrane. 2. Their cell membranes contain a variety of ion channels (pores) that may be open or ...
... basic properties of their cell membranes: 1. There is an electrical voltage, called the resting membrane potential, across the cell membrane. 2. Their cell membranes contain a variety of ion channels (pores) that may be open or ...
Bioenergetics - Eastern Michigan University
... – Repolarization • Change in membrane permeability, restoring resting membrane potential ...
... – Repolarization • Change in membrane permeability, restoring resting membrane potential ...
Receptors and Neurotransmitters
... . This neurotransmitter is involved in the control of skeletal muscle action in the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), stimulating skeletal muscle contraction at neuromuscular junctions. It can excite or inhibit ANS synapses. Most of the postganglionic fibers of th ...
... . This neurotransmitter is involved in the control of skeletal muscle action in the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), stimulating skeletal muscle contraction at neuromuscular junctions. It can excite or inhibit ANS synapses. Most of the postganglionic fibers of th ...
Somatosensory 2
... The sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Some stimuli that activate nociceptors: Thermal: high heat or extreme cold Mechanical: Intense mechanical stimuli Chemical: Irrita ...
... The sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Some stimuli that activate nociceptors: Thermal: high heat or extreme cold Mechanical: Intense mechanical stimuli Chemical: Irrita ...
The Nervous System
... Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicles 5. Give the role and position of three types of neuron: a. sensory neurons - carry messages from the sense organ to the CNS b. motor neurons ...
... Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicles 5. Give the role and position of three types of neuron: a. sensory neurons - carry messages from the sense organ to the CNS b. motor neurons ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.