Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
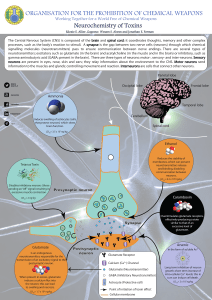
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
The Nervous System : communication
... inhalation, swallowing or absorption through eyes or mouth Strychnine is a neurotoxin which acts as an antagonist of acetylcholine receptors. It primarily affects the motor nerves in the spinal cord which control muscle contraction. An impulse is triggered at one end of a nerve by the binding of neu ...
... inhalation, swallowing or absorption through eyes or mouth Strychnine is a neurotoxin which acts as an antagonist of acetylcholine receptors. It primarily affects the motor nerves in the spinal cord which control muscle contraction. An impulse is triggered at one end of a nerve by the binding of neu ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior: The Neuron
... Norepinephrine: (NE) This compound is secreted principally from the adrenal gland. Contributes to the modulation of mood and arousal. Cocaine and amphetamines elevate activity at the NE synapses. Dopamine: (DA) Dopamine facilitates critical brain functions and voluntary movement, pleasurable emotion ...
... Norepinephrine: (NE) This compound is secreted principally from the adrenal gland. Contributes to the modulation of mood and arousal. Cocaine and amphetamines elevate activity at the NE synapses. Dopamine: (DA) Dopamine facilitates critical brain functions and voluntary movement, pleasurable emotion ...
Neurophysiology-Organization of central nervous system
... When they convert these energy into electrical energy, they transmit action potential through afferent neuron bcoz what reach cerebral cortex only nerve impulse (action potential) wither the sensation was touch, pressure,……….. etc. BUT how can I discriminate this kind of sensation as touch or tempe ...
... When they convert these energy into electrical energy, they transmit action potential through afferent neuron bcoz what reach cerebral cortex only nerve impulse (action potential) wither the sensation was touch, pressure,……….. etc. BUT how can I discriminate this kind of sensation as touch or tempe ...
document
... Postsynaptic potentials are produced by the flow of ions in and out of the cell. Each NT produces a specific postsynaptic potential ...
... Postsynaptic potentials are produced by the flow of ions in and out of the cell. Each NT produces a specific postsynaptic potential ...
Lecture 12
... perception - conscious registration of conditions stimulus - change that can initiate nerve impulse receptor (sense organ) - converts stimulus to impulse transduction - changing stimulus signal into nerve signal generator potential - electrical impulse in receptor receptor potential - receptor relea ...
... perception - conscious registration of conditions stimulus - change that can initiate nerve impulse receptor (sense organ) - converts stimulus to impulse transduction - changing stimulus signal into nerve signal generator potential - electrical impulse in receptor receptor potential - receptor relea ...
Notes Outline I (Part I)
... __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are otherwise know as ________________ _______________. 21. Movement of s ...
... __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are otherwise know as ________________ _______________. 21. Movement of s ...
Powerpoint
... – Na+ permeability suddenly increases, resulting in an inward rush (action potential) ...
... – Na+ permeability suddenly increases, resulting in an inward rush (action potential) ...
Chapter 12 The Nervous System
... • The nervous system is responsible for receiving information from internal and external stimuli and then respond quickly to that information. ...
... • The nervous system is responsible for receiving information from internal and external stimuli and then respond quickly to that information. ...
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
... B. Neurons- excitable little cells that make use of their potential! C. Functional Properties of Neurons 1. Irritability- neurons have the ability to respond to a stimulus 2. Conductivity- the ability to transmit an impulse 3. The plasma membrane at rest is polarized, this is called the Resting pot ...
... B. Neurons- excitable little cells that make use of their potential! C. Functional Properties of Neurons 1. Irritability- neurons have the ability to respond to a stimulus 2. Conductivity- the ability to transmit an impulse 3. The plasma membrane at rest is polarized, this is called the Resting pot ...
Nervous system lecture 1
... potentials at the axon hillock can bring about an action potential or inhibit the generation of the action potential. – Spatial: stimulation by many neurons at one time. – Temporal: increased numbers of impulses per minute. ...
... potentials at the axon hillock can bring about an action potential or inhibit the generation of the action potential. – Spatial: stimulation by many neurons at one time. – Temporal: increased numbers of impulses per minute. ...
overview of neural f..
... The sodium-potassium pump is an active process that returns & maintains levels of Na+ and K+ ...
... The sodium-potassium pump is an active process that returns & maintains levels of Na+ and K+ ...
Sensory Systems - Cedar Crest College
... • “What kind” information is transmitted by which neurons respond to the signal • “How much” information is transmitted by the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
... • “What kind” information is transmitted by which neurons respond to the signal • “How much” information is transmitted by the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
Slide ()
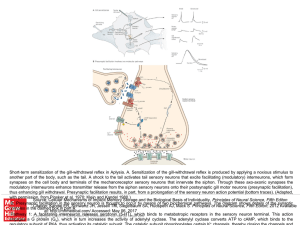
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
CH 8 Nervous part 1
... humans and animals and can occur by inhalation, swallowing or absorption through eyes or mouth Strychnine is a neurotoxin which acts as an antagonist of acetylcholine receptors. It primarily affects the motor nerves in the spinal cord which control muscle contraction. An impulse is triggered at one ...
... humans and animals and can occur by inhalation, swallowing or absorption through eyes or mouth Strychnine is a neurotoxin which acts as an antagonist of acetylcholine receptors. It primarily affects the motor nerves in the spinal cord which control muscle contraction. An impulse is triggered at one ...
Nervous System notes
... b. functional- based on the direction in which they transmit nerve impulses - sensory (afferent) – transmit form receptors in skin, sensory organs muscles, joints, and viscera to the brain and spinal cord - motor (efferent) – convey impulses from brain and spinal cord to effectors which may be muscl ...
... b. functional- based on the direction in which they transmit nerve impulses - sensory (afferent) – transmit form receptors in skin, sensory organs muscles, joints, and viscera to the brain and spinal cord - motor (efferent) – convey impulses from brain and spinal cord to effectors which may be muscl ...
Ch.10
... potassium, and calcium. Ion pumps and channels generate resting and action potentials. • Sodium/potassium pump uses energy to move the ions against their concentration gradient. • K+ leaks out, because the membrane is more permeable to K+, and Na/K pump keeps the concentration of K+ inside the cell ...
... potassium, and calcium. Ion pumps and channels generate resting and action potentials. • Sodium/potassium pump uses energy to move the ions against their concentration gradient. • K+ leaks out, because the membrane is more permeable to K+, and Na/K pump keeps the concentration of K+ inside the cell ...
the nervous system
... • Long axons are covered in a myelin sheath • Nodes of Ranvier are intermittent gaps in the sheath ...
... • Long axons are covered in a myelin sheath • Nodes of Ranvier are intermittent gaps in the sheath ...
5-2_NeurotransmRelease_BenseM
... Neurotransmitters are endogenous bioactive substances, synthesized by neurons, and that are released from the cells, act via specific receptors, coupled to the membrane of postsynaptic target, structure and modify the electric and metabolic conditions of the affected cells. Main stages of neurotrans ...
... Neurotransmitters are endogenous bioactive substances, synthesized by neurons, and that are released from the cells, act via specific receptors, coupled to the membrane of postsynaptic target, structure and modify the electric and metabolic conditions of the affected cells. Main stages of neurotrans ...
SENSATION - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... different rates & causes neural impulses to be sent at different rates. Pitch is determined by how fast the neural signals move along to the brain. ...
... different rates & causes neural impulses to be sent at different rates. Pitch is determined by how fast the neural signals move along to the brain. ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.