Neuronal Activation in the Medulla Oblongata During Selective
... same neural pathways may be involved in each. Our interest is in which part of these pathways are involved when only the LAR is elicited. Because the LAR can be elicited using a single stimulus (Sasaki and Suzuki 1976), we used a very low rate of stimulation, 0.5 Hz, to prevent the occurrence of swa ...
... same neural pathways may be involved in each. Our interest is in which part of these pathways are involved when only the LAR is elicited. Because the LAR can be elicited using a single stimulus (Sasaki and Suzuki 1976), we used a very low rate of stimulation, 0.5 Hz, to prevent the occurrence of swa ...
1 - Libreria Universo
... and prostaglandin F2a) appear to play a crucial role in this process [22, 23]. These substances activate G-protein coupled receptors that initiate a cascade leading to the increased production of inositol triphosphate and diacylglycerol. In turn, these substances lead to an increase in intracellular ...
... and prostaglandin F2a) appear to play a crucial role in this process [22, 23]. These substances activate G-protein coupled receptors that initiate a cascade leading to the increased production of inositol triphosphate and diacylglycerol. In turn, these substances lead to an increase in intracellular ...
Neuronal morphology in the African elephant (Loxodonta africana
... Deep pyramidal neurons were qualitatively described according to nomenclature found in previous neuromorphological research (e.g., Ngowyang 1932; Ferrer et al. 1986a, b). Descriptions for each neuron used qualitative criteria, such as cortical location, size, dendritic field patterns, presence of sp ...
... Deep pyramidal neurons were qualitatively described according to nomenclature found in previous neuromorphological research (e.g., Ngowyang 1932; Ferrer et al. 1986a, b). Descriptions for each neuron used qualitative criteria, such as cortical location, size, dendritic field patterns, presence of sp ...
Placing prediction into the fear circuit
... fear responses after being paired with an aversive US, so it is natural to regard these pathways as carrying a teaching signal that instructs learning, and synaptic plasticity, across CS–US pairings. Aversive USs might act as teaching signals to trigger plasticity at CS input synapses to the LA, at ...
... fear responses after being paired with an aversive US, so it is natural to regard these pathways as carrying a teaching signal that instructs learning, and synaptic plasticity, across CS–US pairings. Aversive USs might act as teaching signals to trigger plasticity at CS input synapses to the LA, at ...
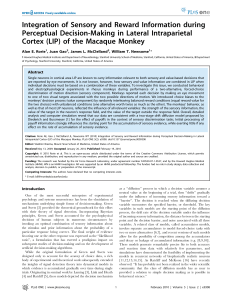
Integration of Sensory and Reward Information
... 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Neurobiology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, United States of America, 2 Department of Psychology, Stanford University, Stanford, California, United States of America ...
... 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Neurobiology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, United States of America, 2 Department of Psychology, Stanford University, Stanford, California, United States of America ...
Orientadora de Dissertação DOUTORA RAQUEL DE ORNELAS
... List of figures Figure 1. Sensory saccular epithelium from adult (20-23cm SL) to posthatched fry (1.3-1.4 cm SL) divided in three main areas separated by the dashed line: Rostral, Middle and Caudal (From left to right). The arrows represent the length and width of each area. The Rostral width was d ...
... List of figures Figure 1. Sensory saccular epithelium from adult (20-23cm SL) to posthatched fry (1.3-1.4 cm SL) divided in three main areas separated by the dashed line: Rostral, Middle and Caudal (From left to right). The arrows represent the length and width of each area. The Rostral width was d ...
BMP4 expression in the adult rat brain
... early development of central nervous system (CNS), little information is available for its expression in the adult CNS. We, thus, investigated BMP4 expression in the adult rat CNS using immunohistochemistry. BMP4 is intensely expressed in most neurons and their dendrites. In addition, intense BMP4 e ...
... early development of central nervous system (CNS), little information is available for its expression in the adult CNS. We, thus, investigated BMP4 expression in the adult rat CNS using immunohistochemistry. BMP4 is intensely expressed in most neurons and their dendrites. In addition, intense BMP4 e ...
NEUROTRANSMITTER SYSTEMS IN THE VISUAL CORTEX OF
... is focused on NMDA receptors channel which is permeable to Ca++ ions only if the postsynaptic membrane is sufficiently depolarized. Thus the NMDA receptor permits current flow only if there is coincident pre- and postsynaptic activation (26). Therefore it is not surprising that the involvement of NM ...
... is focused on NMDA receptors channel which is permeable to Ca++ ions only if the postsynaptic membrane is sufficiently depolarized. Thus the NMDA receptor permits current flow only if there is coincident pre- and postsynaptic activation (26). Therefore it is not surprising that the involvement of NM ...
Layer II/III of the Prefrontal Cortex: Inhibition by the Serotonin
... BX50WI microscope. Regular ACSF at 31⫺33°C was bubbled with 95% oxygen and 5% carbon dioxide and flowed over the slice at a rate of 3– 4 ml/min. The temperatures used during brain removal and recordings were found to be critical for measuring serotonin currents. ...
... BX50WI microscope. Regular ACSF at 31⫺33°C was bubbled with 95% oxygen and 5% carbon dioxide and flowed over the slice at a rate of 3– 4 ml/min. The temperatures used during brain removal and recordings were found to be critical for measuring serotonin currents. ...
Total Wiring Length Minimization of C. elegans Neural
... not significantly vary from animal to animal. In particular, number of neurons (302) in the hermaphrodite worm is consistent across the individuals [1, 2], and synapses (both chemical synapses and electric gap junctions) are stereotypical with more than 75% reproducibility [3]. This consistency make ...
... not significantly vary from animal to animal. In particular, number of neurons (302) in the hermaphrodite worm is consistent across the individuals [1, 2], and synapses (both chemical synapses and electric gap junctions) are stereotypical with more than 75% reproducibility [3]. This consistency make ...
CCNBook/Neuron
... capturing important cognitive phenomena. This level of modeling explores how consideration of neural mechanisms inform the workings of the mind, and reciprocally, how cognitive and computational constraints afford a richer understanding of the problems these mechanisms evolved to solve. It can thus ...
... capturing important cognitive phenomena. This level of modeling explores how consideration of neural mechanisms inform the workings of the mind, and reciprocally, how cognitive and computational constraints afford a richer understanding of the problems these mechanisms evolved to solve. It can thus ...
Galanin in Alzheimer s disease: Neuroinhibitory or neuroprotective?
... GAL has facilitated the study of GAL overexpression in the brain and provides a unique model for the investigation of this peptide in the area of cognition [14, 86]. For example, mice expressing GAL ectopically under control of the dopamine b-hydroxylase promoter (GAL-tg mice) displayed increased GA ...
... GAL has facilitated the study of GAL overexpression in the brain and provides a unique model for the investigation of this peptide in the area of cognition [14, 86]. For example, mice expressing GAL ectopically under control of the dopamine b-hydroxylase promoter (GAL-tg mice) displayed increased GA ...
Chemosensory pathways in the brainstem controlling
... of cardiac vagal motoneurons ensures that any stimulus that enhances inspiration actively increases heart rate (by vagal withdrawal), while inputs, peripheral or central, that suppress ventilation or prolong expiration lower heart rate via cardiac vagal activation. Populations of cardiac vagal moton ...
... of cardiac vagal motoneurons ensures that any stimulus that enhances inspiration actively increases heart rate (by vagal withdrawal), while inputs, peripheral or central, that suppress ventilation or prolong expiration lower heart rate via cardiac vagal activation. Populations of cardiac vagal moton ...
Imaging development and plasticity in the mouse visual system
... Neuronal activity, both intrinsically generated and sensory-evoked, is known to play an important role in the development of the brain. Sensory experiences continue to exert a strong influence on the functional connectivity of neuronal circuits, especially in the cerebral cortex, allowing for learni ...
... Neuronal activity, both intrinsically generated and sensory-evoked, is known to play an important role in the development of the brain. Sensory experiences continue to exert a strong influence on the functional connectivity of neuronal circuits, especially in the cerebral cortex, allowing for learni ...
C-fos Expression in the Pons and Medulla of the Cat during
... Tables I, 2). Because the activity in a number of pontomedullary structures is known to be correlated during active sleep, a multivariate method for comparing mean profiles between groups, such as a multivariate ANOVA (MANOVA) test, is necessary. However, a MANOVA comparison of mean profiles require ...
... Tables I, 2). Because the activity in a number of pontomedullary structures is known to be correlated during active sleep, a multivariate method for comparing mean profiles between groups, such as a multivariate ANOVA (MANOVA) test, is necessary. However, a MANOVA comparison of mean profiles require ...
PDF file
... generated throughout the lifetime of each individual life. “Epi” here means “after”. By “epigenetic”, we mean that the genes inside every cell regulate, but do not totally determine, the developmental process of the body and the brain through which the body and the brain interact with the internal a ...
... generated throughout the lifetime of each individual life. “Epi” here means “after”. By “epigenetic”, we mean that the genes inside every cell regulate, but do not totally determine, the developmental process of the body and the brain through which the body and the brain interact with the internal a ...
Chapter 2 in PDF - International Clinic of Rehabilitation
... Phases for establishing theories related to movement systems both the development and complications of body functions, as well as the successive phases of a child’s neuropsychic development. Thus, the combined efforts of many researchers revealed the fundamental mechanisms involved in regulating th ...
... Phases for establishing theories related to movement systems both the development and complications of body functions, as well as the successive phases of a child’s neuropsychic development. Thus, the combined efforts of many researchers revealed the fundamental mechanisms involved in regulating th ...
Alan Peters
... or at a factory t h a t made bicycles. Nevertheless, it was a friendly neighborhood and not a bad place to grow up. Because the houses were so close to each other, the neighbors looked after one another and socialized; everyone knew everyone else's business, where the children were, and when anyone ...
... or at a factory t h a t made bicycles. Nevertheless, it was a friendly neighborhood and not a bad place to grow up. Because the houses were so close to each other, the neighbors looked after one another and socialized; everyone knew everyone else's business, where the children were, and when anyone ...
Neutrophil Contribution in Facilitating Optic Nerve Regeneration
... factor (LIF), and interleukin 6 (IL-6) were also tested in vitro for their capacity to induce axonal outgrowth; however, only oncomodulin induced a significant twofold rise in axonal outgrowth of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) (Kurimoto et al., 2013, their Fig. 5). From these studies, the authors con ...
... factor (LIF), and interleukin 6 (IL-6) were also tested in vitro for their capacity to induce axonal outgrowth; however, only oncomodulin induced a significant twofold rise in axonal outgrowth of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) (Kurimoto et al., 2013, their Fig. 5). From these studies, the authors con ...
The neural encoding of self-generated and externally applied
... afferents and their target neurons in the vestibular nuclei has been well characterized in alert behaving monkeys. Notably, neurons predominantly encode rotational head velocity and linear head ...
... afferents and their target neurons in the vestibular nuclei has been well characterized in alert behaving monkeys. Notably, neurons predominantly encode rotational head velocity and linear head ...
What and Where Information in the Caudate Tail Guides Saccades
... (“where”) information and object (“what”) information is roughly segregated into the dorsal and ventral cortical visual pathways (Mishkin et al., 1983; Goodale and Milner, 1992). This hypothetical scheme poses a problem, however, when we plan to make a motor action aiming at a particular object, say ...
... (“where”) information and object (“what”) information is roughly segregated into the dorsal and ventral cortical visual pathways (Mishkin et al., 1983; Goodale and Milner, 1992). This hypothetical scheme poses a problem, however, when we plan to make a motor action aiming at a particular object, say ...
Uncovering the Forgotten Effect of Superior Cervical Ganglia on
... edema and this swelling is responsible for the involvement. Changes in pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibers of oculomotor nerve result in mydriasis in the late phase of SAH (39). Oculomotor nerve palsy seems to be the most common cause of pupillary irregularities, but we believe that the role of th ...
... edema and this swelling is responsible for the involvement. Changes in pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibers of oculomotor nerve result in mydriasis in the late phase of SAH (39). Oculomotor nerve palsy seems to be the most common cause of pupillary irregularities, but we believe that the role of th ...
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY OF SLEEP By Dr. Mohammad
... “repeated difficulty with sleep initiation, maintenance, consolidation, or quality that occurs despite adequate time and opportunity for sleep and that results in some form of daytime ...
... “repeated difficulty with sleep initiation, maintenance, consolidation, or quality that occurs despite adequate time and opportunity for sleep and that results in some form of daytime ...
Potassium channels in C. elegans
... 2.1. Voltage-gated potassium channels Voltage-gated potassium channels are the largest class of 6TM channels. These channels are activated by depolarization, but function with a wide diversity of activation and inactivation kinetics. In mammals, these channels are widely expressed in brain, muscle a ...
... 2.1. Voltage-gated potassium channels Voltage-gated potassium channels are the largest class of 6TM channels. These channels are activated by depolarization, but function with a wide diversity of activation and inactivation kinetics. In mammals, these channels are widely expressed in brain, muscle a ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.