PDF
... belonged to bushy or stellate cell categories. The latencies of IPSPs evoked by stimulation of the contralateral AN ranged between 3.3 and 7.6 ms for the majority of neurons, and were similar to those of contralaterally-induced IPSPs in the PVCN and DCN [14]. As discussed previously [14], these late ...
... belonged to bushy or stellate cell categories. The latencies of IPSPs evoked by stimulation of the contralateral AN ranged between 3.3 and 7.6 ms for the majority of neurons, and were similar to those of contralaterally-induced IPSPs in the PVCN and DCN [14]. As discussed previously [14], these late ...
Introduction to United States Government, POSC 2103
... parts in the specific system of the body and interlocks the dependency of one system upon another with contributions of each system to the well being of the body as a whole. This course also begins the application of anatomy and physiology facts to the nursing process and its relationship to medical ...
... parts in the specific system of the body and interlocks the dependency of one system upon another with contributions of each system to the well being of the body as a whole. This course also begins the application of anatomy and physiology facts to the nursing process and its relationship to medical ...
NEUROSCIENCE 2. THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM 2.1
... of the CNS is highly conserved throughout the different species of vertebrates and during evolution. The major trend that can be observed is towards a progressive telencephalisation. The telencephalon of reptiles is only an appendix to the large olfactory bulb, while in mammals it makes up most of t ...
... of the CNS is highly conserved throughout the different species of vertebrates and during evolution. The major trend that can be observed is towards a progressive telencephalisation. The telencephalon of reptiles is only an appendix to the large olfactory bulb, while in mammals it makes up most of t ...
Spinal Cord – Gross Anatomy
... Has two grooves that run its length separating it into right and left halves ...
... Has two grooves that run its length separating it into right and left halves ...
Ch 17
... • Marine worms range in size from 10-40 cm • Known as acorn worms • Dioecious with external fertilization • Larval stage called tornaria, which eventually settle to the substrate and grow into adult form ...
... • Marine worms range in size from 10-40 cm • Known as acorn worms • Dioecious with external fertilization • Larval stage called tornaria, which eventually settle to the substrate and grow into adult form ...
[j26]Chapter 8#
... critical interpretive areas and are vital relay centers for information traveling into and out of the brain. In addition, these more primitive areas of the brain provide essential electrical links to the many hormones released by the complex endocrine system. Triggered by nerve impulses, endocrine g ...
... critical interpretive areas and are vital relay centers for information traveling into and out of the brain. In addition, these more primitive areas of the brain provide essential electrical links to the many hormones released by the complex endocrine system. Triggered by nerve impulses, endocrine g ...
The Electrotonic Transformation: a Tool for Relating Neuronal Form
... inputs. Furthermore, membrane capacitance and cytoplasmic resistance dictate that membrane potential will almost never be uniform throughout a living neuron embedded in the circuitry of the brain. The combination of ever-changing synaptic inputs with cellular anatomical and biophysical properties gu ...
... inputs. Furthermore, membrane capacitance and cytoplasmic resistance dictate that membrane potential will almost never be uniform throughout a living neuron embedded in the circuitry of the brain. The combination of ever-changing synaptic inputs with cellular anatomical and biophysical properties gu ...
File
... The Peripheral Nervous System includes a- somatic and bautonomic nerves. Somatic nerves mediate voluntary movement. The autonomic nerves serve the involuntary action. At the cellular level The nervous system is defined by the presence of a special type of cell, called the neuron, also known as a "n ...
... The Peripheral Nervous System includes a- somatic and bautonomic nerves. Somatic nerves mediate voluntary movement. The autonomic nerves serve the involuntary action. At the cellular level The nervous system is defined by the presence of a special type of cell, called the neuron, also known as a "n ...
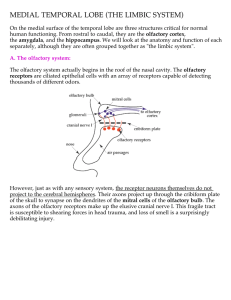
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
... cortex. In fact, they are GABA-ergic, unlike other cells of the same name. There are two populations of granule cells in the olfactory bulb - the external, or periglomerular cells, and the internal granule cells. The latter lie deep to the mitral cell layer. The mitral cell axons travel back to the ...
... cortex. In fact, they are GABA-ergic, unlike other cells of the same name. There are two populations of granule cells in the olfactory bulb - the external, or periglomerular cells, and the internal granule cells. The latter lie deep to the mitral cell layer. The mitral cell axons travel back to the ...
Organization of the Nervous System and Motor unit BY
... 3 Axon hillock بروزat which nerve impulses begin &pass in one direction from soma to the axon( nerve fiber) then to axon terminal. 4-Axon and axon terminal end on skeletal muscle via neuromuscular junction Nerve cell axons are very thin, about 1 micrometer. However, they are extraordinarily long. ...
... 3 Axon hillock بروزat which nerve impulses begin &pass in one direction from soma to the axon( nerve fiber) then to axon terminal. 4-Axon and axon terminal end on skeletal muscle via neuromuscular junction Nerve cell axons are very thin, about 1 micrometer. However, they are extraordinarily long. ...
Summary - VU Research Portal
... Each neuron the the primary visual cortex responds to a small area of the visual scene. This area is the receptive field of the neuron. A neuron with a receptive field that overlaps with a figure fires action potentials at a higher rate than neurons with a receptive field on a background. The differ ...
... Each neuron the the primary visual cortex responds to a small area of the visual scene. This area is the receptive field of the neuron. A neuron with a receptive field that overlaps with a figure fires action potentials at a higher rate than neurons with a receptive field on a background. The differ ...
This Week in The Journal - The Journal of Neuroscience
... Aix-Marseille Universite´, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, LNC Unite´ Mixte de Recherche 7291, 13331 Marseille Cedex 3, France, 2Amsterdam Center for the study of Adaptive Control in Brain and Behavior (Acacia), University of Amsterdam, 1018 XA Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and 3Amsterda ...
... Aix-Marseille Universite´, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, LNC Unite´ Mixte de Recherche 7291, 13331 Marseille Cedex 3, France, 2Amsterdam Center for the study of Adaptive Control in Brain and Behavior (Acacia), University of Amsterdam, 1018 XA Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and 3Amsterda ...
Loss of orexin/NARP neurons in human narcolepsy
... People with narcolepsy have a loss of orexin/hypocretin (ORX) immunoreactivity and mRNA, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of ORX are often reduced in patients with cataplexy. Mice and dogs lacking ORX or ORX receptors display narcolepsy-like symptoms similar to those observed in people. Further, mice ...
... People with narcolepsy have a loss of orexin/hypocretin (ORX) immunoreactivity and mRNA, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of ORX are often reduced in patients with cataplexy. Mice and dogs lacking ORX or ORX receptors display narcolepsy-like symptoms similar to those observed in people. Further, mice ...
September 21, 2011
... Synaptic sculpting (“pruning”) Synaptic connections strengthen and increase with use Synaptic connections dissolve and die with disuse Rate of sculpting decreases with age ...
... Synaptic sculpting (“pruning”) Synaptic connections strengthen and increase with use Synaptic connections dissolve and die with disuse Rate of sculpting decreases with age ...
Lecture notes for October 9, 2015 FINAL
... Delivers sensations to the CNS The cell body is in the dorsal or cranial root ganglion o Second-order neuron An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain o Third-order neuron Transmits information from the thalamus to the cerebral cortex Neurons in the sensory tracts are arr ...
... Delivers sensations to the CNS The cell body is in the dorsal or cranial root ganglion o Second-order neuron An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain o Third-order neuron Transmits information from the thalamus to the cerebral cortex Neurons in the sensory tracts are arr ...
Escape behavior and neuronal responses to looming stimuli in the
... displacements of the ball were prevented by four set points provided by two optical mice and by two flexible sheets located at right angles from each other. The rotation of the ball was recorded by the two mice that have their optical reading systems protected by transparent acetate sheets, which al ...
... displacements of the ball were prevented by four set points provided by two optical mice and by two flexible sheets located at right angles from each other. The rotation of the ball was recorded by the two mice that have their optical reading systems protected by transparent acetate sheets, which al ...
Extended Liquid Computing in Networks of Spiking Neurons
... that can cope with real-time computations on RNNs without the constraint of reaching stable states is called reservoir computing or liquid computing. One can use the latter expression to describe intuitively the motivations behind this new framework. Let us imagine that we can use a liquid (e.g a gl ...
... that can cope with real-time computations on RNNs without the constraint of reaching stable states is called reservoir computing or liquid computing. One can use the latter expression to describe intuitively the motivations behind this new framework. Let us imagine that we can use a liquid (e.g a gl ...
Fast and slow neurons in the nucleus of the
... TF combination for each neuron. At the end of the experiments, the birds were given an overdose of sodium pentobarbitol (100 mg/kg intraperitoneally (i.p.)) and immediately perfused with saline followed by 4% paraformaldehyde. The brains were extracted and sectioned such that the electrode tracts co ...
... TF combination for each neuron. At the end of the experiments, the birds were given an overdose of sodium pentobarbitol (100 mg/kg intraperitoneally (i.p.)) and immediately perfused with saline followed by 4% paraformaldehyde. The brains were extracted and sectioned such that the electrode tracts co ...
vocabulary - anatomy and physiology one
... Describe the relative and absolute refractory period and discuss their importance. Discuss how the absolute and relative refractory periods relate to depolarization and repolarization of the cell membrane. Define the term action potential frequency. Define the term subthreshold stimulus and its effe ...
... Describe the relative and absolute refractory period and discuss their importance. Discuss how the absolute and relative refractory periods relate to depolarization and repolarization of the cell membrane. Define the term action potential frequency. Define the term subthreshold stimulus and its effe ...
Cortical mechanisms of sensory learning and object recognition
... us are known to us only via brief, often occluded, twodimensional blips somewhere on our retina. The rest of the process is up to our brains, and will be based on a foundation of extensive visual experience. What is the nature of this constructive process? What parts of the brain are critical for ob ...
... us are known to us only via brief, often occluded, twodimensional blips somewhere on our retina. The rest of the process is up to our brains, and will be based on a foundation of extensive visual experience. What is the nature of this constructive process? What parts of the brain are critical for ob ...
Parallel Transformation of Tactile Signals in Central Circuits of
... manually clipped with fine forceps to approximately 25% of its full length. We chose this bristle because it is among the largest on the prothoracic leg (Hannah-Alava, 1958), and we found it more difficult to record spikes from smaller bristles. To record bristle neuron signals, a glass recording pi ...
... manually clipped with fine forceps to approximately 25% of its full length. We chose this bristle because it is among the largest on the prothoracic leg (Hannah-Alava, 1958), and we found it more difficult to record spikes from smaller bristles. To record bristle neuron signals, a glass recording pi ...
Neuronal Selectivities to Complex Object
... posterior IT and anterior IT was suggested on the basis of lesion studies (Iwai and Mishkin 1968), this concept has not been further developed, probably because of the lack of related data at the cellular level. As a step towards this goal, we compared selectivity of cell responses for complex objec ...
... posterior IT and anterior IT was suggested on the basis of lesion studies (Iwai and Mishkin 1968), this concept has not been further developed, probably because of the lack of related data at the cellular level. As a step towards this goal, we compared selectivity of cell responses for complex objec ...
Hormonal Regulation of Sodium and Water Balance
... many similarities with principal cells of the cortical collecting duct They have apical Na+ and K+ channels that mediate Na+ reabsorption and K+ secretion, respectively have vasopressin-regulated water channels (aquaporin-2 on the apical membrane, aquaporin-3 and -4 on the basolateral membrane In th ...
... many similarities with principal cells of the cortical collecting duct They have apical Na+ and K+ channels that mediate Na+ reabsorption and K+ secretion, respectively have vasopressin-regulated water channels (aquaporin-2 on the apical membrane, aquaporin-3 and -4 on the basolateral membrane In th ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... For instance, when you start to run, the autonomic nervous system speeds up your heart rate and blood flow to the skeletal muscles, stimulates the sweat glands, and slows down the contractions of smooth muscles in the digestive system. ...
... For instance, when you start to run, the autonomic nervous system speeds up your heart rate and blood flow to the skeletal muscles, stimulates the sweat glands, and slows down the contractions of smooth muscles in the digestive system. ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.




![[j26]Chapter 8#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009531099_1-530d7c194a24d89985e18840d7e0199e-300x300.png)