A framework for the first-person internal sensation of visual
... elements of the various higher brain functions due to the following reasons. (1) Since different sets of dendritic spine inputs (postsynaptic potentials) can lead to the same action potential, neuronal firing is non-specific with regards to its inputs. For example, in a pyramidal neuron with thousan ...
... elements of the various higher brain functions due to the following reasons. (1) Since different sets of dendritic spine inputs (postsynaptic potentials) can lead to the same action potential, neuronal firing is non-specific with regards to its inputs. For example, in a pyramidal neuron with thousan ...
item[`#file`]
... Response limited to the muscle (or part) that was stretched and the antagonist muscle Tonically active in extensor muscles of the trunk and legs (antigravity muscles), but may be elicited from any skeletal muscle Receptor: the Muscle Spindle Small connective tissue capsule containing intrafusal musc ...
... Response limited to the muscle (or part) that was stretched and the antagonist muscle Tonically active in extensor muscles of the trunk and legs (antigravity muscles), but may be elicited from any skeletal muscle Receptor: the Muscle Spindle Small connective tissue capsule containing intrafusal musc ...
The NEURON Simulation Environment
... Representing biological neurons Information processing in the nervous system involves the spread and interaction of electrical and chemical signals within and between neurons and glia. These signals are continuous functions of time and space and are described by the diffusion equation and the closel ...
... Representing biological neurons Information processing in the nervous system involves the spread and interaction of electrical and chemical signals within and between neurons and glia. These signals are continuous functions of time and space and are described by the diffusion equation and the closel ...
Neural Networks (NN)
... If the step activation function is used (i.e., the neuron's output is 0 if the input is less than zero, and 1 if the input is greater than or equal to 0) then the neuron acts just like the biological neuron described earlier (subtracting the threshold from the weighted sum and comparing with zero is ...
... If the step activation function is used (i.e., the neuron's output is 0 if the input is less than zero, and 1 if the input is greater than or equal to 0) then the neuron acts just like the biological neuron described earlier (subtracting the threshold from the weighted sum and comparing with zero is ...
EFFECTS OF INTERLEUKM 1p ON JSOLATED RAT
... CNS, where it can interact wiai circulating EPs. It is a srnall. semisphencal protnision situated at the rostro-dorsal quadrant of the third œrebral ventricle, attached to the hippocampal commissure (Dellman. 1985). ...
... CNS, where it can interact wiai circulating EPs. It is a srnall. semisphencal protnision situated at the rostro-dorsal quadrant of the third œrebral ventricle, attached to the hippocampal commissure (Dellman. 1985). ...
Glossary of Neuroanatomical Terms and Eponyms
... Fenestra. L. window. A hole. Fenestra rotunda (round) and fenestra ovale (oval) are between the middle and inner ear. Capillary blood vessels are fenestrated when their endothelial cells have pores, each closed by a diaphragm that does not prevent the egress of large molecules. Such vessels typicall ...
... Fenestra. L. window. A hole. Fenestra rotunda (round) and fenestra ovale (oval) are between the middle and inner ear. Capillary blood vessels are fenestrated when their endothelial cells have pores, each closed by a diaphragm that does not prevent the egress of large molecules. Such vessels typicall ...
Expanding Our Understanding of Central Sensitization
... regeneration. However, these agents are also irritants and change the properties of the primary sensory neurons surrounding the area of trauma. Thus, the major features triggering inflammatory pain include damage to the high-threshold nociceptors (peripheral sensitization), modifications and modulat ...
... regeneration. However, these agents are also irritants and change the properties of the primary sensory neurons surrounding the area of trauma. Thus, the major features triggering inflammatory pain include damage to the high-threshold nociceptors (peripheral sensitization), modifications and modulat ...
Bio_246_files/Clinical Considerations of the Nervous System
... – During sleep we go through different stages. That gives you the ability to respond to your environment. – Stress is a leading cause of insomnia. This may have kept you out of the tiger’s stomach. ...
... – During sleep we go through different stages. That gives you the ability to respond to your environment. – Stress is a leading cause of insomnia. This may have kept you out of the tiger’s stomach. ...
The importance of mixed selectivity in complex
... A majority of neurons are selective to at least 1 of the 3 task relevant aspects in 1 or more epochs. A large proportion also showed nonlinear-mixed selectivity a/b – a cell that is selective to a mixture of Cue1 identity and task-type. It responds to object C when presented as a first cue(more stro ...
... A majority of neurons are selective to at least 1 of the 3 task relevant aspects in 1 or more epochs. A large proportion also showed nonlinear-mixed selectivity a/b – a cell that is selective to a mixture of Cue1 identity and task-type. It responds to object C when presented as a first cue(more stro ...
Nervous System Lesson Plan Grades 3-5
... Dendrites - Neuron fibers that carry impulses or signals to the cell body. These are the receptors in the nervous system. Axons - Carry signals away from the cell body. Information travels through many Sensory and motor neurons going to and from the Central Nervous System. When a neuron is stimulate ...
... Dendrites - Neuron fibers that carry impulses or signals to the cell body. These are the receptors in the nervous system. Axons - Carry signals away from the cell body. Information travels through many Sensory and motor neurons going to and from the Central Nervous System. When a neuron is stimulate ...
The Loss of Glutamate-GABA Harmony in Anxiety Disorders
... homeostasis, which is itself maintained and regulated by two opposite forces acting independently to each other, flowing into a natural cycle and always seeking the balance. The thing is about two main amino acid neurotransmitters, glutamate and GABA, creating the opposite excitatory/inhibitory forc ...
... homeostasis, which is itself maintained and regulated by two opposite forces acting independently to each other, flowing into a natural cycle and always seeking the balance. The thing is about two main amino acid neurotransmitters, glutamate and GABA, creating the opposite excitatory/inhibitory forc ...
7- Introduction and functional anatomy of vascular physiology
... Types of blood vessels: 1- Arteries: The arteries are thick-walled structures with extensive development of elastic tissue. They are stretched during systole and recoil during diastole, such property prevents an excessive rise in blood pressure (during systole) and excessive fall (during diastole). ...
... Types of blood vessels: 1- Arteries: The arteries are thick-walled structures with extensive development of elastic tissue. They are stretched during systole and recoil during diastole, such property prevents an excessive rise in blood pressure (during systole) and excessive fall (during diastole). ...
excitation and inhibition of the reflex eye withdrawal of the crab
... brains were prepared for electrophysiological studies by dissecting the anterior portion of the carapace away from the rest of the body leaving the eyes, brain and statocysts intact. The oesophageal connectives and part of the tegumentary nerves are the only nerves of the brain which are interrupted ...
... brains were prepared for electrophysiological studies by dissecting the anterior portion of the carapace away from the rest of the body leaving the eyes, brain and statocysts intact. The oesophageal connectives and part of the tegumentary nerves are the only nerves of the brain which are interrupted ...
Lecture 26
... The relatively recent discovery of so-called mirror neuron systems in humans and other primates holds some potential for helping to understand the neural basis of imitation learning. The classical concept of motor and sensory pathways is that these are quite separate systems, though linked so that s ...
... The relatively recent discovery of so-called mirror neuron systems in humans and other primates holds some potential for helping to understand the neural basis of imitation learning. The classical concept of motor and sensory pathways is that these are quite separate systems, though linked so that s ...
Neuroscience-Alzheimer`s products (, 1.78 kB)
... detection of proteins containing MetO residues by western blotting. MetO-containing samples of interest include those from cell or tissue lysates as well as semi-pure or purified proteins. Samples may be prepared with reducing or non-reducing sample buffer prior to SDS-PAGE and tested alongside one ...
... detection of proteins containing MetO residues by western blotting. MetO-containing samples of interest include those from cell or tissue lysates as well as semi-pure or purified proteins. Samples may be prepared with reducing or non-reducing sample buffer prior to SDS-PAGE and tested alongside one ...
Scientific Explanation of Kinesio® Tex Tape
... mechanical compensation in other areas. If this fascial contraction persists, fibroblasts will secrete collagen and other proteins into the extracellular matrix where they bind to existing proteins, making the composition thicker and less extensible. While this increases the tensile strength of the ...
... mechanical compensation in other areas. If this fascial contraction persists, fibroblasts will secrete collagen and other proteins into the extracellular matrix where they bind to existing proteins, making the composition thicker and less extensible. While this increases the tensile strength of the ...
Psychology 10th Edition David Myers - AP Psychology
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
kn35l1SvSY1SkTqq
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
File
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
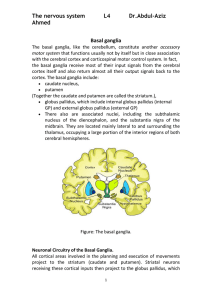
1.In the direct pathway
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
Finding Clues to Schizophrenia Outside Neurons
... Complement C4 is closely associated with another complement factor, termed C3, which is deposited on synapses to mark them as destined for pruning; C4 directs C3 to move from glia to synapses between neurons. Thus, microglia eliminate synapses by identifying which synapses are to be eliminated and t ...
... Complement C4 is closely associated with another complement factor, termed C3, which is deposited on synapses to mark them as destined for pruning; C4 directs C3 to move from glia to synapses between neurons. Thus, microglia eliminate synapses by identifying which synapses are to be eliminated and t ...
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE
... Ganglion- a bundle of cell bodies in PNS; the two ANS motor neurons synapse at a ganglion (AT of first synapses with CB of 2nd) Sympathetic- are located on either side of the spinal cord. Parasympathetic - located at or near the effector ...
... Ganglion- a bundle of cell bodies in PNS; the two ANS motor neurons synapse at a ganglion (AT of first synapses with CB of 2nd) Sympathetic- are located on either side of the spinal cord. Parasympathetic - located at or near the effector ...
The Binding Problem
... Background There are few, if any, places in the nervous system where all the information necessary to carry out a particular task is localized. This means that sensory, cognitive and motor processes result from parallel interactions among large populations o neurons in different regions of the brain ...
... Background There are few, if any, places in the nervous system where all the information necessary to carry out a particular task is localized. This means that sensory, cognitive and motor processes result from parallel interactions among large populations o neurons in different regions of the brain ...
Evolution of Animal Neural Systems
... code within neurons, and those underlying the synaptic code between neurons. Each of these two sections can be further divided into three sub-modules. Proteins from all modules were present in the unicellular ancestor of animals. ...
... code within neurons, and those underlying the synaptic code between neurons. Each of these two sections can be further divided into three sub-modules. Proteins from all modules were present in the unicellular ancestor of animals. ...
PDF
... signalling is widely believed to be regulated in an autocrine feedback loop by another Egfr ligand, Spitz, and the Egfr inhibitor Argos. On p. 2893, however, Laura Nilson and colleagues challenge this view by showing that the SpitzArgos feedback loop is not required for dorsal appendage patterning a ...
... signalling is widely believed to be regulated in an autocrine feedback loop by another Egfr ligand, Spitz, and the Egfr inhibitor Argos. On p. 2893, however, Laura Nilson and colleagues challenge this view by showing that the SpitzArgos feedback loop is not required for dorsal appendage patterning a ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.
![item[`#file`]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015956740_1-3f6ed5c9f9134adf505bbe94b8655b27-300x300.png)