The basis of the stress reaction
... sensitive pathways, are processed in the thalamus and then conducted to specific brain regions. These pathways may comprise of different nerves (cranial, viscerosensitive and somatosensitive); neuronal pathways are not the only ones are activated by stressors. Especially chemical signals (such as hy ...
... sensitive pathways, are processed in the thalamus and then conducted to specific brain regions. These pathways may comprise of different nerves (cranial, viscerosensitive and somatosensitive); neuronal pathways are not the only ones are activated by stressors. Especially chemical signals (such as hy ...
Subthalamic Stimulation-Induced Synaptic Responses in Substantia
... Tepper. Subthalamic stimulation-induced synaptic responses in substantia nigra pars compacta dopaminergic neurons in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 82: 925–933, 1999. The subthalamic nucleus (STN) is one of the principal sources of excitatory glutamatergic input to dopaminergic neurons of the substantia ni ...
... Tepper. Subthalamic stimulation-induced synaptic responses in substantia nigra pars compacta dopaminergic neurons in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 82: 925–933, 1999. The subthalamic nucleus (STN) is one of the principal sources of excitatory glutamatergic input to dopaminergic neurons of the substantia ni ...
A Lipid Gate for the Peripheral Control of Pain
... the brain and spinal cord (Herkenham, 1991), CB1 cannabinoid receptors are also present in neural and non-neural cells throughout the body (for review, see Guindon and Hohmann, 2009). They are synthesized in cell bodies of DRG neurons and are transported to peripheral nerve terminals, where they are ...
... the brain and spinal cord (Herkenham, 1991), CB1 cannabinoid receptors are also present in neural and non-neural cells throughout the body (for review, see Guindon and Hohmann, 2009). They are synthesized in cell bodies of DRG neurons and are transported to peripheral nerve terminals, where they are ...
Autonomic Nervous System I and II
... Release hormones into blood- 80% epinephrine, 20% norepinephrine. Some sympathetic preganglionic axons pass through the sympathetic trunk without terminating in it. Beyond the trunk they form nerves called splanchnic nerves which extend to prevertebral ganglia. T5-T9 or T10- Greater splanchnic nerve ...
... Release hormones into blood- 80% epinephrine, 20% norepinephrine. Some sympathetic preganglionic axons pass through the sympathetic trunk without terminating in it. Beyond the trunk they form nerves called splanchnic nerves which extend to prevertebral ganglia. T5-T9 or T10- Greater splanchnic nerve ...
Stem cell factor induces outgrowth of c-kit-positive
... stained with ACK2 mAb (Fig. 2B). In contrast, when DRGs were cultured in the absence of rmSCF, most outgrowing neurites remained within the area of fibroblast-like cells (Fig. 2C). None of outgrowing neurites were stained with ACK2 mAb (Fig. 2D). The magnitude of neurite outgrowth was dependent on t ...
... stained with ACK2 mAb (Fig. 2B). In contrast, when DRGs were cultured in the absence of rmSCF, most outgrowing neurites remained within the area of fibroblast-like cells (Fig. 2C). None of outgrowing neurites were stained with ACK2 mAb (Fig. 2D). The magnitude of neurite outgrowth was dependent on t ...
Mental Processes -- How the Mind Arises from the Brain Roger Ellman
... Humans perceive, recognize, a very large number of universals, of course. Some examples, in order to clarify the concept, are: - recognition of the letter E, whether capital or lower case, hand written or mechanically produced, large or small, alone or among other symbols, even though the particular ...
... Humans perceive, recognize, a very large number of universals, of course. Some examples, in order to clarify the concept, are: - recognition of the letter E, whether capital or lower case, hand written or mechanically produced, large or small, alone or among other symbols, even though the particular ...
A neurocomputational model of the mammalian fear
... neutral stimulus (NS) can be any sensory stimulus such as an auditory, visual, olfactory, or tactile cue, that does not have a significant emotional meaning to the animal. The stimulus with inherent emotional meaning to the animal is called the unconditioned stimulus (US), and can be a cue related t ...
... neutral stimulus (NS) can be any sensory stimulus such as an auditory, visual, olfactory, or tactile cue, that does not have a significant emotional meaning to the animal. The stimulus with inherent emotional meaning to the animal is called the unconditioned stimulus (US), and can be a cue related t ...
- Orange Coast College
... Forms most of the walls of the 3rd ventricle. Acts as relay center through which all sensory information (except olfactory) passes to the cerebrum. ...
... Forms most of the walls of the 3rd ventricle. Acts as relay center through which all sensory information (except olfactory) passes to the cerebrum. ...
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
... Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules ...
... Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules ...
Controlling the Elements: An Optogenetic Approach to
... known to be activated during specific time periods of fear conditioning (example, CS or US periods), but in most cases, their temporally limited, functional role in behavior and neural processing is unknown. In addition, within specific areas of the fear circuit, there are neuronal subpopulations (s ...
... known to be activated during specific time periods of fear conditioning (example, CS or US periods), but in most cases, their temporally limited, functional role in behavior and neural processing is unknown. In addition, within specific areas of the fear circuit, there are neuronal subpopulations (s ...
Articles in PresS. J Neurophysiol (March 20, 2003). 10.1152/jn
... in our model, Kir2 and Ksi (si, slowly inactivating), have been shown (Nisenbaum and Wilson 1995) to account for the characteristic nonlinear voltage dependence of the outward current measured in spiny neurons. We recognize that the si K+ current is likely to arise from at least two channel types, b ...
... in our model, Kir2 and Ksi (si, slowly inactivating), have been shown (Nisenbaum and Wilson 1995) to account for the characteristic nonlinear voltage dependence of the outward current measured in spiny neurons. We recognize that the si K+ current is likely to arise from at least two channel types, b ...
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
... Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules ...
... Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules ...
CHAPTER 39
... elongation, and differentiation of cells. Some hormones also mediate shorter-term physiological responses of plants to environmental stimuli. Each hormone has multiple effects, depending on its site of action, its concentration, and the developmental stage of the plant. Response to a hormone usually ...
... elongation, and differentiation of cells. Some hormones also mediate shorter-term physiological responses of plants to environmental stimuli. Each hormone has multiple effects, depending on its site of action, its concentration, and the developmental stage of the plant. Response to a hormone usually ...
Dopamine`s Actions in Primate Prefrontal Cortex
... from DA “salience cells” that respond to aversive as well as rewarding stimuli. dlPFC Delay cells generate persistent representations of visual spatial position across the delay epoch and are thought to be concentrated in deep layer III (and possibly superficial layer V), whereas Response-related ce ...
... from DA “salience cells” that respond to aversive as well as rewarding stimuli. dlPFC Delay cells generate persistent representations of visual spatial position across the delay epoch and are thought to be concentrated in deep layer III (and possibly superficial layer V), whereas Response-related ce ...
Robo1 Regulates the Migration and Laminar Distribution of Upper
... Indeed, an increasing number of genes have been identified that control the early phase of radial migration (Caviness and Rakic 1978; Gupta et al. 2002; Nadarajah and Parnavelas 2002; Tsai and Gleeson 2005; Cooper 2008; Huang 2009; Honda et al. 2011). In contrast, much less is known about how the ter ...
... Indeed, an increasing number of genes have been identified that control the early phase of radial migration (Caviness and Rakic 1978; Gupta et al. 2002; Nadarajah and Parnavelas 2002; Tsai and Gleeson 2005; Cooper 2008; Huang 2009; Honda et al. 2011). In contrast, much less is known about how the ter ...
The Role of Histamine H1 , H2 and H3 Receptors on Enteric
... Mg11) also blocked the contractile effect of both dimaprit (fig. 1) and amphamine (data not shown). The H3 agonist R-a-methylhistamine, applied to the anal compartment, did not produce any contraction. Effect of H1, H2 and H3 agonists and antagonists on the ascending excitatory pathways activated by ...
... Mg11) also blocked the contractile effect of both dimaprit (fig. 1) and amphamine (data not shown). The H3 agonist R-a-methylhistamine, applied to the anal compartment, did not produce any contraction. Effect of H1, H2 and H3 agonists and antagonists on the ascending excitatory pathways activated by ...
Single Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons Form Widely Spread
... palGFP-labeled neurons were examined to determine whether they expressed immunoreactivity for TH (Fig. 1 A–A⬙). Double immunoperoxidase staining for GFP and -opioid receptor. All the sections containing single palGFP-labeled and TH-immunopositive neurons were incubated overnight with a mixture of 0 ...
... palGFP-labeled neurons were examined to determine whether they expressed immunoreactivity for TH (Fig. 1 A–A⬙). Double immunoperoxidase staining for GFP and -opioid receptor. All the sections containing single palGFP-labeled and TH-immunopositive neurons were incubated overnight with a mixture of 0 ...
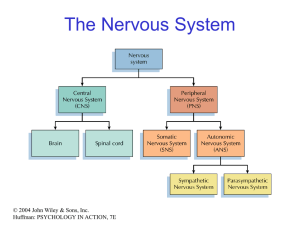
Huffman PowerPoint Slides
... Neurons • Neurons are cells that transmit information • Neurons are composed of: – Dendrites: receive information and pass it to cell body – Cell Body: summarizes information – Axon: extends from cell body, carries electrical potential, sends a chemical message to adjacent neurons © 2004 John Wiley ...
... Neurons • Neurons are cells that transmit information • Neurons are composed of: – Dendrites: receive information and pass it to cell body – Cell Body: summarizes information – Axon: extends from cell body, carries electrical potential, sends a chemical message to adjacent neurons © 2004 John Wiley ...
A Neuroscientific Approach to Emotion System for Intelligent Agents.
... its reward value. This value is decreased by feeding to satiety, since neurons in the orbitofrontal cortex decrease their responses as the reward value of the food decreases. Rewards and punishers can be defined as reinforcers, because they change the probability of behavior [8]. There are two types ...
... its reward value. This value is decreased by feeding to satiety, since neurons in the orbitofrontal cortex decrease their responses as the reward value of the food decreases. Rewards and punishers can be defined as reinforcers, because they change the probability of behavior [8]. There are two types ...
Retrograde Signaling in the Development and Modification of
... selective gene expression. Moreover, presynaptic functions are under the regulation of retrograde signals in an activity-dependent manner with a rapid time course. Finally, although retrograde signals can exert localized presynaptic regulation, long-range presynaptic propagation of the retrograde si ...
... selective gene expression. Moreover, presynaptic functions are under the regulation of retrograde signals in an activity-dependent manner with a rapid time course. Finally, although retrograde signals can exert localized presynaptic regulation, long-range presynaptic propagation of the retrograde si ...
Central nervous system control of food intake and body
... has provided an insight into the molecular, cellular and behavioural mechanisms that link changes of body fat stores to adaptive adjustments of feeding behaviour. The physiological importance of this homeostatic control system is highlighted by the severe obesity that results from dysfunction of any ...
... has provided an insight into the molecular, cellular and behavioural mechanisms that link changes of body fat stores to adaptive adjustments of feeding behaviour. The physiological importance of this homeostatic control system is highlighted by the severe obesity that results from dysfunction of any ...
Pain Lotion Ingredient List
... helps decrease blood pressure by encouraging vasodilation. Vasodilator agents can lead to substantial improvements in neuronal blood flow with corresponding improvements in nerve conduction which can help with diabetic neuropathy. Although Nifedipine’s mode of action in pain management remains uncle ...
... helps decrease blood pressure by encouraging vasodilation. Vasodilator agents can lead to substantial improvements in neuronal blood flow with corresponding improvements in nerve conduction which can help with diabetic neuropathy. Although Nifedipine’s mode of action in pain management remains uncle ...
Brain Anatomy and Histology of Orange Spotted Grouper
... sense of smell, the so called "rhinencephalo" is very different, but one can still recognize a common structural plan related to the morphology of this part of brain among all vertebrates. It seems probable that the early vertebrates possessed a well developed olfactory apparatus and this condition ...
... sense of smell, the so called "rhinencephalo" is very different, but one can still recognize a common structural plan related to the morphology of this part of brain among all vertebrates. It seems probable that the early vertebrates possessed a well developed olfactory apparatus and this condition ...
CLM UMR-S 839 INSERM/UPMC Institut du Fer a Moulin
... behavior. Two sessions will examine the recent technological advances in a wide range of topics spanning from synaptic integration, and transduction mechanisms implicated in the plasticity of synaptic signaling, to the probing of neural circuits during sensory modalities, action and development. Thi ...
... behavior. Two sessions will examine the recent technological advances in a wide range of topics spanning from synaptic integration, and transduction mechanisms implicated in the plasticity of synaptic signaling, to the probing of neural circuits during sensory modalities, action and development. Thi ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.