Ch02
... Caption: (a) Action potentials are recorded from neurons with tiny microelectrodes that are positioned inside or right next to the neuron’s axon. These potentials are displayed on the screen of an oscilloscope and are also sent to a computer for analysis. (b) An action potential recorded by a micro ...
... Caption: (a) Action potentials are recorded from neurons with tiny microelectrodes that are positioned inside or right next to the neuron’s axon. These potentials are displayed on the screen of an oscilloscope and are also sent to a computer for analysis. (b) An action potential recorded by a micro ...
chapter 11-nerve tissue
... a) Chemically-gated channels-open and close in response to certain chemical stimuli. Hormones, neurotransmitters and certain ions can force these channels to open and close. b) Voltage-gated channels-open and close in response to changes in membrane potential. Neurons have sodium and potassium volta ...
... a) Chemically-gated channels-open and close in response to certain chemical stimuli. Hormones, neurotransmitters and certain ions can force these channels to open and close. b) Voltage-gated channels-open and close in response to changes in membrane potential. Neurons have sodium and potassium volta ...
Nervous System
... potential that would be maintained if there were no action potentials, synaptic potentials, or other active changes in the membrane potential. 57 The ________ is a region of the brain that plays an important role in the integration of sensory perception and motor control, using constant feedback on ...
... potential that would be maintained if there were no action potentials, synaptic potentials, or other active changes in the membrane potential. 57 The ________ is a region of the brain that plays an important role in the integration of sensory perception and motor control, using constant feedback on ...
here - STAO
... receptors on various postsynaptic membranes, certain actions are stimulated. There are quite a variety of other molecules that are structurally similar to various neurotransmitters. As you can imagine, if these molecules interact with your nervous system, there can be peculiar responses. Stimulants ...
... receptors on various postsynaptic membranes, certain actions are stimulated. There are quite a variety of other molecules that are structurally similar to various neurotransmitters. As you can imagine, if these molecules interact with your nervous system, there can be peculiar responses. Stimulants ...
Neurophysiology – Action Potential, Nerve Impulse, and Synapses
... The outside surface of a cell membrane is electrically charged or polarized with respect to the inside. This polarization is due to an unequal distribution of positive and negative ions between sides of the membrane. A. Distribution of Ions The distribution of ions inside and outside cell membranes ...
... The outside surface of a cell membrane is electrically charged or polarized with respect to the inside. This polarization is due to an unequal distribution of positive and negative ions between sides of the membrane. A. Distribution of Ions The distribution of ions inside and outside cell membranes ...
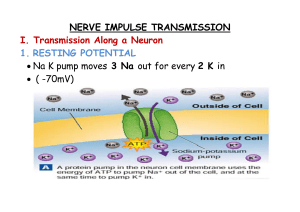
steps in nerve impulse transmission
... 3. UNDERSHOOT (AKA REFRACTORY PERIOD) Na and K channels close but NaK pump restores order (-70mV) after hyperpolarization ...
... 3. UNDERSHOOT (AKA REFRACTORY PERIOD) Na and K channels close but NaK pump restores order (-70mV) after hyperpolarization ...
Chapter 6 Chapter Review Questions Q2. This would be a
... c) Parasympathetic for eating food and Somatic for watching a movie d) Somatic ...
... c) Parasympathetic for eating food and Somatic for watching a movie d) Somatic ...
Visual Prostheses: Current Progress and Challenges
... surgical challenge. As to epi-retinal versus sub-retinal, the epiretinal approach is easier form a surgical point of view but the mechanical anchoring of the implant to the epi-retinal surface is difficult[2]. This can be partially alleviated by placing the device subretinally[3], though the surgery ...
... surgical challenge. As to epi-retinal versus sub-retinal, the epiretinal approach is easier form a surgical point of view but the mechanical anchoring of the implant to the epi-retinal surface is difficult[2]. This can be partially alleviated by placing the device subretinally[3], though the surgery ...
video slide - ScienceToGo
... Most of a neuron’s organelles are in the cell body Most neurons have dendrites, highly branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons The axon is typically a much longer extension that transmits signals to other cells at synapses An axon joins the cell body at the axon ...
... Most of a neuron’s organelles are in the cell body Most neurons have dendrites, highly branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons The axon is typically a much longer extension that transmits signals to other cells at synapses An axon joins the cell body at the axon ...
File
... Neuron Structure There are gaps in the myelin sheath, called nodes, where the membrane is exposed. • Impulses jump from one node to the next. ...
... Neuron Structure There are gaps in the myelin sheath, called nodes, where the membrane is exposed. • Impulses jump from one node to the next. ...
Answers
... 4. The dolphin brain is the most “convoluted” of all. What does this suggest? (The answer is not stated; can you come up with a plausible explanation?” _____MOST CEREBRAL CORTEX _ _______________________________________________________________ Choose one other topic from the list of items under Expl ...
... 4. The dolphin brain is the most “convoluted” of all. What does this suggest? (The answer is not stated; can you come up with a plausible explanation?” _____MOST CEREBRAL CORTEX _ _______________________________________________________________ Choose one other topic from the list of items under Expl ...
Pipecleaner Neuron Guide - spectrUM Discovery Area
... one neuron is transmitted to the dendrite of another neuron (via a chemical signal. • Synapse- space between the axon of one neuron sending the message (releases neurotransmitter) to the dendrite of another neuron. Neurotransmitters work like key and lock with the lock being on the receiving neuron ...
... one neuron is transmitted to the dendrite of another neuron (via a chemical signal. • Synapse- space between the axon of one neuron sending the message (releases neurotransmitter) to the dendrite of another neuron. Neurotransmitters work like key and lock with the lock being on the receiving neuron ...
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Notes
... Neurotransmitters Are Made and Stored in the Pre-synaptic Terminal The end of the neuron enlarges into an axon terminal Neurotransmitters are produced in the cell body of a neuron and then transported to the ends of the axon terminals in small membrane-enclosed sacs called “synaptic vesicles”. At th ...
... Neurotransmitters Are Made and Stored in the Pre-synaptic Terminal The end of the neuron enlarges into an axon terminal Neurotransmitters are produced in the cell body of a neuron and then transported to the ends of the axon terminals in small membrane-enclosed sacs called “synaptic vesicles”. At th ...
The Nervous System
... occur between cells, the signal must be transferred across this gap Function – Provides an area for the transfer of signals between neurons, usually between axon and dendrite ...
... occur between cells, the signal must be transferred across this gap Function – Provides an area for the transfer of signals between neurons, usually between axon and dendrite ...
48_Lectures_PPT
... • The vast majority of synapses are chemical synapses • In a chemical synapse, a presynaptic neuron releases chemical neurotransmitters stored in the synaptic terminal ...
... • The vast majority of synapses are chemical synapses • In a chemical synapse, a presynaptic neuron releases chemical neurotransmitters stored in the synaptic terminal ...
Nervous Tissue (Ch
... 1. soma (cell body) - contains typical organelles * Nissl bodies – dense networks of rough endoplasmic reticulum, compartmentalized by * neurofibrils - intermediate filaments (actin) of cytoskeleton 2. dendrites - receive - short, highly branched - not usually myelinated 3. axon - sends - long, few ...
... 1. soma (cell body) - contains typical organelles * Nissl bodies – dense networks of rough endoplasmic reticulum, compartmentalized by * neurofibrils - intermediate filaments (actin) of cytoskeleton 2. dendrites - receive - short, highly branched - not usually myelinated 3. axon - sends - long, few ...
to Psychology 3
... membrane causing an electrical potential of -70 millivolts 2. The Action Potential - the stable voltage is disrupted upon the stimulation by neurotransmitters at dendrites - channels along the axon membrane open to allow cations into the cell easily resulting in an electric current along the axon - ...
... membrane causing an electrical potential of -70 millivolts 2. The Action Potential - the stable voltage is disrupted upon the stimulation by neurotransmitters at dendrites - channels along the axon membrane open to allow cations into the cell easily resulting in an electric current along the axon - ...
Central nervous system
... • Neuromodulators modify synaptic transmission – raise or lower number of receptors – alter neurotransmitter release, synthesis or breakdown – Some postsynaptic neurons release nitric oxide (NO) – ------“give me more!” ...
... • Neuromodulators modify synaptic transmission – raise or lower number of receptors – alter neurotransmitter release, synthesis or breakdown – Some postsynaptic neurons release nitric oxide (NO) – ------“give me more!” ...
Reply to “Letter to the editor: `Systemic cell theory, protoplasmic
... We appreciate the interest expressed by Dr. MüllerStrahl in our article (2) for American Journal of PhysiologyCell Physiology (AJP-Cell). He raises concerns regarding our historiographical approach to the notions of “protoplasmic theory” and “cellular systems biology” that feature prominently in our ...
... We appreciate the interest expressed by Dr. MüllerStrahl in our article (2) for American Journal of PhysiologyCell Physiology (AJP-Cell). He raises concerns regarding our historiographical approach to the notions of “protoplasmic theory” and “cellular systems biology” that feature prominently in our ...
Nervous Systems (ch. 48 & 49) Sum13
... 1. All sensory, motor, and interneurons neurons 2. Sensory neuron dendrites & cell bodies AND motor neuron axons 3. Interneurons only 4. Motor neuron dendrites and interneuron axons ...
... 1. All sensory, motor, and interneurons neurons 2. Sensory neuron dendrites & cell bodies AND motor neuron axons 3. Interneurons only 4. Motor neuron dendrites and interneuron axons ...
Count the black dots
... • Wigner concludes with “A much more difficult and confusing situation would arise if we could, some day, establish a theory of the phenomena of consciousness, or of biology, which would be as coherent and convincing as our present theories of the inanimate world.” • “There is only one thing which i ...
... • Wigner concludes with “A much more difficult and confusing situation would arise if we could, some day, establish a theory of the phenomena of consciousness, or of biology, which would be as coherent and convincing as our present theories of the inanimate world.” • “There is only one thing which i ...
Notes
... Bipolar cells are retinal interneurons that receive synaptic input from rods and cones. The ON cells depolarize when glutamate secretion from photoreceptors is decreased (respond to a light stimulus) and OFF cells hyperpolarize in the same situation. OFF have kainic acid Glut receptors, and ON have ...
... Bipolar cells are retinal interneurons that receive synaptic input from rods and cones. The ON cells depolarize when glutamate secretion from photoreceptors is decreased (respond to a light stimulus) and OFF cells hyperpolarize in the same situation. OFF have kainic acid Glut receptors, and ON have ...
File
... Cytoplasmic Determinants Begin to Differentiate Cells WHAT INFLUENCES DIFFERENTIATION? from the First Mitotic Division ...
... Cytoplasmic Determinants Begin to Differentiate Cells WHAT INFLUENCES DIFFERENTIATION? from the First Mitotic Division ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.