Organization of the Nervous System and the Neuron
... Nervous tissue is made up of two types of cellsSupporting and Neurons Supporting cells of the CNS are called Neuroglia or “nerve glue”. ...
... Nervous tissue is made up of two types of cellsSupporting and Neurons Supporting cells of the CNS are called Neuroglia or “nerve glue”. ...
Slide 1
... • A neuron has a pre-set level of stimulation that needs to be met or exceeded in order for it to pass the received impulses on to the next neuron. This is called a neuron’s threshold. ...
... • A neuron has a pre-set level of stimulation that needs to be met or exceeded in order for it to pass the received impulses on to the next neuron. This is called a neuron’s threshold. ...
Research Interests: Reading neural codes Current:
... Past: I had previously engaged in reading neural codes in the early visual system, in a structure that receives directly from the retina known as the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). We presented short videos of animals at the zoo to awake monkeys, and then attempted to calculate backwards what th ...
... Past: I had previously engaged in reading neural codes in the early visual system, in a structure that receives directly from the retina known as the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). We presented short videos of animals at the zoo to awake monkeys, and then attempted to calculate backwards what th ...
PP text version
... a refractory period follows action potential because Na channels turn themselves off (inactivate) and take some time to recover. The nerve can’t be stimulated again until they recover. the speed that the action potential travels (propagates) is determined by a) the diameter of the axon: larger i ...
... a refractory period follows action potential because Na channels turn themselves off (inactivate) and take some time to recover. The nerve can’t be stimulated again until they recover. the speed that the action potential travels (propagates) is determined by a) the diameter of the axon: larger i ...
Neurons
... • Has two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • BOTH are composed of neurons, or nerve cells, that transmit messages to different parts of the body. • Neurons have three main parts: cell body (produces energy), dendrites (DELIVERS info to the cell body), and axo ...
... • Has two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • BOTH are composed of neurons, or nerve cells, that transmit messages to different parts of the body. • Neurons have three main parts: cell body (produces energy), dendrites (DELIVERS info to the cell body), and axo ...
File
... 6.5.5 – Explain how a nerve impulse passes along a nonmyelinated neuron. Step 1: Depolarization • First, the Na+ pores suddenly open • Because of the high concentration outside the cell, Na+ diffuses into the cell • Also the electrical forces will cause sodium to go from positively charged environm ...
... 6.5.5 – Explain how a nerve impulse passes along a nonmyelinated neuron. Step 1: Depolarization • First, the Na+ pores suddenly open • Because of the high concentration outside the cell, Na+ diffuses into the cell • Also the electrical forces will cause sodium to go from positively charged environm ...
No Slide Title
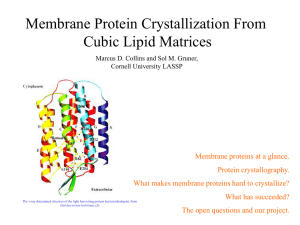
... However, proteins are much harder to grow than salts, and by 1975 only 37 structures had been placed in the Protein Data Bank. These crystals tend to be extremely fragile and sensitive to conditions such as pH, specific ion concentrations, and other factors. They are also easily damaged by the X-ray ...
... However, proteins are much harder to grow than salts, and by 1975 only 37 structures had been placed in the Protein Data Bank. These crystals tend to be extremely fragile and sensitive to conditions such as pH, specific ion concentrations, and other factors. They are also easily damaged by the X-ray ...
Cell Types and Physiology in the CANS
... (These are the two primary acoustic cues for localizing sounds) ...
... (These are the two primary acoustic cues for localizing sounds) ...
Document
... Irritability – ability to respond to a stimulus & convert it into a nerve impulse Conductivity – ability to transmit the impulse to other neurons, muscles or glands A nerve cell at rest is polarized, that is there is a charge across the membrane. ...
... Irritability – ability to respond to a stimulus & convert it into a nerve impulse Conductivity – ability to transmit the impulse to other neurons, muscles or glands A nerve cell at rest is polarized, that is there is a charge across the membrane. ...
Answer Key Chapter 28 - Scarsdale Public Schools
... 13. Briefly explain how a neuron can receive both excitatory and inhibitory signals and yet still fire an action potential in the receiving cell. The neuron will be able to fire an action potential as long as the incoming signals are collectively strong enough to bring the neuron’s membrane pot ...
... 13. Briefly explain how a neuron can receive both excitatory and inhibitory signals and yet still fire an action potential in the receiving cell. The neuron will be able to fire an action potential as long as the incoming signals are collectively strong enough to bring the neuron’s membrane pot ...
Nervous_System_Neurons
... Endorphins are neurotransmitters produced in the brain that reduce pain They have also been known to induce euphoria. Drugs such as morphine, heroine and cocaine are classic endorphin-releasing entities Laughter, chocolate, acupuncture, exercise trigger an endorphin release “runner’s high” ...
... Endorphins are neurotransmitters produced in the brain that reduce pain They have also been known to induce euphoria. Drugs such as morphine, heroine and cocaine are classic endorphin-releasing entities Laughter, chocolate, acupuncture, exercise trigger an endorphin release “runner’s high” ...
Nerve Tissue
... particles between one point and another • electrical current – a flow of charged particles from one point to another – in the body, currents are movement of ions, such as Na+ or K+ through gated channels in the plasma membrane – gated channels enable cells to turn electrical currents on and off ...
... particles between one point and another • electrical current – a flow of charged particles from one point to another – in the body, currents are movement of ions, such as Na+ or K+ through gated channels in the plasma membrane – gated channels enable cells to turn electrical currents on and off ...
Membrane potential synchrony of simultaneously recorded striatal
... threshold for the generation of action potentials, we recorded intracellularly from pairs of spiny neurons in vivo. Here we report that the transitions between depolarized and hyperpolarized states were highly correlated among neurons. Within individual depolarized states, some signi®cant synchronou ...
... threshold for the generation of action potentials, we recorded intracellularly from pairs of spiny neurons in vivo. Here we report that the transitions between depolarized and hyperpolarized states were highly correlated among neurons. Within individual depolarized states, some signi®cant synchronou ...
ACTION POTENTIALS
... become very positively charged (up to +40 millevolts). This is depolarization. Potassium leaves the neruon at this point, due to the repelling polarity of positive sodium ions. After this the channels close, and the sodium pumps remove sodium ions from the membrane this repolarizes the membrane to a ...
... become very positively charged (up to +40 millevolts). This is depolarization. Potassium leaves the neruon at this point, due to the repelling polarity of positive sodium ions. After this the channels close, and the sodium pumps remove sodium ions from the membrane this repolarizes the membrane to a ...
Cell Membranes - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
... Make up 20% of the outer membrane surface Composed of sphingolipids and cholesterol Can include or exclude various proteins Are concentrating platforms for cell-signaling molecules ...
... Make up 20% of the outer membrane surface Composed of sphingolipids and cholesterol Can include or exclude various proteins Are concentrating platforms for cell-signaling molecules ...
neurons
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
A. What is a neuron? 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and
... Chemical Events At The Synapse A. In most cases, synaptic transmission depends on chemical rather than electrical stimulation. This was demonstrated by Otto Loewi's experiments where fluid from a stimulated frog heart was transferred to another heart. The fluid caused the new heart to react as if st ...
... Chemical Events At The Synapse A. In most cases, synaptic transmission depends on chemical rather than electrical stimulation. This was demonstrated by Otto Loewi's experiments where fluid from a stimulated frog heart was transferred to another heart. The fluid caused the new heart to react as if st ...
Lecture-24-2012-Bi
... Late stage: AD patients may become anxious or aggressive, or wander away from home. Eventually, patients need total care. ...
... Late stage: AD patients may become anxious or aggressive, or wander away from home. Eventually, patients need total care. ...
Nervous System - Serrano High School AP Biology
... membrane protein called the SODIUM POTASSIUM PUMP. This pump uses ATP to actively transport sodium out of the cell and potassium in the cell. These pumps move 3 Na+ out for each 2 K+ in. As the Na+ is moved out and the K+ is moved in, a concentration gradient is established. Along with this gradient ...
... membrane protein called the SODIUM POTASSIUM PUMP. This pump uses ATP to actively transport sodium out of the cell and potassium in the cell. These pumps move 3 Na+ out for each 2 K+ in. As the Na+ is moved out and the K+ is moved in, a concentration gradient is established. Along with this gradient ...
What is EEG? Elana Zion
... They bring about the release of chemical substances called “neurotransmitters,” which are absorbed by adjacent neurons. Action potentials occur at a rate of over 200 Hertz and are highly localized (since they are generated by a single neuron), which makes them impossible to pick up by electrodes pla ...
... They bring about the release of chemical substances called “neurotransmitters,” which are absorbed by adjacent neurons. Action potentials occur at a rate of over 200 Hertz and are highly localized (since they are generated by a single neuron), which makes them impossible to pick up by electrodes pla ...
Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... of the fiber that reaches deep within the fiber through the TRANSVERSE TUBULES ...
... of the fiber that reaches deep within the fiber through the TRANSVERSE TUBULES ...
Local Copy - Synthetic Neurobiology Group
... timescale. In many diseases, specific computations mediated by the brain are thrown into disarray when specific classes of neuron are compromised. Such neurological and psychiatric disorders affect billions of people worldwide and are some of the most intractable medical needs of our time. To treat ...
... timescale. In many diseases, specific computations mediated by the brain are thrown into disarray when specific classes of neuron are compromised. Such neurological and psychiatric disorders affect billions of people worldwide and are some of the most intractable medical needs of our time. To treat ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.