
III. NEURAL COMMUNICATION A. Resting Potential In this section
... there is a deficit of Act), animals’, performance on memory and learning tasks are also impaired. Also, if Ach is increased, there appears to be increased learning and retention. Ach deficit in extreme is found in the brain of ...
... there is a deficit of Act), animals’, performance on memory and learning tasks are also impaired. Also, if Ach is increased, there appears to be increased learning and retention. Ach deficit in extreme is found in the brain of ...
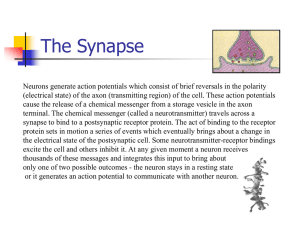
The Synapse
... (electrical state) of the axon (transmitting region) of the cell. These action potentials cause the release of a chemical messenger from a storage vesicle in the axon terminal. The chemical messenger (called a neurotransmitter) travels across a synapse to bind to a postsynaptic receptor protein. The ...
... (electrical state) of the axon (transmitting region) of the cell. These action potentials cause the release of a chemical messenger from a storage vesicle in the axon terminal. The chemical messenger (called a neurotransmitter) travels across a synapse to bind to a postsynaptic receptor protein. The ...
An introduction to hearing
... Hair cell tuning • each hair cell tuned to characteristic frequency of basilar membrane at that position – successive hair cells differ in tuning by 0.2% (piano notes differ by 6%) – tuning curves show the SPL required for 1mV depolarisation ...
... Hair cell tuning • each hair cell tuned to characteristic frequency of basilar membrane at that position – successive hair cells differ in tuning by 0.2% (piano notes differ by 6%) – tuning curves show the SPL required for 1mV depolarisation ...
Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]
... • One person holds the yard stick up • Second person is being tested at how fast they can respond to the yard stick falling • The first person will release the yard stick and the second person will catch it. They will record where their hand grabs the yard stick. • Using this formula: t = √2y/g , y ...
... • One person holds the yard stick up • Second person is being tested at how fast they can respond to the yard stick falling • The first person will release the yard stick and the second person will catch it. They will record where their hand grabs the yard stick. • Using this formula: t = √2y/g , y ...
04/04 PPT
... Pyramidal cells -- large, pyramid shaped cell bodies, spiny dendrites, project to other areas, connect to other local neurons, all excitatory. Non-pyramidal cells -- small and stellate shape (spiny stellate or smooth stellate), local interneurons (>40 types), either excitatory (spiny) or inhibitory ...
... Pyramidal cells -- large, pyramid shaped cell bodies, spiny dendrites, project to other areas, connect to other local neurons, all excitatory. Non-pyramidal cells -- small and stellate shape (spiny stellate or smooth stellate), local interneurons (>40 types), either excitatory (spiny) or inhibitory ...
Nervous system
... Parts of the Ear • The Ear is divided into three sections: • 1. Outer Ear - consists of the pinna and auditory canal. • 2. Middle Ear - consists of the tympanic membrane, the ossicles, (malleus, incus, and stapes), the eustachian tube, and the round and oval window. • 3. Inner Ear - consists of the ...
... Parts of the Ear • The Ear is divided into three sections: • 1. Outer Ear - consists of the pinna and auditory canal. • 2. Middle Ear - consists of the tympanic membrane, the ossicles, (malleus, incus, and stapes), the eustachian tube, and the round and oval window. • 3. Inner Ear - consists of the ...
Neurons - University of San Diego Home Pages
... K+ flux via passive (leaky) K+ channels is most important contributor to Vm Na+ flux also contributes to Vm ...
... K+ flux via passive (leaky) K+ channels is most important contributor to Vm Na+ flux also contributes to Vm ...
- Eye, Brain, and Vision
... still not understood, this arrival of calcium inside the cell leads to the expulsion, across the membrane from inside to outside, of packages of special chemicals call neurotransmitters. About twenty transmitter chemicals have been identified, and to judge from the rate of new discoveries the total ...
... still not understood, this arrival of calcium inside the cell leads to the expulsion, across the membrane from inside to outside, of packages of special chemicals call neurotransmitters. About twenty transmitter chemicals have been identified, and to judge from the rate of new discoveries the total ...
chapt10_holes_lecture_animation
... • Neuron receives input from several neurons • Incoming impulses represent information from different types of sensory receptors ...
... • Neuron receives input from several neurons • Incoming impulses represent information from different types of sensory receptors ...
Genotype - White Plains Public Schools
... Action Potentials • Neurons receive excitatory (“fire”) or inhibitory (“don’t fire”) inputs • Neural communication is produced by the flow of elec. charged particles – ions • Inactive/Resting State- more potassium ions inside, more sodium ions outside the neuron • Membrane of the cell has a pump to ...
... Action Potentials • Neurons receive excitatory (“fire”) or inhibitory (“don’t fire”) inputs • Neural communication is produced by the flow of elec. charged particles – ions • Inactive/Resting State- more potassium ions inside, more sodium ions outside the neuron • Membrane of the cell has a pump to ...
What is the neuron`s resting potential?
... and negatively charged protein ions are distributed unevenly across the neuron’s membrane. • The ratio of negative to positive charges is greater inside the resting neuron than outside. ...
... and negatively charged protein ions are distributed unevenly across the neuron’s membrane. • The ratio of negative to positive charges is greater inside the resting neuron than outside. ...
Chapter 2 - Pearland ISD
... contains selective channel proteins that allow water and small, charged particles to pass into and out of the cell. How do cells move and change their shape? The cytoskeleton rearranges itself when necessary. How do cells obtain and use energy to accomplish tasks? Cell mitochondria are responsible f ...
... contains selective channel proteins that allow water and small, charged particles to pass into and out of the cell. How do cells move and change their shape? The cytoskeleton rearranges itself when necessary. How do cells obtain and use energy to accomplish tasks? Cell mitochondria are responsible f ...
Functional imaging of hippocampal palace cells at celluar resolution
... circuit dynamics 2. To apply advanced electrophysiological, imaging, and genetic techniques to study the mechanisms of persistent neural activity in experimental preparations in goldfish. 3. Two-photon laser scanning microscopy for the study of calcium concentration dynamics in dendrites and nerve t ...
... circuit dynamics 2. To apply advanced electrophysiological, imaging, and genetic techniques to study the mechanisms of persistent neural activity in experimental preparations in goldfish. 3. Two-photon laser scanning microscopy for the study of calcium concentration dynamics in dendrites and nerve t ...
Nervous System Objectives
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
CHAPTER 12- Nervous Tissue
... B) usually propagate down the length of an axon. C) occur when voltage-gated channels open. D) are most often observed in axons. E) are usually associated with ion movement through leakage channels. 21) Action potentials A) arise slowly and are observed primarily in dendrites and cell bodies. B) ari ...
... B) usually propagate down the length of an axon. C) occur when voltage-gated channels open. D) are most often observed in axons. E) are usually associated with ion movement through leakage channels. 21) Action potentials A) arise slowly and are observed primarily in dendrites and cell bodies. B) ari ...
VI. The vertebrate nervous system is a hierarchy of structural and
... An action potential has four phases. (See Campbell, Figure 44.7) • Resting state, no channels are open. • Large depolarizing phase during which the membrane briefly reverses polarity (cell interior becomes positive to the exterior). The Na+ activation gates open allowing an influx of Na+, while pota ...
... An action potential has four phases. (See Campbell, Figure 44.7) • Resting state, no channels are open. • Large depolarizing phase during which the membrane briefly reverses polarity (cell interior becomes positive to the exterior). The Na+ activation gates open allowing an influx of Na+, while pota ...
unit 3 study sheet - El Camino College
... 3. What are glial cells and glial cell function? 4. How does neural growth and neural regeneration happen in the CNS and PNS? 5. What makes a cell an excitable cell? What cells in the body are considered excitable? 6. Explain what type of information is obtained from the following formulas and when ...
... 3. What are glial cells and glial cell function? 4. How does neural growth and neural regeneration happen in the CNS and PNS? 5. What makes a cell an excitable cell? What cells in the body are considered excitable? 6. Explain what type of information is obtained from the following formulas and when ...
Chapter 2A Practice Test
... of heroin the brain ceases production of all neurotransmittersdunng withdrawai the brain's production of all neurotransmitters is greatly increased heroin destroys endoqphin receptors in the brain' ...
... of heroin the brain ceases production of all neurotransmittersdunng withdrawai the brain's production of all neurotransmitters is greatly increased heroin destroys endoqphin receptors in the brain' ...
In The Name of Allah The Most Beneficent The
... due to movement of ions across the membrane of neurons Mainly due to movement of Na and K ions Inside the cell: more K and less Na Outside the cell: less K and more Na Inside of the cell is negative with respect to outside of the cells due to larger size of the K ions as compared Na ions ...
... due to movement of ions across the membrane of neurons Mainly due to movement of Na and K ions Inside the cell: more K and less Na Outside the cell: less K and more Na Inside of the cell is negative with respect to outside of the cells due to larger size of the K ions as compared Na ions ...
Document
... sensory receptors in fingers respond to the hot metal ii. an impulse relaying this information is sent via sensory neuron to the spinal cord iii. the impulse passes to an interneuron in the spinal cord iv. impulses are immediately sent to the motor neurons in your arm causing you to move your hand C ...
... sensory receptors in fingers respond to the hot metal ii. an impulse relaying this information is sent via sensory neuron to the spinal cord iii. the impulse passes to an interneuron in the spinal cord iv. impulses are immediately sent to the motor neurons in your arm causing you to move your hand C ...
neuroprotective effect of quercetin during hydrogen peroxide
... signaling, has been implicated in dysfunctions of mammalian brain in numerous diseases and injuries. The aim of this study was to better understand the molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration induced via oxidative stress and the protective effect of flavonoid quercetin on the neuronal cell death i ...
... signaling, has been implicated in dysfunctions of mammalian brain in numerous diseases and injuries. The aim of this study was to better understand the molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration induced via oxidative stress and the protective effect of flavonoid quercetin on the neuronal cell death i ...
Fundamentals of Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... Inter-neurons receive information from sensory neurons and integrate it, interpret the meaning and pass instructions to motor neurons to act. Neurons (on basis # of appendages) Multipolar Neurons – many dendrites and 1 axon; most neurons in nervous system Unipolar Neurons – 1 appendage, one end acts ...
... Inter-neurons receive information from sensory neurons and integrate it, interpret the meaning and pass instructions to motor neurons to act. Neurons (on basis # of appendages) Multipolar Neurons – many dendrites and 1 axon; most neurons in nervous system Unipolar Neurons – 1 appendage, one end acts ...
AP Biology - Revere Local Schools
... Many possible outcomes This example shows a transcription response ...
... Many possible outcomes This example shows a transcription response ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.

![Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008568661_1-062fb6959798aae5bb439e7880889016-300x300.png)




















