The Nervous System
... The Resting Neuron • Not transmitting an impulse • If the outside of the cell has a positive charge and inside of the cell is a negative charge, then the neuron is said to be at resting potential ...
... The Resting Neuron • Not transmitting an impulse • If the outside of the cell has a positive charge and inside of the cell is a negative charge, then the neuron is said to be at resting potential ...
Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi © 2016 Ebneshahidi
... 1. The membrane is semi-permeable some things get through, while others do not get through. Important ions to be concerned with are Na+, K+, Cl- ,and anions-. 2. There are differences in concentration of these various ions between the inside and outside of the cell, so there are conc. gradients ...
... 1. The membrane is semi-permeable some things get through, while others do not get through. Important ions to be concerned with are Na+, K+, Cl- ,and anions-. 2. There are differences in concentration of these various ions between the inside and outside of the cell, so there are conc. gradients ...
5.4 Muscle Tissues
... – Involuntary control • Moves food through digestive system • Constricts blood vessels • Empties urinary bladder ...
... – Involuntary control • Moves food through digestive system • Constricts blood vessels • Empties urinary bladder ...
Biology 3201 - Corner Brook Regional High
... Transmitters move across the synapse to send messages from one neuron to the other. Receptor molecules pick up the message. ...
... Transmitters move across the synapse to send messages from one neuron to the other. Receptor molecules pick up the message. ...
Nervous System Function
... NT binding site – NT activates a “second messenger” (1st is the NT) inside the cell Change function of cell (e.g., change protein production to permanently alter cell function for learning) ...
... NT binding site – NT activates a “second messenger” (1st is the NT) inside the cell Change function of cell (e.g., change protein production to permanently alter cell function for learning) ...
1. Impulse Conduction
... 1.5 Effect of drugs on synaptic processes Knowledge of neurotransmitters helps us to understand the effect of drugs on behaviour because drugs effects the synaptic processes 2 main classes of drugs: (examples p. 70) a) agonists= drugs having a similar effect to some neurotransmitters b) antagoni ...
... 1.5 Effect of drugs on synaptic processes Knowledge of neurotransmitters helps us to understand the effect of drugs on behaviour because drugs effects the synaptic processes 2 main classes of drugs: (examples p. 70) a) agonists= drugs having a similar effect to some neurotransmitters b) antagoni ...
February 27
... processes. It is a complex series of events that occurs every second we are alive. In this lesson, students will explore communication inside the body by looking at the interaction between the cells of the nervous system, the neurons. The human body has literally billions of neurons, some of which f ...
... processes. It is a complex series of events that occurs every second we are alive. In this lesson, students will explore communication inside the body by looking at the interaction between the cells of the nervous system, the neurons. The human body has literally billions of neurons, some of which f ...
Dopamine axons of substantia nigra pars compacta neurons and
... Although mutated genes, protein aggregates, environmental toxins and other factors associated with PD are widely distributed in the nervous system and affect many classes of neurons, dopamine (DA) neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) show exceptional and selective vulnerability. One f ...
... Although mutated genes, protein aggregates, environmental toxins and other factors associated with PD are widely distributed in the nervous system and affect many classes of neurons, dopamine (DA) neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) show exceptional and selective vulnerability. One f ...
9.1-9.4 Notes
... – Multipolar – Carry impulse out of CNS to the effectors – Stimulate muscle and glands to respond ...
... – Multipolar – Carry impulse out of CNS to the effectors – Stimulate muscle and glands to respond ...
Chapter 15 - missdannocksyear11biologyclass
... form the stimulus before you feel the pain. This occurs because the scnsory receptor on your finger has sent a message via the sensory neuron to the CNS where interneurons connect this neuron to motor neruron to send a message back to an effector mucle to contract and escape the stimulus causing the ...
... form the stimulus before you feel the pain. This occurs because the scnsory receptor on your finger has sent a message via the sensory neuron to the CNS where interneurons connect this neuron to motor neruron to send a message back to an effector mucle to contract and escape the stimulus causing the ...
Nervous System Part 1
... arising from cell bodies, commonly found in the CNS. 2. Bipolar neurons have a single axon and a single dendrite extending from opposite sides of the cell body, found only in eyes, nose, and ears 3. Unipolar neurons are found in ganglia outside the CNS and have one axon that divides; the peripheral ...
... arising from cell bodies, commonly found in the CNS. 2. Bipolar neurons have a single axon and a single dendrite extending from opposite sides of the cell body, found only in eyes, nose, and ears 3. Unipolar neurons are found in ganglia outside the CNS and have one axon that divides; the peripheral ...
Membrane Domains and Membrane Potential
... membrane potential will return to the resting potential. If the neuron is at resting potential (-70mV) and the conductance to K+ increases, the membrane potential will be hyperpolarized (it will move toward -90mV). Transmission along the axon of a neuron occurs due to sequential activation of voltag ...
... membrane potential will return to the resting potential. If the neuron is at resting potential (-70mV) and the conductance to K+ increases, the membrane potential will be hyperpolarized (it will move toward -90mV). Transmission along the axon of a neuron occurs due to sequential activation of voltag ...
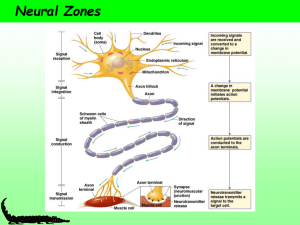
Nervous Dia rams
... The nerve celt that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
... The nerve celt that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
Nano-sized voltmeter measures electric fields deep within
... electric fields in cytosol—the jellylike material that makes up most of a cell's interior. ...
... electric fields in cytosol—the jellylike material that makes up most of a cell's interior. ...
chapter29_Sections 6
... ion channels and no myelin • After an action potential occurs at a node, positive ions diffuse quickly through the cytoplasm to the next node because myelin prevents them from leaking out across the membrane • Arrival of positive ions at the next node pushes the region to threshold, and an action po ...
... ion channels and no myelin • After an action potential occurs at a node, positive ions diffuse quickly through the cytoplasm to the next node because myelin prevents them from leaking out across the membrane • Arrival of positive ions at the next node pushes the region to threshold, and an action po ...
Neurons
... • Vary in size and structure, but have common features: 1. Cell Body 2. Dendrites 3. Axon ...
... • Vary in size and structure, but have common features: 1. Cell Body 2. Dendrites 3. Axon ...
Synapses - UBC Zoology
... An excitatory impulse, an excitatory post-synaptic potential raises the membrane potential above rest 1.An excitatory impulse at a synapse on the soma causes a depolarization of the whole soma including the beginning of the axon. The beginning of the axon is also known as the spike initialization zo ...
... An excitatory impulse, an excitatory post-synaptic potential raises the membrane potential above rest 1.An excitatory impulse at a synapse on the soma causes a depolarization of the whole soma including the beginning of the axon. The beginning of the axon is also known as the spike initialization zo ...
Resting Potential
... Importance of Ions • An incr. in extracellular K+ causes neuron to be less negative; threshold is reached sooner & neurons are very excitable; may result in convulsions ...
... Importance of Ions • An incr. in extracellular K+ causes neuron to be less negative; threshold is reached sooner & neurons are very excitable; may result in convulsions ...
How Ca2+ triggers neurotransmitter release
... Molecular mechanisms of neurotransmitter release Thomas C. Südhof Thomas Südhof's research investigates how neurons in brain communicate with each other during synaptic transmission, which is the process that underlies all brain activity, from consciousness over memory to sensory perception and move ...
... Molecular mechanisms of neurotransmitter release Thomas C. Südhof Thomas Südhof's research investigates how neurons in brain communicate with each other during synaptic transmission, which is the process that underlies all brain activity, from consciousness over memory to sensory perception and move ...
Hypotonic
... movement of substances in and out of cell, needed to maintain homeostasis What substances does a cell need to move in and out? Water moves freely through aquaporins. O2 and CO2 move freely through membrane. Polar particles need specialized carrier proteins: ions, glucose ...
... movement of substances in and out of cell, needed to maintain homeostasis What substances does a cell need to move in and out? Water moves freely through aquaporins. O2 and CO2 move freely through membrane. Polar particles need specialized carrier proteins: ions, glucose ...
AP Biology - Pleasantville High School
... membrane in a lock and key manner. (Inhibitor substances stop the impulse because they can fit into the receptor sites and block the normal neurotransmitter.) -this generates an action potential in the postsynaptic membrane and the nerve impulse continues on -after their release the neurotransmitter ...
... membrane in a lock and key manner. (Inhibitor substances stop the impulse because they can fit into the receptor sites and block the normal neurotransmitter.) -this generates an action potential in the postsynaptic membrane and the nerve impulse continues on -after their release the neurotransmitter ...
Lecture 3
... that grows out very rapidly. Both rate and direction of outgrowth are influenced by the nature of the substrate the axon encounters. This movie follows the elongation of the axon on a uniform substrate over a period of 16 hours. Note how the axon elongates in spurts. Time lapse: 16.5 hours (one loop ...
... that grows out very rapidly. Both rate and direction of outgrowth are influenced by the nature of the substrate the axon encounters. This movie follows the elongation of the axon on a uniform substrate over a period of 16 hours. Note how the axon elongates in spurts. Time lapse: 16.5 hours (one loop ...
The Nervous System
... • The current affects the nearby protein channels for Na+ and causes them to open. ...
... • The current affects the nearby protein channels for Na+ and causes them to open. ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.