Answer Key Introduction to Ecology Study Guide Chapter 1: Marking
... 14. 38 pheasants 15. Between 1974-1982 the population decreased 16. Point B in 1974 the population was 50 pheasants 17. The rapid decrease could be caused by a rise in predators, extreme weather, or human destruction 18. The pheasants would either emigrate or expire if their habitat was decimated by ...
... 14. 38 pheasants 15. Between 1974-1982 the population decreased 16. Point B in 1974 the population was 50 pheasants 17. The rapid decrease could be caused by a rise in predators, extreme weather, or human destruction 18. The pheasants would either emigrate or expire if their habitat was decimated by ...
1 - SanfordChemistry
... Which organism is in the secondary trophic level? What is the trophic level of the top carnivore? Define the term “biodiversity”. Give an example of an ecosystem that has high biodiversity and one that has low biodiversity. Explain the difference between abiotic and biotic factors in an ecosystem. L ...
... Which organism is in the secondary trophic level? What is the trophic level of the top carnivore? Define the term “biodiversity”. Give an example of an ecosystem that has high biodiversity and one that has low biodiversity. Explain the difference between abiotic and biotic factors in an ecosystem. L ...
ENVIRONMENTAL
... and defined by another renowned biologist, Ernst Haeckel in 1870: “Scientific study of the relationships of living organisms with each other and with their environment.” The term is derived from the Greek roots ‘Oikos’ (meaning home) and ‘logos’ (meaning study or discourse). The living organisms and ...
... and defined by another renowned biologist, Ernst Haeckel in 1870: “Scientific study of the relationships of living organisms with each other and with their environment.” The term is derived from the Greek roots ‘Oikos’ (meaning home) and ‘logos’ (meaning study or discourse). The living organisms and ...
Chapter 19 * Introduction to Ecology
... In addition to the natural ways, nitrogencontaining fertilizer contributes to the total amount of nitrogen materials in ecosystems. ...
... In addition to the natural ways, nitrogencontaining fertilizer contributes to the total amount of nitrogen materials in ecosystems. ...
Chapter 3: Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work
... 1. Rate at which an ecosystem’s producers convert solar energy into chemical energy as biomass. v. NPP = GPP – R 1. Rate at which producers use photosynthesis to store energy minus the rate at which they use some of this energy through respiration (R) ...
... 1. Rate at which an ecosystem’s producers convert solar energy into chemical energy as biomass. v. NPP = GPP – R 1. Rate at which producers use photosynthesis to store energy minus the rate at which they use some of this energy through respiration (R) ...
Ecology Powerpoint Review
... Population – group of a single species living in the same place Communities - group of interacting populations Ecosystem – the community and its environment Biome – group of ecosystems with the same communities Biosphere – the circle of life ...
... Population – group of a single species living in the same place Communities - group of interacting populations Ecosystem – the community and its environment Biome – group of ecosystems with the same communities Biosphere – the circle of life ...
Chapter 16
... Genetic diversity-the total genetic information contained in the genes of all species. Species Diversity-The variety of species, refers to the number of species and the number of individuals in a species. Ecosystem Diversity- the variety of habitats natural communities and ecological ...
... Genetic diversity-the total genetic information contained in the genes of all species. Species Diversity-The variety of species, refers to the number of species and the number of individuals in a species. Ecosystem Diversity- the variety of habitats natural communities and ecological ...
Unit 9: Ecology A. Definitions 1. biotic(bio = living)
... 1. invasive nonnative species (aka exotic species) were brought here for use as ornamental lawn or garden plants 2. when the invasive organism is able to survive and reproduce, it can invade the natural habitat and crowd out the native species reducing biodiversity 3. habitats with low plant ...
... 1. invasive nonnative species (aka exotic species) were brought here for use as ornamental lawn or garden plants 2. when the invasive organism is able to survive and reproduce, it can invade the natural habitat and crowd out the native species reducing biodiversity 3. habitats with low plant ...
Ecosystems Review Sheet - Liberty Union High School District
... Energy Flow in Ecosystems What is the 10% rule and how does it relate to the 2nd law of thermodynamics? ...
... Energy Flow in Ecosystems What is the 10% rule and how does it relate to the 2nd law of thermodynamics? ...
What might disrupt ecosystem processes? - Rawlins A
... What is a nutrient cycle? Functioning ecosystems have a continual flow of nutrients and energy through them These systems are self-regulating, but prone to human disruption: Deforestation or over fishing depletes the biomass store in the nutrient cycle Climate change may affect precipitatio ...
... What is a nutrient cycle? Functioning ecosystems have a continual flow of nutrients and energy through them These systems are self-regulating, but prone to human disruption: Deforestation or over fishing depletes the biomass store in the nutrient cycle Climate change may affect precipitatio ...
Ecosystems PowerPoint #2
... 2. Commensalism - One benefits and the other is unaffected 1. The whale and the barnacles 2. The clownfish and the anemones 3. The burdocks seeds and the fur ...
... 2. Commensalism - One benefits and the other is unaffected 1. The whale and the barnacles 2. The clownfish and the anemones 3. The burdocks seeds and the fur ...
1.2 PowerPoint - WordPress.com
... • By studying past and present ecosystems, we can better understand what may happen in the future. Historical ecology is the study of natural and written materials to better understand the ecology of a certain area. Many First Nations sources provide detailed knowledge of plants, animals, and na ...
... • By studying past and present ecosystems, we can better understand what may happen in the future. Historical ecology is the study of natural and written materials to better understand the ecology of a certain area. Many First Nations sources provide detailed knowledge of plants, animals, and na ...
5th grade ecology study guide
... Sun is the main energy source for life on earth During photosynthesis producers produce oxygen B). Energy Flow in Ecosystems Describe how energy flows from the sun in an ecosystem Food web / food chain – how are they different, can you read energy flow in? Trophic level – can you identify ...
... Sun is the main energy source for life on earth During photosynthesis producers produce oxygen B). Energy Flow in Ecosystems Describe how energy flows from the sun in an ecosystem Food web / food chain – how are they different, can you read energy flow in? Trophic level – can you identify ...
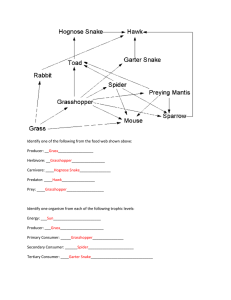
Identify one of the following from the food web shown above
... All of the following can overwhelm the stability of an ecosystem and result in long-term irreversible changes for organisms EXCEPT ___. A. loss of grasses and other vegetation due to sustained high temperatures accompanied with low precipitation B. loss of fish production in a stream, due to death o ...
... All of the following can overwhelm the stability of an ecosystem and result in long-term irreversible changes for organisms EXCEPT ___. A. loss of grasses and other vegetation due to sustained high temperatures accompanied with low precipitation B. loss of fish production in a stream, due to death o ...
Ecology Practice Questions
... b. precipitation c. the biotic community d. wind Which of the following is the smallest ecological unit? a. a community b. a population c. the biosphere d. an ecosystem Collectively, physical factors such as light, temperature, and moisture that affect an organism's life and survival are called the ...
... b. precipitation c. the biotic community d. wind Which of the following is the smallest ecological unit? a. a community b. a population c. the biosphere d. an ecosystem Collectively, physical factors such as light, temperature, and moisture that affect an organism's life and survival are called the ...
Unit 4 (2nd unit covered) Sustainability of Ecosystems Pg
... Trophic Level is a category of organisms defined by how they get energy: Primary producers, primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), tertiary consumers (top carnivores). Biomass is the total mass of living organisms in a defined group or area. All energy comes from the sun ...
... Trophic Level is a category of organisms defined by how they get energy: Primary producers, primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), tertiary consumers (top carnivores). Biomass is the total mass of living organisms in a defined group or area. All energy comes from the sun ...
Other Definitions-Ecosystem Forest Health Habitat Old Growth
... Ecological terms related to ecosystems, vegetation, wildlife and wildlife habitat Note: All definitions are context dependent disturbance Any relatively discrete event in time that changes or disrupts ecosystem components, such as fire, flood, insects, diseases, invasive plants and animals, and clim ...
... Ecological terms related to ecosystems, vegetation, wildlife and wildlife habitat Note: All definitions are context dependent disturbance Any relatively discrete event in time that changes or disrupts ecosystem components, such as fire, flood, insects, diseases, invasive plants and animals, and clim ...
Energy Flow through an Ecosystem
... • How does energy enter an ecosystem? – Plants = Photosynthesis – Balance equation • 6CO2 + 6H2O ...
... • How does energy enter an ecosystem? – Plants = Photosynthesis – Balance equation • 6CO2 + 6H2O ...
Ch. 4 Ecosystems study guide. Change the underlined word in each
... Change the underlined word in each sentence to make it true. ...
... Change the underlined word in each sentence to make it true. ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.