Interdependence Among Living Systems
... There is interdependence between organisms and their environment. — What are the biotic factors an ecosystem? — What are some abiotic factors in an ecosystem? — For what resources may organisms have to compete? — In what ways do organisms depend on each other? — How are organisms and their environme ...
... There is interdependence between organisms and their environment. — What are the biotic factors an ecosystem? — What are some abiotic factors in an ecosystem? — For what resources may organisms have to compete? — In what ways do organisms depend on each other? — How are organisms and their environme ...
What Else Changes the Environment?
... flood, fire, earthquake, mudslide, hurricane or volcanic eruption can instantly change an environment and kill the communities that live there. If this happens, a new community will replace the old community over time. This is called succession. An example of succession is when a field is left untou ...
... flood, fire, earthquake, mudslide, hurricane or volcanic eruption can instantly change an environment and kill the communities that live there. If this happens, a new community will replace the old community over time. This is called succession. An example of succession is when a field is left untou ...
Relationships Among Organisms and Energy Flow
... interactions between organisms but some ecosystems are considered stable • An ecosystem can be considered stable when: – The population numbers of each organism fluctuate at a predictable rate – The supply of resources fluctuates at a predictable rate – Energy flows through the ecosystem at a fairly ...
... interactions between organisms but some ecosystems are considered stable • An ecosystem can be considered stable when: – The population numbers of each organism fluctuate at a predictable rate – The supply of resources fluctuates at a predictable rate – Energy flows through the ecosystem at a fairly ...
ecology definitions
... transfers energy from sunlight and carbon from inorganic compounds such as carbon dioxide into food chains. The process results in biomass. The energy stored is termed the gross primary production and net primary production if respiration losses are taken into account. ...
... transfers energy from sunlight and carbon from inorganic compounds such as carbon dioxide into food chains. The process results in biomass. The energy stored is termed the gross primary production and net primary production if respiration losses are taken into account. ...
File ap notes chapter 54
... very little nutrients Soils in temperate deciduous forest may contain 50% of all of the organic materials in the ecosystem Decomposition in tundra can take up to 50 years ...
... very little nutrients Soils in temperate deciduous forest may contain 50% of all of the organic materials in the ecosystem Decomposition in tundra can take up to 50 years ...
Ecosystem Services of Mangrove Forests
... Focus: Consequences of Ecosystem Change for Human Well-being ...
... Focus: Consequences of Ecosystem Change for Human Well-being ...
Ecology Notes
... It takes a large number of producers to support a small number of primary consumers It takes a large number of primary consumers to support a small number of secondary consumers ...
... It takes a large number of producers to support a small number of primary consumers It takes a large number of primary consumers to support a small number of secondary consumers ...
Ecosystem vocabulary
... Is made up of all different kinds of populations living in the same area. ...
... Is made up of all different kinds of populations living in the same area. ...
Ecosystem
... The energy flowing through and ecosystem can be charted in one of two ways 1) food chain- simple path through the ecosystem 2) food web- an interconnected group of food chains which provides a more realistic energy pathway Food chain: sun, plant, animal, animal Food web: (arrows go towards organism ...
... The energy flowing through and ecosystem can be charted in one of two ways 1) food chain- simple path through the ecosystem 2) food web- an interconnected group of food chains which provides a more realistic energy pathway Food chain: sun, plant, animal, animal Food web: (arrows go towards organism ...
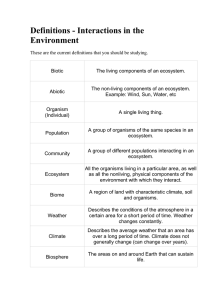
Definitions - Interactions in the Environment These are the current
... Describes the average weather that an area has over a long period of time. Climate does not generally change (can change over years). ...
... Describes the average weather that an area has over a long period of time. Climate does not generally change (can change over years). ...
Intro to Ecology Flow of Energy Vocabulary Review
... ____ 16. Chemical reactions that convert light energy or inorganic compounds are known as a. autotroph and heterotroph c. producer and consumer b. photosynthesis and chemosynthesis d. predator and prey ____ 17. An animal that feeds on plant and animal remains and other dead matter a. omnivore b. her ...
... ____ 16. Chemical reactions that convert light energy or inorganic compounds are known as a. autotroph and heterotroph c. producer and consumer b. photosynthesis and chemosynthesis d. predator and prey ____ 17. An animal that feeds on plant and animal remains and other dead matter a. omnivore b. her ...
Ms. Hall Environmental Science Study Guide Midterm
... 1) A group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area is a(n) ___________________________________. 2) __________________________________ and _____________________________ account account for much of the transformation and movement of carbon in the carbon cycle. 3) What level of cons ...
... 1) A group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area is a(n) ___________________________________. 2) __________________________________ and _____________________________ account account for much of the transformation and movement of carbon in the carbon cycle. 3) What level of cons ...
Ecosystem dynamics in the salt marsh
... and ask for the students to come up with plausible explanations for what they see. Then the teacher will introduce the concepts of ecosystem – a community (all the organisms in a given area) and the abiotic factors (such as water, soil, or climate) that affect them. stable ecosystem - population ...
... and ask for the students to come up with plausible explanations for what they see. Then the teacher will introduce the concepts of ecosystem – a community (all the organisms in a given area) and the abiotic factors (such as water, soil, or climate) that affect them. stable ecosystem - population ...
Interactions and Ecosystems Review JEOPARDY
... different species that live and interact in the same place form ….. ...
... different species that live and interact in the same place form ….. ...
Standard 6 - Bulldogbiology.com
... Marshlands and swamps are often protected to ensure that an organism’s habitat is not destroyed. Human effects on the environment are also long term. Global warming and global climate change can both affect ecosystems and biodiversity. o Introduction of invasive, non-native species - By introduc ...
... Marshlands and swamps are often protected to ensure that an organism’s habitat is not destroyed. Human effects on the environment are also long term. Global warming and global climate change can both affect ecosystems and biodiversity. o Introduction of invasive, non-native species - By introduc ...
Energy Flow in the Coral Reef Ecosystem
... Scavengers and decomposers also play an important role in an ecosystem: They are its primary recyclers. Scavengers are animals that feed on dead members of different trophic levels. Decomposers, which include bacteria and fungi, break down organic waste material and return essential elements, such a ...
... Scavengers and decomposers also play an important role in an ecosystem: They are its primary recyclers. Scavengers are animals that feed on dead members of different trophic levels. Decomposers, which include bacteria and fungi, break down organic waste material and return essential elements, such a ...
Ecosystems Study Guide
... - evaporation= change from water to water vapor - condensation= water vapor condenses to form small droplets of water - precipitation= any form of water that falls from the sky - transpiration= some water within plants evaporates into the atmosphere B. Carbon cycle -begins with photosynthesis (in pl ...
... - evaporation= change from water to water vapor - condensation= water vapor condenses to form small droplets of water - precipitation= any form of water that falls from the sky - transpiration= some water within plants evaporates into the atmosphere B. Carbon cycle -begins with photosynthesis (in pl ...
Ecosystems and communities Ecology
... One species benefits by living in or on the other and the other is harmed ...
... One species benefits by living in or on the other and the other is harmed ...
Kera Crosby
... 7) Autotrophs – Transform ____________ energy (light) into ______________ energy 8) Primary productivity – The net production of stored ___________ produced by the _______________ in an ecosystem 9) Heterotrophs – Organisms that must obtain their energy by ________ other organisms 10)Food chain – Sh ...
... 7) Autotrophs – Transform ____________ energy (light) into ______________ energy 8) Primary productivity – The net production of stored ___________ produced by the _______________ in an ecosystem 9) Heterotrophs – Organisms that must obtain their energy by ________ other organisms 10)Food chain – Sh ...
4 Ecology - Kerboodle
... nutrients from simple inorganic compounds obtained from its environment. Biotic factors attributes in an ecosystem that refer to living organisms. Chi-squared test a statistical test of the fit between a theoretical frequency distribution and a frequency distribution of observed data for which each ...
... nutrients from simple inorganic compounds obtained from its environment. Biotic factors attributes in an ecosystem that refer to living organisms. Chi-squared test a statistical test of the fit between a theoretical frequency distribution and a frequency distribution of observed data for which each ...
EndofUnitTestReviewA.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Why might an organic farmer add manure to a field? Animal manure, which contains nitrogen compounds, can be used as a natural plant fertilizer. The manure is broken down by decomposers in the soil to release ammonia, which can be used directly by some plants as a source of nitrogen. The ammonia can ...
... Why might an organic farmer add manure to a field? Animal manure, which contains nitrogen compounds, can be used as a natural plant fertilizer. The manure is broken down by decomposers in the soil to release ammonia, which can be used directly by some plants as a source of nitrogen. The ammonia can ...
Traditional Ecological Knowledge
... What is the knowledge about? Valuable data on: • Local climate and resources • Biotic and abiotic characteristics • Animal and plant life cycles • Soil types • Plant and animal species • Practices that enhance the productivity and health of the ecosystem ...
... What is the knowledge about? Valuable data on: • Local climate and resources • Biotic and abiotic characteristics • Animal and plant life cycles • Soil types • Plant and animal species • Practices that enhance the productivity and health of the ecosystem ...
2.8 Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Ecosystems Limiting Factors • A
... 2.8 Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Ecosystems Limiting Factors ...
... 2.8 Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Ecosystems Limiting Factors ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.