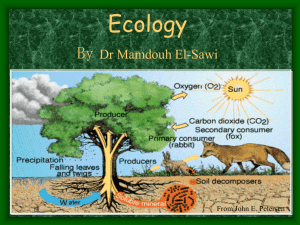
Principles of Ecology
... amount of energy available in a food web decreases with each higher feeding level. Most energy taken into an organism as food is lost to the environment as heat (only about 10% is actually used)! As you move up the food chain/web (trophic levels), the number of organisms decreases (as does the ...
... amount of energy available in a food web decreases with each higher feeding level. Most energy taken into an organism as food is lost to the environment as heat (only about 10% is actually used)! As you move up the food chain/web (trophic levels), the number of organisms decreases (as does the ...
Station 4: Cycles and Ecosystems
... a. Animals and plants cannot directly use all the nitrogen found in our _____________. b. Only special bacteria can directly use nitrogen in our atmosphere and “fix” it so other organisms can benefit. These Bacteria are called ____________________ bacteria. c. Higher organisms use nitrogen to make t ...
... a. Animals and plants cannot directly use all the nitrogen found in our _____________. b. Only special bacteria can directly use nitrogen in our atmosphere and “fix” it so other organisms can benefit. These Bacteria are called ____________________ bacteria. c. Higher organisms use nitrogen to make t ...
FOURTH QUARTER EXAM STUDY GUIDE I. CHANGE OVER TIME
... 1. All living and nonliving things in an area make up an ecosystem. 2. The living things in an ecosystem are the biotic factors. 3. Sunlight and temperature are examples of nonliving factors, or abiotic factors, in an ecosystem. B. How does matter move in ecosystems? 1. Many types of matter are used ...
... 1. All living and nonliving things in an area make up an ecosystem. 2. The living things in an ecosystem are the biotic factors. 3. Sunlight and temperature are examples of nonliving factors, or abiotic factors, in an ecosystem. B. How does matter move in ecosystems? 1. Many types of matter are used ...
Invasive species
... early then drops over time since introduction • Another group is already focused on temporal dynamics – we need to find out what they are doing ...
... early then drops over time since introduction • Another group is already focused on temporal dynamics – we need to find out what they are doing ...
population
... • The vast majority of natural ecosystems experience regular environmental change, or disturbances. • Most ecologists describe ecosystem stability as the ability of an ecosystem to maintain its structure and function over long periods of time despite disturbances. ...
... • The vast majority of natural ecosystems experience regular environmental change, or disturbances. • Most ecologists describe ecosystem stability as the ability of an ecosystem to maintain its structure and function over long periods of time despite disturbances. ...
Ecology
... Autotrophs - often make their own food by using sunlight, photosynthesis, carbon dioxide, and water to form sugars which they can use for energy. Autotrophs are important because they are a food source for heterotrophs (consumers). Some examples of autotrophs include plants, algae, and even so ...
... Autotrophs - often make their own food by using sunlight, photosynthesis, carbon dioxide, and water to form sugars which they can use for energy. Autotrophs are important because they are a food source for heterotrophs (consumers). Some examples of autotrophs include plants, algae, and even so ...
World Biomes - Appoquinimink High School
... • Population- A group of organisms all of the same species living in the same area at the same time. • Community- A collection of several populations that inhabit a common area. • Population Density- How many individuals occupying a certain area • Limiting Factor- anything that would keep something ...
... • Population- A group of organisms all of the same species living in the same area at the same time. • Community- A collection of several populations that inhabit a common area. • Population Density- How many individuals occupying a certain area • Limiting Factor- anything that would keep something ...
Ecology - Union County College
... • Niche : the ecological role of an organism in a community. For example, the niche of the green plants is to produce sugar by photosynthesis, which is used by the plant and also consumed by animals. • Habitat : the place where a species is most usually found. ...
... • Niche : the ecological role of an organism in a community. For example, the niche of the green plants is to produce sugar by photosynthesis, which is used by the plant and also consumed by animals. • Habitat : the place where a species is most usually found. ...
Living Things and Their Environment
... Abiotic Factors • Non living parts of an organisms habitat are the Abiotic Factors • Examples… Water, sunlight, temperature, oxygen, soil • Photosynthesis… Process by which plants make food and oxygen from Carbon Dioxide ...
... Abiotic Factors • Non living parts of an organisms habitat are the Abiotic Factors • Examples… Water, sunlight, temperature, oxygen, soil • Photosynthesis… Process by which plants make food and oxygen from Carbon Dioxide ...
Marine Ecosystems
... This energy transfers up through the food web but only 10% of it is available to pass on to the next trophic level This limits the number of organisms at each trophic level Numbers of organisms drastically decline as you go from primary producers to high level predators There are far more pr ...
... This energy transfers up through the food web but only 10% of it is available to pass on to the next trophic level This limits the number of organisms at each trophic level Numbers of organisms drastically decline as you go from primary producers to high level predators There are far more pr ...
Review Questions for ecology test
... 5. List 1 way carbon is put into the air. a. burning wood or fossil fuels, respiration 6. List 1 way carbon is stored/taken out of the air. a. oceans, photosynthesis, trees/plants 7. In the water cycle, water changing from a gas to a liquid is called a. evaporation 8. What is the next step in the wa ...
... 5. List 1 way carbon is put into the air. a. burning wood or fossil fuels, respiration 6. List 1 way carbon is stored/taken out of the air. a. oceans, photosynthesis, trees/plants 7. In the water cycle, water changing from a gas to a liquid is called a. evaporation 8. What is the next step in the wa ...
Ecology - St. Ambrose School
... energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web. Types of ecological pyramids are energy pyramids, biomass pyramids, and pyramids of numbers. Energy pyramids show how much energy is available within each trophic level. ...
... energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web. Types of ecological pyramids are energy pyramids, biomass pyramids, and pyramids of numbers. Energy pyramids show how much energy is available within each trophic level. ...
Tropical Rain Forests
... They are alike. They are capable of breeding with one another. Examples are: sunfish in a lake, people in a city. ...
... They are alike. They are capable of breeding with one another. Examples are: sunfish in a lake, people in a city. ...
Interactions and Ecosystems Notes
... • Acid Rain: occurs when pollutants containing sulfur and nitrogen are found in high levels in the air. ...
... • Acid Rain: occurs when pollutants containing sulfur and nitrogen are found in high levels in the air. ...
Food Webs Within Ecosystems
... Parasite/Host Relationships • Parasite – organism that feeds off other living ...
... Parasite/Host Relationships • Parasite – organism that feeds off other living ...
KEY AN ORGANISM`S NICHE IS ITS ROLE IN THE COMMUNITY
... * the non-living parts of the environment * they directly affect the ability of organisms to live and reproduce ex. hot temperature, little water are examples of abiotic factors BIOTIC FACTORS * all the living things that directly or indirectly affect the ecosystem * biotic factors interact with oth ...
... * the non-living parts of the environment * they directly affect the ability of organisms to live and reproduce ex. hot temperature, little water are examples of abiotic factors BIOTIC FACTORS * all the living things that directly or indirectly affect the ecosystem * biotic factors interact with oth ...
Environmental Science A Test 1
... 36.) A wolf pack hunts, kills, and feeds on a moose. In this interaction, the wolves are____________________________ 37.) What is a predator? 38.) A symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit is______________________________________ 39.) A symbiotic relationship in which one organism is ha ...
... 36.) A wolf pack hunts, kills, and feeds on a moose. In this interaction, the wolves are____________________________ 37.) What is a predator? 38.) A symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit is______________________________________ 39.) A symbiotic relationship in which one organism is ha ...
Habitat loss - College of Forestry, University of Guangxi
... Human influence on nutrient cycle and its outcome • As we move to talking about conservation biology and global ecology, we will talk more about how humans have altered nutrient cycling, especially: • N deposition(沉淀物) (added to atmosphere by industrial activity, then falls down). • CO2 increase an ...
... Human influence on nutrient cycle and its outcome • As we move to talking about conservation biology and global ecology, we will talk more about how humans have altered nutrient cycling, especially: • N deposition(沉淀物) (added to atmosphere by industrial activity, then falls down). • CO2 increase an ...
WFSC 420 Lesson 2 - Southern Columbia Area School District
... Shares many of the species and characteristics of both ecosystems May also include unique conditions that support distinctive plant and animal species ...
... Shares many of the species and characteristics of both ecosystems May also include unique conditions that support distinctive plant and animal species ...
primary consumers?
... Shares many of the species and characteristics of both ecosystems May also include unique conditions that support distinctive plant and animal species ...
... Shares many of the species and characteristics of both ecosystems May also include unique conditions that support distinctive plant and animal species ...
File
... • The vast majority of natural ecosystems experience regular environmental change, or disturbances. • Most ecologists describe ecosystem stability as the ability of an ecosystem to maintain its structure and function over long periods of time despite disturbances. ...
... • The vast majority of natural ecosystems experience regular environmental change, or disturbances. • Most ecologists describe ecosystem stability as the ability of an ecosystem to maintain its structure and function over long periods of time despite disturbances. ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.