Document
... interactions between organisms and their environments, focusing on energy transfer Ecology is a science of relationships ...
... interactions between organisms and their environments, focusing on energy transfer Ecology is a science of relationships ...
任课院系:资源环境学院 环境系 任课教师:张颖
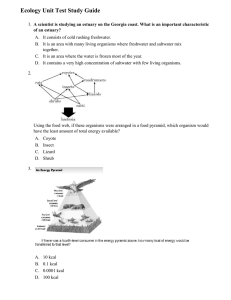
... numbers of offspring than unsuccessful individuals can reproduce is called a: natural selection b: predation c: mutualism d: speciation A trout cannot live in a slow, warm stream because the oxygen concentration in the water is too low. In this case, the oxygen concentration is a: a range of toleran ...
... numbers of offspring than unsuccessful individuals can reproduce is called a: natural selection b: predation c: mutualism d: speciation A trout cannot live in a slow, warm stream because the oxygen concentration in the water is too low. In this case, the oxygen concentration is a: a range of toleran ...
Notes - Biology Junction
... ___________ cycle___________________ nitrogen (N2) makes up nearly ___ %-___ % of air. Organisms ____ _____ use it in that form. _____________ and ___________ convert nitrogen into ___________ forms. Only in certain ____________ and industrial ______________ can _____ nitrogen. Nitrogen_____________ ...
... ___________ cycle___________________ nitrogen (N2) makes up nearly ___ %-___ % of air. Organisms ____ _____ use it in that form. _____________ and ___________ convert nitrogen into ___________ forms. Only in certain ____________ and industrial ______________ can _____ nitrogen. Nitrogen_____________ ...
No Slide Title
... farm. Every third year clover, a legume, is planted and plowed under. This improves the nitrogen content and physical structure of the soil for growing wheat and corn the other two years of the rotation cycle. ...
... farm. Every third year clover, a legume, is planted and plowed under. This improves the nitrogen content and physical structure of the soil for growing wheat and corn the other two years of the rotation cycle. ...
Unit 5 Ecology II Study Guide
... ___________ cycle___________________ nitrogen (N2) makes up nearly ___ %-___ % of air. Organisms ____ _____ use it in that form. _____________ and ___________ convert nitrogen into ___________ forms. Only in certain ____________ and industrial ______________ can _____ nitrogen. Nitrogen_____________ ...
... ___________ cycle___________________ nitrogen (N2) makes up nearly ___ %-___ % of air. Organisms ____ _____ use it in that form. _____________ and ___________ convert nitrogen into ___________ forms. Only in certain ____________ and industrial ______________ can _____ nitrogen. Nitrogen_____________ ...
Exit Ticket
... 3. Do you think the government’s decision to exempt the city from the endangered species act is right/wrong? Why? ...
... 3. Do you think the government’s decision to exempt the city from the endangered species act is right/wrong? Why? ...
ecology unit study guide
... B. The dominant trees found in a deciduous forest lose their leaves in the winter whereas the dominant trees in the taiga retain their leaves year round. C. The dominant trees found in a taiga lose their leaves in the winter whereas the dominant trees in the deciduous forest retain their leaves year ...
... B. The dominant trees found in a deciduous forest lose their leaves in the winter whereas the dominant trees in the taiga retain their leaves year round. C. The dominant trees found in a taiga lose their leaves in the winter whereas the dominant trees in the deciduous forest retain their leaves year ...
Ocean Acidification Workshop Slides
... impacting present day and future marine ecosystems in ways that we are just beginning to recognize and understand. More research is needed to determine the temporal and spatial changes of the carbon system in the global oceans and their impacts on biological communities and ecosystems. Manipulat ...
... impacting present day and future marine ecosystems in ways that we are just beginning to recognize and understand. More research is needed to determine the temporal and spatial changes of the carbon system in the global oceans and their impacts on biological communities and ecosystems. Manipulat ...
Ecosystems
... the same habitat different processes may occur, such as cooperation, symbiosis, but also competition and predation. An aquarium or a terrarium are good examples of a shared habitat. V. Function of ecosystems Considering the benefit from ecosystems for the human race, ecosystems may be regarded as pr ...
... the same habitat different processes may occur, such as cooperation, symbiosis, but also competition and predation. An aquarium or a terrarium are good examples of a shared habitat. V. Function of ecosystems Considering the benefit from ecosystems for the human race, ecosystems may be regarded as pr ...
1.4.8 Nutrient Recycling Crossword
... of 78% of this gas (8) 7. The conversion of ammonia to nitrites and nitrates ...
... of 78% of this gas (8) 7. The conversion of ammonia to nitrites and nitrates ...
answers
... __biotic factors___________________ 1. all living organisms in a habitat __biodiversity___________________ 2. number of species living within an ecosystem __succession___________________ 3. change in a community’s characteristics over time __community______________ 4. deer, squirrels, and rabbits li ...
... __biotic factors___________________ 1. all living organisms in a habitat __biodiversity___________________ 2. number of species living within an ecosystem __succession___________________ 3. change in a community’s characteristics over time __community______________ 4. deer, squirrels, and rabbits li ...
Notes - Humble ISD
... the energy stored in an organism is passed to the next trophic level. ________% of the energy is either used by the organism to maintain ____________________ or lost as ___________ to the environment. Because of this, most food chains typically consist of only _____ or ______ trophic levels. Ecologi ...
... the energy stored in an organism is passed to the next trophic level. ________% of the energy is either used by the organism to maintain ____________________ or lost as ___________ to the environment. Because of this, most food chains typically consist of only _____ or ______ trophic levels. Ecologi ...
CH-4 Sect 4
... a. They generally weaken but do not kill their host. b. They obtain all or part of their nutritional needs from the host. c. They neither help nor harm the host. d. They are usually smaller than the host. 16. What is ecological succession? (pg 94-97)__________________________________________________ ...
... a. They generally weaken but do not kill their host. b. They obtain all or part of their nutritional needs from the host. c. They neither help nor harm the host. d. They are usually smaller than the host. 16. What is ecological succession? (pg 94-97)__________________________________________________ ...
File
... • This is a natural process • Humans are altering ecosystems all over the world, we are also an element of ecological succession • The scale that we are changing ecosystems is huge, and unprecedented ...
... • This is a natural process • Humans are altering ecosystems all over the world, we are also an element of ecological succession • The scale that we are changing ecosystems is huge, and unprecedented ...
Document
... organisms and from their surroundings. Ex. Nutrients in the green grass pass to the cow that eats the grass. The cycle continues until the last consumer dies. Detritivores return the nutrients to the cycle, and the process begins again. ...
... organisms and from their surroundings. Ex. Nutrients in the green grass pass to the cow that eats the grass. The cycle continues until the last consumer dies. Detritivores return the nutrients to the cycle, and the process begins again. ...
Chp 4 Questions
... Distinguish among the atmosphere, troposphere, stratosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. How does the sun help sustain life on the earth? How is this related to the earth’s natural greenhouse effect? What are biomes, and how are they related to climate? What are aquatic life zones? Dist ...
... Distinguish among the atmosphere, troposphere, stratosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. How does the sun help sustain life on the earth? How is this related to the earth’s natural greenhouse effect? What are biomes, and how are they related to climate? What are aquatic life zones? Dist ...
Which Factors Affect Ecosystems
... not have the rabbits to eat; therefore, they might go hungry. Or, they would have to find another food source which might cause another species to go hungry. Can you see how a change in population could upset the balance of an ecosystem? ...
... not have the rabbits to eat; therefore, they might go hungry. Or, they would have to find another food source which might cause another species to go hungry. Can you see how a change in population could upset the balance of an ecosystem? ...
Biogeographic Processes
... In mid to high latitudes light controls seasonal activity of plants in through changes in photoperiod or daylight length Deciduous vegetation in mid-latitudes responds to changes both light and temperature with seasons ...
... In mid to high latitudes light controls seasonal activity of plants in through changes in photoperiod or daylight length Deciduous vegetation in mid-latitudes responds to changes both light and temperature with seasons ...
File
... Includes place in the food web, range of survivable temps, type of food eaten, physical conditions needed for survival… ...
... Includes place in the food web, range of survivable temps, type of food eaten, physical conditions needed for survival… ...
Unit_8_MHS_Bio_Review_Guide_ANSWERS
... 6. Define biotic factors and give 2 examples. Biotic factors = activities of living organisms that affect other organisms (EX: ...
... 6. Define biotic factors and give 2 examples. Biotic factors = activities of living organisms that affect other organisms (EX: ...
Theory & Practice
... Umbrella species are those that have habitat requirements such that managing for that species will de facto protect a much broader suite of species. This is also called a “spillover effect” (see Box 5.1 in Falk et al) Mussels are the classic umbrella species in our part of the world. Require cold, c ...
... Umbrella species are those that have habitat requirements such that managing for that species will de facto protect a much broader suite of species. This is also called a “spillover effect” (see Box 5.1 in Falk et al) Mussels are the classic umbrella species in our part of the world. Require cold, c ...
Lecture Seven: Ecology
... system, are strictly limited to marine environments, and their tissues have the same salinity as sea water. We can also categorize animals based on (1) where they get their heat and (2) how they regulate their body temperature: * ectotherm - obtains heat primarily from the environment (a conformer) ...
... system, are strictly limited to marine environments, and their tissues have the same salinity as sea water. We can also categorize animals based on (1) where they get their heat and (2) how they regulate their body temperature: * ectotherm - obtains heat primarily from the environment (a conformer) ...
Ch 3-4 Reading Guide
... 17. What do you think a limiting factor/resource is? Give an example. Explain how it might lead to ...
... 17. What do you think a limiting factor/resource is? Give an example. Explain how it might lead to ...
Ecology Review from 7th Grade PowerPoint
... • At any step along the way, an organism might die and be consumed by other scavengers or break down through the work of decomposers, such as insects and bacteria. ...
... • At any step along the way, an organism might die and be consumed by other scavengers or break down through the work of decomposers, such as insects and bacteria. ...
Unit 7 Review - 2 - Iowa State University
... 31. What of the following forms of nitrogen can be used by living organisms? a. N2 b. NO3 c. NH3 d. None of the above 32. Which of the following processes is not how CO2 gets from the Earth to the atmosphere? a. Photosynthesis b. Decomposition c. Deforestation d. Burning Fossil Fuels e. Cellular Res ...
... 31. What of the following forms of nitrogen can be used by living organisms? a. N2 b. NO3 c. NH3 d. None of the above 32. Which of the following processes is not how CO2 gets from the Earth to the atmosphere? a. Photosynthesis b. Decomposition c. Deforestation d. Burning Fossil Fuels e. Cellular Res ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.