Root–root interactions: extending our perspective
... into account. Recent research on plant communication and behaviour, however, has opened up our perspective towards non-resourcedriven interactions once again, and provides impetus to consider both resource-driven and non-resource-driven mechanisms when studying plant interactions (see Fig. 2). Going ...
... into account. Recent research on plant communication and behaviour, however, has opened up our perspective towards non-resourcedriven interactions once again, and provides impetus to consider both resource-driven and non-resource-driven mechanisms when studying plant interactions (see Fig. 2). Going ...
2000 - CiteSeerX
... (2) facultative and costly antipredator defense by the prey20; (3) density dependent and time-consuming social interactions among the predators; (4) aggressive interactions between searching predators that encounter each other21,22; and (5) a limited number of high-quality sites where predators capt ...
... (2) facultative and costly antipredator defense by the prey20; (3) density dependent and time-consuming social interactions among the predators; (4) aggressive interactions between searching predators that encounter each other21,22; and (5) a limited number of high-quality sites where predators capt ...
WINSLOW Biology Quick View Biology Standards Washington State
... Commensalism: a symbiotic relationship between two species in which one of them benefits and the other neither benefits nor is harmed. An example of commensalism is the relationship between sharks and remoras. The remora benefits and the shark is not affected either positively or negatively. Communi ...
... Commensalism: a symbiotic relationship between two species in which one of them benefits and the other neither benefits nor is harmed. An example of commensalism is the relationship between sharks and remoras. The remora benefits and the shark is not affected either positively or negatively. Communi ...
Interindividual Variation in Prey Selection by the Snail Nucella
... Activity and the process of predation by N. emarginata were observed in the field. After selecting its prey, Nucella normally drills through the shell, inserts its proboscis, and rasps out the soft body parts with the radula. Observations made at both low and high tides indicate that the snails are ...
... Activity and the process of predation by N. emarginata were observed in the field. After selecting its prey, Nucella normally drills through the shell, inserts its proboscis, and rasps out the soft body parts with the radula. Observations made at both low and high tides indicate that the snails are ...
Patch area, substrate depth, and richness affect giving
... harvest rate which under random search yields the same GUD independent of initial food abundance. At the other extreme, the forager may be unable to make any assessment of current patch quality. Such a forager should devote the same amount of search time to each patch resulting in the same proportio ...
... harvest rate which under random search yields the same GUD independent of initial food abundance. At the other extreme, the forager may be unable to make any assessment of current patch quality. Such a forager should devote the same amount of search time to each patch resulting in the same proportio ...
life on the coral reef - Cayman Islands Department of Environment
... portion of the trunk to obtain oxygen. ...
... portion of the trunk to obtain oxygen. ...
Prey size, prey nutrition, and food handling by shrews of different
... Although energy is the most popular currency for use in optimal foraging models, many studies have concentrated on relationships between prey size or taxon and predator search time, handling time, and capture efficiency, and only few studies have assessed prey energy values (Brooks et al., 1996). As ...
... Although energy is the most popular currency for use in optimal foraging models, many studies have concentrated on relationships between prey size or taxon and predator search time, handling time, and capture efficiency, and only few studies have assessed prey energy values (Brooks et al., 1996). As ...
REV_ISS_WEB_JPE_12709_53-6 1823..1830
... annual crops can enhance the impact of arthropod generalist predators. An accumulation of studies in annual systems shows that hedgerows and ditches or temporary structures such as field margins, grass covered earth banks or strips with herbaceous ground flora can act as refuges to reduce winter mor ...
... annual crops can enhance the impact of arthropod generalist predators. An accumulation of studies in annual systems shows that hedgerows and ditches or temporary structures such as field margins, grass covered earth banks or strips with herbaceous ground flora can act as refuges to reduce winter mor ...
Food choice by the introduced crayfish Procambarus clarkii
... assess resource availability, which is the “Achilles heal” of in situ feeding studies. Information on resource availability can be estimated by the determination of the relative abundance of prey items in the environment. Some criticism has arisen to the application of this technique, because habita ...
... assess resource availability, which is the “Achilles heal” of in situ feeding studies. Information on resource availability can be estimated by the determination of the relative abundance of prey items in the environment. Some criticism has arisen to the application of this technique, because habita ...
Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 339:65
... The coexistence of multiple species within a trophic level can be regulated by consumer preferences and nutrient supply, but the influence of these factors on the co-occurrence of seagrass species is not well understood. We examined the biomass and density responses of two seagrass species in the Fl ...
... The coexistence of multiple species within a trophic level can be regulated by consumer preferences and nutrient supply, but the influence of these factors on the co-occurrence of seagrass species is not well understood. We examined the biomass and density responses of two seagrass species in the Fl ...
Tricas 1989b
... (Reese 1975, Sutton 1985, Tricas 1985, 1989) . Corals are non-cryptic, relatively easy to identify, and are a stable food resource . The combined features of butterflyfishes and their food corals make it relatively easy to quantify feeding rates on specific prey items as well as associated behaviors ...
... (Reese 1975, Sutton 1985, Tricas 1985, 1989) . Corals are non-cryptic, relatively easy to identify, and are a stable food resource . The combined features of butterflyfishes and their food corals make it relatively easy to quantify feeding rates on specific prey items as well as associated behaviors ...
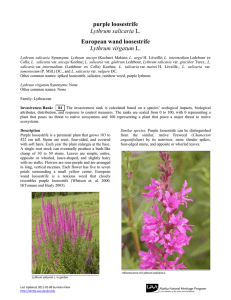
purple loosestrife Lythrum salicaria L. European wand loosestrife
... Dakota, and Tennessee (Invaders 2010). Legal Listings for Lythrum salicaria L. ...
... Dakota, and Tennessee (Invaders 2010). Legal Listings for Lythrum salicaria L. ...
Soil and vegetation nutrient response to bison carcasses in Białowie
... large herbivore carcasses on the surrounding vegetation was found to be dramatic, lasting for several years. Inorganic N concentrations were significantly higher both in the soil (Towne 2000) and vegetation (Danell et al. 2002) around the carcass sites, declining along a gradient the further from the ...
... large herbivore carcasses on the surrounding vegetation was found to be dramatic, lasting for several years. Inorganic N concentrations were significantly higher both in the soil (Towne 2000) and vegetation (Danell et al. 2002) around the carcass sites, declining along a gradient the further from the ...
Invasion of a stream food web by a new top predator
... the asymptotic value for different species. Smaller predators were more prone to underestimation of links than larger species higher in the web. 4. The number of feeding links, trophic status and the degree of omnivory increased progressively with predator body size, both within and among species. T ...
... the asymptotic value for different species. Smaller predators were more prone to underestimation of links than larger species higher in the web. 4. The number of feeding links, trophic status and the degree of omnivory increased progressively with predator body size, both within and among species. T ...
Trait and density mediated indirect interactions in simple
... Our purpose here is to motivate new kinds of field research that quantifies the contribution of traitmediated and predation-mediated effects on population dynamics. We present a collection of models that are caricatures of simple food webs. We use these to illustrate the principles involved in trans ...
... Our purpose here is to motivate new kinds of field research that quantifies the contribution of traitmediated and predation-mediated effects on population dynamics. We present a collection of models that are caricatures of simple food webs. We use these to illustrate the principles involved in trans ...
Test 2 Ch 3 and 4.2 - Kenton County Schools
... ____ 15. Only ____ percent of the energy stored in an organism can be passed on to the next trophic level. a. 100 c. 10 b. 50 d. 0 ____ 16. What is the process by which bacteria convert nitrogen gas in the air to ammonium? a. nitrogen fixation c. decomposition b. excretion d. denitrification ____ 1 ...
... ____ 15. Only ____ percent of the energy stored in an organism can be passed on to the next trophic level. a. 100 c. 10 b. 50 d. 0 ____ 16. What is the process by which bacteria convert nitrogen gas in the air to ammonium? a. nitrogen fixation c. decomposition b. excretion d. denitrification ____ 1 ...
Herbivore
_grazing_-_20050809.jpg?width=300)
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material.