Human Nervous System
... • The cranial nerves are arranged in 12 pairs, so the two nerves on a pair are identical in function and structure. • These nerves serve both sensory and motor functions. ...
... • The cranial nerves are arranged in 12 pairs, so the two nerves on a pair are identical in function and structure. • These nerves serve both sensory and motor functions. ...
Sir Charles Scott Sherrington English Neurophysiologist 1857
... respond. He found that when the spinal cord is severed or a nerve detached from muscle, the reflex fails to respond. In this way, Sherrington determined that simple reflexes are governed by the spinal cord. In addition to explaining spinal reflex activity, Sherrington uncovered the concept of propri ...
... respond. He found that when the spinal cord is severed or a nerve detached from muscle, the reflex fails to respond. In this way, Sherrington determined that simple reflexes are governed by the spinal cord. In addition to explaining spinal reflex activity, Sherrington uncovered the concept of propri ...
The Nervous System
... – Support cells for neurons that can divide – Astrocytes – anchor blood vessels to nerves – Microglia – act as phagocytes – Oligodendrocytes – assist with production of myelin sheath ...
... – Support cells for neurons that can divide – Astrocytes – anchor blood vessels to nerves – Microglia – act as phagocytes – Oligodendrocytes – assist with production of myelin sheath ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... • Excitatory and Inhibitory Actions of Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Stimulation a. Sympathetic stimulation causes excitatory effects in some organs but inhibitory effects in others b. Parasympathetic likewise is excitatory or inhibitory depending on the organ affected c. See Table 60.2 in the tex ...
... • Excitatory and Inhibitory Actions of Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Stimulation a. Sympathetic stimulation causes excitatory effects in some organs but inhibitory effects in others b. Parasympathetic likewise is excitatory or inhibitory depending on the organ affected c. See Table 60.2 in the tex ...
File
... motor nucleus Middle cerebellar peduncle Trigeminal nerve (V) Medial lemniscus Pons © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... motor nucleus Middle cerebellar peduncle Trigeminal nerve (V) Medial lemniscus Pons © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided Genicular Nerve
... with bony landmarks using fluoroscopic imaging. Ultrasound allowed them to locate the nerves more accurately in this single case. However, it could be suggested that ultrasound imaging of that kind of small nerve may not be achieved every time due to possible technical issues regarding the low perfo ...
... with bony landmarks using fluoroscopic imaging. Ultrasound allowed them to locate the nerves more accurately in this single case. However, it could be suggested that ultrasound imaging of that kind of small nerve may not be achieved every time due to possible technical issues regarding the low perfo ...
Anterior and Middle Deltoid Are Functionally Critical Targets for
... possible while minimizing a cost function related to muscle effort [5]. Shoulder elevation and flexion angles were evaluated to determine whether each scenario could abduct the shoulder to 90° and maintain neutral shoulder flexion. ...
... possible while minimizing a cost function related to muscle effort [5]. Shoulder elevation and flexion angles were evaluated to determine whether each scenario could abduct the shoulder to 90° and maintain neutral shoulder flexion. ...
Nociceptors: the sensors of the pain pathway
... glutamate as their primary neurotransmitter as well as other components including peptides (e.g., substance P, calcitonin generelated peptide [CGRP], somatostatin) important in both central synaptic signaling and efferent signaling in the skin (13). Invasion of action potentials into the nociceptor ...
... glutamate as their primary neurotransmitter as well as other components including peptides (e.g., substance P, calcitonin generelated peptide [CGRP], somatostatin) important in both central synaptic signaling and efferent signaling in the skin (13). Invasion of action potentials into the nociceptor ...
Introduction to Psychology - Shoreline School District
... a simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus Brain Sensory neuron (incoming information) ...
... a simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus Brain Sensory neuron (incoming information) ...
Chapter 15
... skeletal muscles and is voluntary. Visceral motor is directed from hypothalamus and midbrain and is involuntary, but has input from cortex and thalamus. Somatic lower motor neuron is in ventral horn of gray matter and neurotransmitter at skeletal muscle is Ach. Visceral motor comes from cranial nerv ...
... skeletal muscles and is voluntary. Visceral motor is directed from hypothalamus and midbrain and is involuntary, but has input from cortex and thalamus. Somatic lower motor neuron is in ventral horn of gray matter and neurotransmitter at skeletal muscle is Ach. Visceral motor comes from cranial nerv ...
The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... electrical signal comes in, opens up to voltage-gated channels, and signals the vesicles containing neurotransmitters (chemical signal) to be released into the synaptic cleft. • Receptors on the post-synaptic neuron bind to the neurotransmitter signaling it to open its gate and let ions flow through ...
... electrical signal comes in, opens up to voltage-gated channels, and signals the vesicles containing neurotransmitters (chemical signal) to be released into the synaptic cleft. • Receptors on the post-synaptic neuron bind to the neurotransmitter signaling it to open its gate and let ions flow through ...
Neck pain
... examiner attempts to elicit a brachioradialis reflex. Gait should be tested during normal gait as well as with toe to heel walking. ...
... examiner attempts to elicit a brachioradialis reflex. Gait should be tested during normal gait as well as with toe to heel walking. ...
Optical recording of electrical activity in intact neuronal networks
... current techniques for several reasons. Generally, the more precise the method of neuronal recording is (e.g. patch-clamp), the more limited the number of simultaneously recorded neurons becomes. Conversely, global recordings (e.g. field recordings) collect activity from many neurons but lose inform ...
... current techniques for several reasons. Generally, the more precise the method of neuronal recording is (e.g. patch-clamp), the more limited the number of simultaneously recorded neurons becomes. Conversely, global recordings (e.g. field recordings) collect activity from many neurons but lose inform ...
Frankenstein
... cold. ... On moving the second rod from hip to heel, the knee being previously bent, the leg was thrown out with such violence as nearly to overturn one of the assistants, who in vain tried to prevent its extension. The body was also made to perform the movements of breathing by stimulating the phre ...
... cold. ... On moving the second rod from hip to heel, the knee being previously bent, the leg was thrown out with such violence as nearly to overturn one of the assistants, who in vain tried to prevent its extension. The body was also made to perform the movements of breathing by stimulating the phre ...
Treatment of Thalamic Pain by Chronic Motor Cortex Stimulation
... moved to the correct position by using this response. After checking that the stimulating electrode had been placed on the motor cortex by recording the V-iu of the somatosensory evoked potentials, the electrode was connected to a transmitter which was implanted in the subcutaneous area of the anter ...
... moved to the correct position by using this response. After checking that the stimulating electrode had been placed on the motor cortex by recording the V-iu of the somatosensory evoked potentials, the electrode was connected to a transmitter which was implanted in the subcutaneous area of the anter ...
Printable Activities
... specialized and began to "distribute" their functions to the point that it was an evolutionary success, because these divisions generated different systems that can be found in most individual animals (nervous, digestive, respiratory, circulatory, etc.). For this reason, evolutionary advantages were ...
... specialized and began to "distribute" their functions to the point that it was an evolutionary success, because these divisions generated different systems that can be found in most individual animals (nervous, digestive, respiratory, circulatory, etc.). For this reason, evolutionary advantages were ...
Document
... can be isolated in the meropodite, containing axons responding to different manipulations of the joint. In Palinurus, especially, fibres in another bundle also respond. It could be shown that these responses do not originate in the organ but from sense cells of hairs located on the distal part of th ...
... can be isolated in the meropodite, containing axons responding to different manipulations of the joint. In Palinurus, especially, fibres in another bundle also respond. It could be shown that these responses do not originate in the organ but from sense cells of hairs located on the distal part of th ...
Rotatory nystagmus - Besøk daftpunk.no
... Normally with the head at rest, in the neutral position the resting discharges in the two vestibular nerve are equal. Vestibulomotor (vestibuloocular and vestibulospinal) reflexes are elicited when inputs from the two vestibular organs or their central projection are made equal, that is, they are un ...
... Normally with the head at rest, in the neutral position the resting discharges in the two vestibular nerve are equal. Vestibulomotor (vestibuloocular and vestibulospinal) reflexes are elicited when inputs from the two vestibular organs or their central projection are made equal, that is, they are un ...
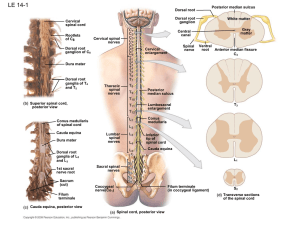
1 Principles of structure and functioning of nervous system
... preservation of the brain motor systems is an important term of accidental moves of a person. Motor system abnormalities happen in the damage of nervous system by many different factors and represent great importance for the diagnostics of the nosologic form of a disease. Motor abnormalities represe ...
... preservation of the brain motor systems is an important term of accidental moves of a person. Motor system abnormalities happen in the damage of nervous system by many different factors and represent great importance for the diagnostics of the nosologic form of a disease. Motor abnormalities represe ...
The Graded Motor Imagery Handbook, 2012
... Left/Right discrimination testing: signs of cortical representation ...
... Left/Right discrimination testing: signs of cortical representation ...
Memory from the dynamics of intrinsic membrane currents
... Another very interesting bistability is seen in theoretical and experimental work on the R15 neuron of Aplysia (16–19). R15 is a prototypic bursting neuron, an extensive biophysical literature on its membrane currents and their modulation has been gathered (19), and a detailed model of this neuron a ...
... Another very interesting bistability is seen in theoretical and experimental work on the R15 neuron of Aplysia (16–19). R15 is a prototypic bursting neuron, an extensive biophysical literature on its membrane currents and their modulation has been gathered (19), and a detailed model of this neuron a ...
Chapter 8: The Nervous System
... 48. Describe the nerve impulse as it travels along a nerve fiber and across a synapse. Ans: A nerve impulse is a wave of depolarization and repolarization, during which sodium ions first move into a neuron and then potassium ions move out of a neuron. This is called an action potential. When the act ...
... 48. Describe the nerve impulse as it travels along a nerve fiber and across a synapse. Ans: A nerve impulse is a wave of depolarization and repolarization, during which sodium ions first move into a neuron and then potassium ions move out of a neuron. This is called an action potential. When the act ...
Chapter 8: The Nervous System
... 48. Describe the nerve impulse as it travels along a nerve fiber and across a synapse. Ans: A nerve impulse is a wave of depolarization and repolarization, during which sodium ions first move into a neuron and then potassium ions move out of a neuron. This is called an action potential. When the act ...
... 48. Describe the nerve impulse as it travels along a nerve fiber and across a synapse. Ans: A nerve impulse is a wave of depolarization and repolarization, during which sodium ions first move into a neuron and then potassium ions move out of a neuron. This is called an action potential. When the act ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.