Human Nerve Chapter
... Receiving sensory input from the internal and external environments through receptors. Integrating the inputs in a central location to determine an appropriate response. Producing a motor response that causes one or more muscles to contract and move a body part, or cause an organ to release molecule ...
... Receiving sensory input from the internal and external environments through receptors. Integrating the inputs in a central location to determine an appropriate response. Producing a motor response that causes one or more muscles to contract and move a body part, or cause an organ to release molecule ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and
... Basic Concepts of Neural Integration (p. 23; Figs. 11.24–11.26) ...
... Basic Concepts of Neural Integration (p. 23; Figs. 11.24–11.26) ...
Nervous System Overview
... • 12 pairs of cranial nerves originate from the base of the brain • They control a variety of functions relating to the head, neck, and internal organs • They can be sensory ,motor or both ...
... • 12 pairs of cranial nerves originate from the base of the brain • They control a variety of functions relating to the head, neck, and internal organs • They can be sensory ,motor or both ...
notes - Mrs. Blackmon`s Science Blackboard
... • White matter is a collection of myelinated fibers. • Gray matter is unmyelinated with only a single layer of Schwann cells. Gray matter is slow and found where distances are short. ...
... • White matter is a collection of myelinated fibers. • Gray matter is unmyelinated with only a single layer of Schwann cells. Gray matter is slow and found where distances are short. ...
The Nervous System - Volunteer State Community College
... Signal transmission along a neuron depends on voltages created by ionic fluxes across neuron plasma membranes. Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. All cells have an electrical potential or voltage across their plasma ...
... Signal transmission along a neuron depends on voltages created by ionic fluxes across neuron plasma membranes. Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. All cells have an electrical potential or voltage across their plasma ...
1. The diagram below is of a nerve cell or neuron. i. Add the following
... The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
... The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
For electrical signaling
... (The Nernst equation applies when the channels allow only one type of ion to pass through them) Some channels are not so selective, and in this case the potential E is estimated by the Goldman equation Reversal potentials takes a value intermediate between the equilibrium potentials of the individua ...
... (The Nernst equation applies when the channels allow only one type of ion to pass through them) Some channels are not so selective, and in this case the potential E is estimated by the Goldman equation Reversal potentials takes a value intermediate between the equilibrium potentials of the individua ...
Name: Block: Date
... part of the CNS, relays information to brain and instruction to body CNS tissue containing mostly myelinated nerve fibers and support cells CNS tissue containing cell bodies and short, non-myelinated fibers highway through which information from body is sorted before being sent to cerbebrum ancient ...
... part of the CNS, relays information to brain and instruction to body CNS tissue containing mostly myelinated nerve fibers and support cells CNS tissue containing cell bodies and short, non-myelinated fibers highway through which information from body is sorted before being sent to cerbebrum ancient ...
sensory neurone
... You burn your hand on a hot plate- which of the following order of events is correct? a) receptor-->sensory neurone-->relay neurone-->motor neurone--> effector b) receptor--> motor neurone-->relay neurone-->sensory neurone-->effector ...
... You burn your hand on a hot plate- which of the following order of events is correct? a) receptor-->sensory neurone-->relay neurone-->motor neurone--> effector b) receptor--> motor neurone-->relay neurone-->sensory neurone-->effector ...
The Nervous System
... Name the common diagnoses, laboratory tests, and clinical procedures used in testing and treating disorders of the nervous system List and define the major pathological conditions of the nervous system Define surgical terms related to the nervous system ...
... Name the common diagnoses, laboratory tests, and clinical procedures used in testing and treating disorders of the nervous system List and define the major pathological conditions of the nervous system Define surgical terms related to the nervous system ...
chapt12 neuron_lecture
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
emg and ncs: a practical approach to
... – Normal OR decreased temperature/pain sensation in a “stocking and glove” distribution – Reflexes are decreased (legs > arms) ...
... – Normal OR decreased temperature/pain sensation in a “stocking and glove” distribution – Reflexes are decreased (legs > arms) ...
Chapter 3 - Morgan Community College
... Diversity in Neurons Both structural and functional features are used to ...
... Diversity in Neurons Both structural and functional features are used to ...
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY Zsolt Liposits and Imre Kalló 2016
... 3) The arrangement of nerve fibers within the spinal cord carrying motor and/or sensory informations from and to supraspinal centers. Test the knowledge you gained: 1) Identify the selected numbered structures by using the schematic drawing of the spinal cord! Then, associate the statements with the ...
... 3) The arrangement of nerve fibers within the spinal cord carrying motor and/or sensory informations from and to supraspinal centers. Test the knowledge you gained: 1) Identify the selected numbered structures by using the schematic drawing of the spinal cord! Then, associate the statements with the ...
Nerve Impulses and Action Potential
... Nerve Impulses •Action potential •The movement of ions initiates an action potential in the neuron due to a stimulus •A graded potential (localized depolarization) exists where the inside of the membrane is more positive and the outside is less positive ...
... Nerve Impulses •Action potential •The movement of ions initiates an action potential in the neuron due to a stimulus •A graded potential (localized depolarization) exists where the inside of the membrane is more positive and the outside is less positive ...
The Nervous System (PowerPoint)
... Transmission of nerve impulses across a Synaptic cleft is carried out by chemicals called Neurotransmitters substances. These substances are stored in vesicles at the end of the Axon. Noradrenalin (speeds up activity) and acetylcholine (slows down activity) are examples of Neurotransmitters. When an ...
... Transmission of nerve impulses across a Synaptic cleft is carried out by chemicals called Neurotransmitters substances. These substances are stored in vesicles at the end of the Axon. Noradrenalin (speeds up activity) and acetylcholine (slows down activity) are examples of Neurotransmitters. When an ...
Nervous System - ocw@unimas - Universiti Malaysia Sarawak
... Neuron (con8nue) • In myelinated neurons, the axons are covered with insula
... Neuron (con8nue) • In myelinated neurons, the axons are covered with insula
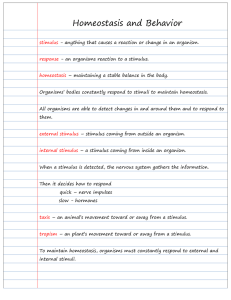
Homeostasis and Behavior
... external stimulus – stimulus coming from outside an organism. internal stimulus – a stimulus coming from inside an organism. When a stimulus is detected, the nervous system gathers the information. Then it decides how to respond quick – nerve impulses slow - hormones taxis – an animal’s movement tow ...
... external stimulus – stimulus coming from outside an organism. internal stimulus – a stimulus coming from inside an organism. When a stimulus is detected, the nervous system gathers the information. Then it decides how to respond quick – nerve impulses slow - hormones taxis – an animal’s movement tow ...
The Nervous System
... Is the changes in the trans-membrane potential that cannot spread far from the area surrounding the site of stimulus. • In this case the membrane is exposed to a chemical that opens chemically regulated Na+ channels. Na+ ions inter the cell & an additional positive charge shifts the trans-membrane p ...
... Is the changes in the trans-membrane potential that cannot spread far from the area surrounding the site of stimulus. • In this case the membrane is exposed to a chemical that opens chemically regulated Na+ channels. Na+ ions inter the cell & an additional positive charge shifts the trans-membrane p ...
Histology of Nerve the Nervous System
... nervous system,composed of nerve fibers and small aggregates of nerve cells called nerve ganglia Structurally,nerve tissue consists of two cell types:nerve cells,or neurons, Usually show numerous long processes, and several types of glial cells which have short processes,support and protect neurons, ...
... nervous system,composed of nerve fibers and small aggregates of nerve cells called nerve ganglia Structurally,nerve tissue consists of two cell types:nerve cells,or neurons, Usually show numerous long processes, and several types of glial cells which have short processes,support and protect neurons, ...
Lecture Outline ()
... The Discovery of Neurotransmitters • Histological observations revealed a 20 to 40 nm gap between neurons (synaptic cleft) • Otto Loewi (1873-1961) first to demonstrate function of neurotransmitters at chemical synapse – flooded exposed hearts of 2 frogs with saline – stimulated vagus nerve of one ...
... The Discovery of Neurotransmitters • Histological observations revealed a 20 to 40 nm gap between neurons (synaptic cleft) • Otto Loewi (1873-1961) first to demonstrate function of neurotransmitters at chemical synapse – flooded exposed hearts of 2 frogs with saline – stimulated vagus nerve of one ...
Chapter 10 – Sensory Physiology
... Sensory Receptor Cells always change Stimuli to graded or action potentials. Sensory Transduction: is transformation of stimulus to electrical response. Stimulus Stimulus is change in environment detected by sensory receptor cell. Stimulus is characterized by Type of energy and its intensity Locatio ...
... Sensory Receptor Cells always change Stimuli to graded or action potentials. Sensory Transduction: is transformation of stimulus to electrical response. Stimulus Stimulus is change in environment detected by sensory receptor cell. Stimulus is characterized by Type of energy and its intensity Locatio ...
Sensory Nerves and Receptors
... pathway which serves this locality. This is called the "law of projection". It explains the phantom limb phenomenon which occurs in ...
... pathway which serves this locality. This is called the "law of projection". It explains the phantom limb phenomenon which occurs in ...
9 Chapter Nervous System Notes (p
... 8. What do dendrites look like and what do they do? 9. What do axons look like and what do they do? ...
... 8. What do dendrites look like and what do they do? 9. What do axons look like and what do they do? ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... relations to the neuron? chloride, sodium, potassium Why do they call it a sodiumpotassium pump? What is a threshold signal? ...
... relations to the neuron? chloride, sodium, potassium Why do they call it a sodiumpotassium pump? What is a threshold signal? ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.